Trigonometry
- The shadow of the tower becomes 60 metres longer when the altitude of the sun changes from 45° to 30°. Then the height of the tower is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
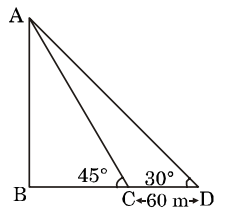
AB = Tower = h metre
∠ADB = 30°
∠ACB = 45°
CD = 60 metre
BC = x metre
From ∆ABC,tan45° = AB BC ⇒ 1 = h ⇒ h = x x
From ∆ABD,tan30° = AB BD ⇒ 1 = 30 √3 x + 60 ⇒ 1 = 30 √3 h + 60
⇒ √3 h = h + 60
⇒ √3 h – h = 60
⇒ h(√3 - 1) = 60⇒ h = 60 = 60(√3 + 1) √3 - 1 (√3 - 1)(√3 + 1)
= 30(√3 + 1) metreCorrect Option: C

AB = Tower = h metre
∠ADB = 30°
∠ACB = 45°
CD = 60 metre
BC = x metre
From ∆ABC,tan45° = AB BC ⇒ 1 = h ⇒ h = x x
From ∆ABD,tan30° = AB BD ⇒ 1 = 30 √3 x + 60 ⇒ 1 = 30 √3 h + 60
⇒ √3 h = h + 60
⇒ √3 h – h = 60
⇒ h(√3 - 1) = 60⇒ h = 60 = 60(√3 + 1) √3 - 1 (√3 - 1)(√3 + 1)
= 30(√3 + 1) metre
- From two points on the ground lying on a straight line through the foot of a pillar, the two angles of elevation of the top of the pillar are complementary to each other. If the distance of the two points from the foot of the pillar are 9 metres and 16 metres and the two points lie on the same side of the pillar, then the height of the pillar is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

AB = Pole = h metre
BC = 9 metre BD = 16 metre
∠ADB = θ ;
∴ ∠ACB = 90° – θ
From ∆ABC,tan (90° – θ) = AB BC ⇒ cotθ = h ......(i) 9
from ∆ABD⇒ tanθ = h ......(ii) 16
By multiplying (i) & (ii)tanθ . cotθ = h × h 9 16 ⇒ h2 = 1 144
⇒ h2 = 144
⇒ h = √144 = 12 metreCorrect Option: D

AB = Pole = h metre
BC = 9 metre BD = 16 metre
∠ADB = θ ;
∴ ∠ACB = 90° – θ
From ∆ABC,tan (90° – θ) = AB BC ⇒ cotθ = h ......(i) 9
from ∆ABD⇒ tanθ = h ......(ii) 16
By multiplying (i) & (ii)tanθ . cotθ = h × h 9 16 ⇒ h2 = 1 144
⇒ h2 = 144
⇒ h = √144 = 12 metre
- The distance between two vertical poles is 60 m. The height of one of the poles is double the height of the other. The angle of elevation of the top of the poles from the middle point of the line segment joining their feet are complementary to each other. The height of the poles are :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

BE = DE = 30 metre
∠AEB = θ ∴ ∠CED = 90° – θ
From ∆ ABE,tan θ = AB BE ⇒ tan θ = h 30
⇒ h = 30 tan θ ................(i)
From ∆ CDE,tan (90° – θ) = 2h 30 ⇒ cot θ = h ⇒ h = 15cotθ ....(ii) 15
By multiplying both equations,
h2 = 30 × 15 × tan θ. cot θ
⇒ h2 = 30 × 15
[∵ tan θ . cot θ = 1]
⇒ h = 15 √2 metre = AB
⇒ 2h = 30 √2 metre = CDCorrect Option: D

BE = DE = 30 metre
∠AEB = θ ∴ ∠CED = 90° – θ
From ∆ ABE,tan θ = AB BE ⇒ tan θ = h 30
⇒ h = 30 tan θ ................(i)
From ∆ CDE,tan (90° – θ) = 2h 30 ⇒ cot θ = h ⇒ h = 15cotθ ....(ii) 15
By multiplying both equations,
h2 = 30 × 15 × tan θ. cot θ
⇒ h2 = 30 × 15
[∵ tan θ . cot θ = 1]
⇒ h = 15 √2 metre = AB
⇒ 2h = 30 √2 metre = CD
- A man standing at a point P is watching the top of a tower, which makes an angle of elevation of 30°. The man walks some distance towards the tower and then his angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 60°. If the height of the tower is 30 m, then the distance he moves is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

AB = Tower = 30 metre
CD = x metre
∠ACB = 30°
∠ADB = 60°
From ∆ ABDtan60° = AB BD ⇒ √3 = 30 BD ⇒ BD = 30 = 10√3 metre √3
From ∆ ABC,tan30° = AB BC ⇒ 1 = 30 √3 10√3 + x
⇒ 10 √3 + x = 30 √3
⇒ x = 30 √3 – 10 √3
= 20 √3 metreCorrect Option: D

AB = Tower = 30 metre
CD = x metre
∠ACB = 30°
∠ADB = 60°
From ∆ ABDtan60° = AB BD ⇒ √3 = 30 BD ⇒ BD = 30 = 10√3 metre √3
From ∆ ABC,tan30° = AB BC ⇒ 1 = 30 √3 10√3 + x
⇒ 10 √3 + x = 30 √3
⇒ x = 30 √3 – 10 √3
= 20 √3 metre
- An aeroplane when flying at a height of 5000 m from the ground passes vertically above another aeroplane at an instant, when the angles of elevation of the two aeroplanes from the same point on the ground are 60° and 45° respectively. The vertical distance between the aeroplanes at that instant is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
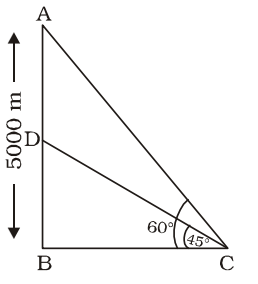
∠ACB = 60°
∠DCB = 45°
AB = 5000 metre
AD = x metre
∴ From ∆ABC,tan 60° = AB BC ⇒ √3 = 5000 BC ⇒ BC = 5000 metre √3
From ∆DBC,tan45° = DB BC ⇒ DB = BC = 5000 √3
∴ AD = AB – BD= 5000 - 5000 √3 5000 
1 - 1 
m √3 Correct Option: C

∠ACB = 60°
∠DCB = 45°
AB = 5000 metre
AD = x metre
∴ From ∆ABC,tan 60° = AB BC ⇒ √3 = 5000 BC ⇒ BC = 5000 metre √3
From ∆DBC,tan45° = DB BC ⇒ DB = BC = 5000 √3
∴ AD = AB – BD= 5000 - 5000 √3 5000 
1 - 1 
m √3

