Trigonometry
- If 0 ≤ θ ≤ (π / 2) and sec²θ + tan²θ =7, then θ is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Using Rule 1,
sec²θ + tan²θ = 7
⇒ 1 + tan²θ + tan²θ = 7
⇒ 2 tan²θ = 7 – 1 = 6
⇒ tan²θ = 3
⇒ tan θ = √3
= tan 60°
⇒ θ = 60°
∵ 180° = π radian∴ 60° = π × 60 = π 180 3
Correct Option: B
Using Rule 1,
sec²θ + tan²θ = 7
⇒ 1 + tan²θ + tan²θ = 7
⇒ 2 tan²θ = 7 – 1 = 6
⇒ tan²θ = 3
⇒ tan θ = √3
= tan 60°
⇒ θ = 60°
∵ 180° = π radian∴ 60° = π × 60 = π 180 3
- From two points on the ground and lying on a straight line through the foot of a pillar, the two angles of elevation of the top of the pillar are complementary to each other. If the distances of the two points from the foot of the pillar are 12 metres and 27 metres and the two points lie on the same side of the pillar, then the height (in metres) of the pillar is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

Let, ∠ACB = θ
∴ ∠ADB = 90° – θ
BC = 12 metre,
BD = 27 metre
AB = Pillar = h metre
From ∆ABC,tan θ = AB = h ......(i) BC 12
From ∆ABDtan(90° – θ) = AB BD ⇒ cotθ = h ......(ii) 27 ∴ tanθ. cotθ = h × h 12 27
⇒ h2 = 12 × 27
⇒ h2 = √12 × 27
= √2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
= 2 × 3 × 3 = 18 metreCorrect Option: B

Let, ∠ACB = θ
∴ ∠ADB = 90° – θ
BC = 12 metre,
BD = 27 metre
AB = Pillar = h metre
From ∆ABC,tan θ = AB = h ......(i) BC 12
From ∆ABDtan(90° – θ) = AB BD ⇒ cotθ = h ......(ii) 27 ∴ tanθ. cotθ = h × h 12 27
⇒ h2 = 12 × 27
⇒ h2 = √12 × 27
= √2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
= 2 × 3 × 3 = 18 metre
- The shadow of a tower standing on a level plane is found to be 40 m longer when the sun’s altitude is 45°, than when it is 60°. The height of the tower is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

∠ACB = 60°; BC = x metre
CD = 40 metre, AB = Tower = h metre
From ∆ABC,tan 60° = AB BC ⇒ √3 = h x
⇒ h = √3 x ...............(i)
From ∆ABD,tan 45° = AB BD ⇒ 1 = h x + 40 ⇒ h = x + 40 = h + 40 √3 ⇒ h - h = 40 √3 ⇒ √3h - h = 40 √3
⇒ ( √3 – 1)h = 40 √3⇒ = 40√3 √3 - 1 ⇒ = 40√3(√3 + 1) (√3 - 1)(√3 + 1)
= 20 (3 + √3 ) metreCorrect Option: C

∠ACB = 60°; BC = x metre
CD = 40 metre, AB = Tower = h metre
From ∆ABC,tan 60° = AB BC ⇒ √3 = h x
⇒ h = √3 x ...............(i)
From ∆ABD,tan 45° = AB BD ⇒ 1 = h x + 40 ⇒ h = x + 40 = h + 40 √3 ⇒ h - h = 40 √3 ⇒ √3h - h = 40 √3
⇒ ( √3 – 1)h = 40 √3⇒ = 40√3 √3 - 1 ⇒ = 40√3(√3 + 1) (√3 - 1)(√3 + 1)
= 20 (3 + √3 ) metre
- The angle of elevation of the top of a tower of height 100 √3 metre from a point at a distance of 100 metre from the foot of the tower on a horizontal plane is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

AB = Tower = 100 √3 metre
BC = 100 metre
From ∆ ABC,tan θ = AB BC ⇒ tan θ = 100√3 = √3 100
⇒ tanθ = tan 60° ⇒ θ = 60°Correct Option: B

AB = Tower = 100 √3 metre
BC = 100 metre
From ∆ ABC,tan θ = AB BC ⇒ tan θ = 100√3 = √3 100
⇒ tanθ = tan 60° ⇒ θ = 60°
- The shadow of a tower standing on a level plane is found to be 30 metre longer when the Sun’s altitude changes from 60° to 45°. The height of the tower is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
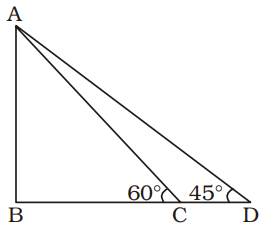
AB = Tower = h metre (let)
CD = 30 metre
BC = x metre (let)
From ∆ABC,tan 60° = AB BC ⇒ √3 = h x
⇒ h = √3x metre ...........(i)
From ∆ABD,tan 45° = AB BD ⇒ 1 = h x + 30
⇒ h = x + 30⇒ h= h + 30 √3
⇒ √3h = h + 30 √3
⇒ √3h – h = 30 √3
⇒ h ( √3 - 1) = 30 √3⇒ h = 30√3 = 30√3(√3 + 1) √3 - 1 (√3 - 1)(√3 + 1) = 30√3(√3 + 1) 3 - 1
= 15 √3 ( √3 +1)
= 15 (3 + √3 ) metreCorrect Option: A

AB = Tower = h metre (let)
CD = 30 metre
BC = x metre (let)
From ∆ABC,tan 60° = AB BC ⇒ √3 = h x
⇒ h = √3x metre ...........(i)
From ∆ABD,tan 45° = AB BD ⇒ 1 = h x + 30
⇒ h = x + 30⇒ h= h + 30 √3
⇒ √3h = h + 30 √3
⇒ √3h – h = 30 √3
⇒ h ( √3 - 1) = 30 √3⇒ h = 30√3 = 30√3(√3 + 1) √3 - 1 (√3 - 1)(√3 + 1) = 30√3(√3 + 1) 3 - 1
= 15 √3 ( √3 +1)
= 15 (3 + √3 ) metre

