Mensuration
- The perimeter of a rhombus is 100 cm and one of its diagonals is 40 cm. Its area (in cm²) is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Using Rule 12,
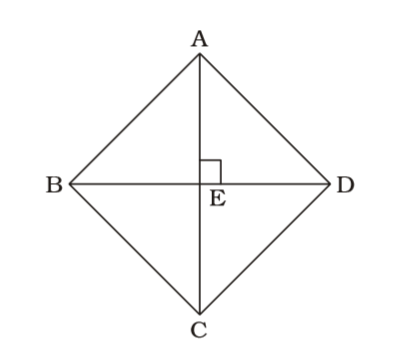
BD = 40 cm
BE = 20 cm
AE = x cmAB = 100 = 25 cm 4
∴ From ∆ ABE,
AE = √25² - 20²
= √45 × 5 = 15cm
∴ AC = 30 cmArea of rhombus ABCD = 1 d1d2 = 1 × 40 × 30 = 600 sq. cm 2 2 Correct Option: C
Using Rule 12,

BD = 40 cm
BE = 20 cm
AE = x cmAB = 100 = 25 cm 4
∴ From ∆ ABE,
AE = √25² - 20²
= √45 × 5 = 15cm
∴ AC = 30 cmArea of rhombus ABCD = 1 d1d2 = 1 × 40 × 30 = 600 sq. cm 2 2
- In •ABC, D and E are the points of sides AB and BC respectively such that DE || AC and AD : DB = 3 : 2. The ratio of area of trapezium ACED to that of ∆ BED is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
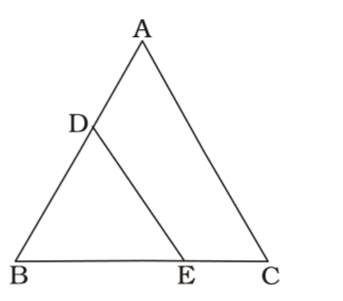
DE ∥ AC ∴ ∆ DBE ≅ ∆ ABC∆ AD = EC = 3 DB EB 2 AD + 1 = 3 + 1 DB 2 ⇒ AB = 5 DB 2 ∴ ∆ ABC = AB² = 25 ∆ DBE BD² 4 ⇒ ∆ ABC - 1 = 25 - 1 ∆ DBE 4 ⇒ ∆ ABC - ∆ DBE = 25 - 4 ∆ DBE 4 ⇒ ∎ ACED = 21 or 21 : 4 ∆ DBE 4 Correct Option: D

DE ∥ AC ∴ ∆ DBE ≅ ∆ ABC∆ AD = EC = 3 DB EB 2 AD + 1 = 3 + 1 DB 2 ⇒ AB = 5 DB 2 ∴ ∆ ABC = AB² = 25 ∆ DBE BD² 4 ⇒ ∆ ABC - 1 = 25 - 1 ∆ DBE 4 ⇒ ∆ ABC - ∆ DBE = 25 - 4 ∆ DBE 4 ⇒ ∎ ACED = 21 or 21 : 4 ∆ DBE 4
- ABCD is a trapezium in which AB||DC and AB = 2 CD. The diagonals AC and BD meet at O. The ratio of area of triangles AOB and COD is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
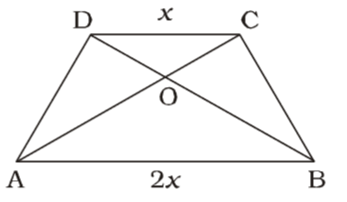
Let CD = x
⇒ AB = 2x. ∆ COD ~ ∆ AOB
because CD|| AB and take BD and AC as transversals.∴ ar (COD) = CD² = x² = 1 ar(AOB) AB² 4x² 4
⇒ ∆ ABD – ∆ AOD
= ∆ ACB – ∆ BOC
⇒ ∆ AOB = ∆ AOB⇒ ∆ AOB = 1 or 1 : 1 ∆ COD 1 Correct Option: A

Let CD = x
⇒ AB = 2x. ∆ COD ~ ∆ AOB
because CD|| AB and take BD and AC as transversals.∴ ar (COD) = CD² = x² = 1 ar(AOB) AB² 4x² 4
⇒ ∆ ABD – ∆ AOD
= ∆ ACB – ∆ BOC
⇒ ∆ AOB = ∆ AOB⇒ ∆ AOB = 1 or 1 : 1 ∆ COD 1
- The length of each side of a rhombus is equal to the length of the side of a square whose diagonal is 40√2 cm. If the length of the diagonals of the rhombus are in the ratio 3 : 4, then its area (in cm²) is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
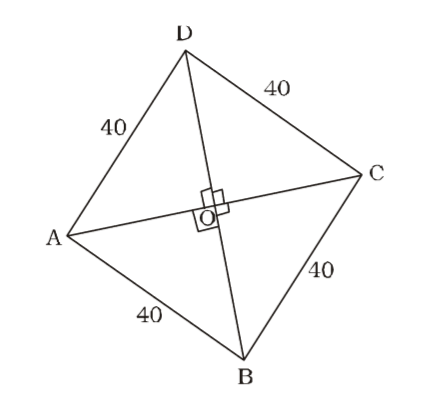
Using Rule 12,
Side of rhombus = side of square.
= √2a = 40√2a ⇒ a = 40
⇒ AC ⊥ BD; ∠AOD = 90°
Let AC = 3x and BD = 4x cm∴ AO = 3x ; OD = 2x cm 2
From ∆ AOD,
OA² + OD² = AD²
3x 
² + 4x² = 40² 2
⇒ 9x² + 16x² = 1600 × 4
⇒ 25x² = 6400
⇒ x² = 6400 ÷ 25 = 256
⇒ x = √256 = 16
∴ AC = 3 × 16 = 48 cm
and BD = 4 × 16 = 64 cm∴ Area of rhombus = 1 × AC × BD 2 = 1 × 48 × 64 = 1536 sq.cm. 2 Correct Option: D

Using Rule 12,
Side of rhombus = side of square.
= √2a = 40√2a ⇒ a = 40
⇒ AC ⊥ BD; ∠AOD = 90°
Let AC = 3x and BD = 4x cm∴ AO = 3x ; OD = 2x cm 2
From ∆ AOD,
OA² + OD² = AD²
3x 
² + 4x² = 40² 2
⇒ 9x² + 16x² = 1600 × 4
⇒ 25x² = 6400
⇒ x² = 6400 ÷ 25 = 256
⇒ x = √256 = 16
∴ AC = 3 × 16 = 48 cm
and BD = 4 × 16 = 64 cm∴ Area of rhombus = 1 × AC × BD 2 = 1 × 48 × 64 = 1536 sq.cm. 2
- The area of the triangle formed by the straight line 3x + 2y = 6 and the co-ordinate axes is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Putting y = 0 in the equation
3x + 2y = 6,
3x + 0 = 6 ⇒ x = 2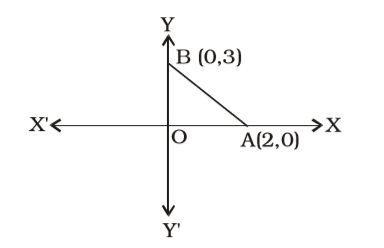
∴ Point of intersection on x-axis = (2, 0)
Putting x = 0, in the equation 3x + 2y = 6,
gives 0 + 2y = 6 ⇒ y = 3
∴ Point of intersection on y-axis = (0, 3)
So, OA = 2, OB = 3∴ ∆ OAB = 1 × OA × OB 2 = 1 × 2 × 3 = 3 sq.units 2 Correct Option: A
Putting y = 0 in the equation
3x + 2y = 6,
3x + 0 = 6 ⇒ x = 2
∴ Point of intersection on x-axis = (2, 0)
Putting x = 0, in the equation 3x + 2y = 6,
gives 0 + 2y = 6 ⇒ y = 3
∴ Point of intersection on y-axis = (0, 3)
So, OA = 2, OB = 3∴ ∆ OAB = 1 × OA × OB 2 = 1 × 2 × 3 = 3 sq.units 2

