Trigonometry
- If cosecθ – sinθ = l and secθ – cosθ = m, then the value of l²m² (l² + m² + 3) is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
(l².m²)(m² + 3)
= (cosec θ - sin θ)²
(sec θ - cos θ)²
{(cosec θ - sin θ)² + (sec θ - cos θ)² + 3}
= cos4θ × sin4θ sin2θ cos2θ 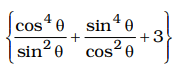
= cos²θ × sin²θ
= cos2 θ + sin6θ + 3cos2θ . sin2θ
= {(cos2θ + sin2θ)
3 – 3 cos2θ . sin2θ(cos2θ + sin2θ)} + 3cos2θ . sin2θ
[∵ a3 + b3 = (a + b)3– 3ab (a + b)]
= 1 – 3 cos2θ . sin2θ + 3 cos2θ .
sin2θ = 1Correct Option: C
(l².m²)(m² + 3)
= (cosec θ - sin θ)²
(sec θ - cos θ)²
{(cosec θ - sin θ)² + (sec θ - cos θ)² + 3}
= cos4θ × sin4θ sin2θ cos2θ 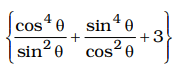
= cos²θ × sin²θ
= cos2 θ + sin6θ + 3cos2θ . sin2θ
= {(cos2θ + sin2θ)
3 – 3 cos2θ . sin2θ(cos2θ + sin2θ)} + 3cos2θ . sin2θ
[∵ a3 + b3 = (a + b)3– 3ab (a + b)]
= 1 – 3 cos2θ . sin2θ + 3 cos2θ .
sin2θ = 1
- An aeroplane when flying at a height of 3125 m from the ground passes vertically below another plane at an instant when the angle of elevation of the two planes from the same point on the ground are 30° and 60° respectively. The distance between the two planes at that instant is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

A and C ⇒ position of planes
BC = 3125m
Let AC = x metre
In ∆ABDtan60° = AB BD ⇒ √3 = 3125 + x BD ⇒ BD = 3125 + x √3
In ∆BCD,tan30° = BC BD ⇒ 1 = 3125 √3 3125 + x √3
⇒ 3 (3125) = 3125 + x
⇒ 9375 = 3125 + x
⇒ x = 9375 – 3125
x = 6250 metreCorrect Option: D

A and C ⇒ position of planes
BC = 3125m
Let AC = x metre
In ∆ABDtan60° = AB BD ⇒ √3 = 3125 + x BD ⇒ BD = 3125 + x √3
In ∆BCD,tan30° = BC BD ⇒ 1 = 3125 √3 3125 + x √3
⇒ 3 (3125) = 3125 + x
⇒ 9375 = 3125 + x
⇒ x = 9375 – 3125
x = 6250 metre
- The elevation of the top of a tower from a point on the ground is 45°. On travelling 60 m from the point towards the tower, the elevation of the top becomes 60°. The height of the tower (in metres) is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

AB = tower = h metre
∠ACB = 45°, ∠ADB = 60°
CD = 60 metre] BD = x metre
From ∆ABC,tan 45° = AB BC ⇒ 1 = h x + 60
⇒ h = x + 60 ....................(i)
From ∆ABDtan 60° = AB BD ⇒ √3 = h x
⇒ h = √3x
⇒ h = √3(h - 60)
⇒ √3h - h= 60√3
⇒ h(√3 - 1) = 60√3⇒ h = 60√3 = 60√3(√3 + 1) √3 - 1 (√3 - 1)(√3 + 1)
= 30√3(√3 + 1)
= 30(3 + √3) metreCorrect Option: C

AB = tower = h metre
∠ACB = 45°, ∠ADB = 60°
CD = 60 metre] BD = x metre
From ∆ABC,tan 45° = AB BC ⇒ 1 = h x + 60
⇒ h = x + 60 ....................(i)
From ∆ABDtan 60° = AB BD ⇒ √3 = h x
⇒ h = √3x
⇒ h = √3(h - 60)
⇒ √3h - h= 60√3
⇒ h(√3 - 1) = 60√3⇒ h = 60√3 = 60√3(√3 + 1) √3 - 1 (√3 - 1)(√3 + 1)
= 30√3(√3 + 1)
= 30(3 + √3) metre
- The length of the shadow of a vertical tower on level ground increases by 10 metres when the altitude of the sun changes from 45° to 30°. Then the height of the tower is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

AB = Tower = h metre
∠BDA = 30°
∠ACB = 45°
CD = 10 metre
From ∆ABC,tan45° = AB BC ⇒ 1 = h ⇒ h = x x
⇒ √3h = h +10 [∵ h = x ]
⇒ √3h - h = 10
⇒ h( √3 - 1) = 10⇒ h = 10 = 10 × √3 + 1 √3 - 1 √3 - 1 √3 + 1 = 10(√3 + 1) = 5(√3 + 1) metre 2 Correct Option: C

AB = Tower = h metre
∠BDA = 30°
∠ACB = 45°
CD = 10 metre
From ∆ABC,tan45° = AB BC ⇒ 1 = h ⇒ h = x x
⇒ √3h = h +10 [∵ h = x ]
⇒ √3h - h = 10
⇒ h( √3 - 1) = 10⇒ h = 10 = 10 × √3 + 1 √3 - 1 √3 - 1 √3 + 1 = 10(√3 + 1) = 5(√3 + 1) metre 2
- The angle of elevation of a tower from a distance 50 m from its foot is 30°. The height of the tower is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

AB = Tower = h metre
BC = 50 metre
∠ ACB = 30°∴ tan 30° = AB BC ⇒ 1 = AB √3 50 ⇒ AB = 50 metre √3 Correct Option: B

AB = Tower = h metre
BC = 50 metre
∠ ACB = 30°∴ tan 30° = AB BC ⇒ 1 = AB √3 50 ⇒ AB = 50 metre √3

