Electric circuits miscellaneous
- A two terminal black box contains one of the R.L.C. elements. The black box is connected to a 220 volts A.C. supply. The current through the source is I. When a capacitance of 0.1F is inserted in the series between the source and the box, the current through the source is 2I. The element is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Initially , I = V R + jX
When capacitance inserted,2I = V R + jX - jωC ⇒ 2 + 6 R + jX R + jX - (j / ωC) ⇒ 2R + 2jX - 2j = R + jX ωC ⇒ R + jX = 2j ωC X = 2 ωC
Here ‘+’ ve sign element is inductance
Correct Option: B
Initially , I = V R + jX
When capacitance inserted,2I = V R + jX - jωC ⇒ 2 + 6 R + jX R + jX - (j / ωC) ⇒ 2R + 2jX - 2j = R + jX ωC ⇒ R + jX = 2j ωC X = 2 ωC
Here ‘+’ ve sign element is inductance
- In the transformer shown in the given figure, the inductance measured across the terminal 1 and 2 was 4 H with open terminals 3 and 4. It was 3 H when the terminal 3 and 4 are were short circuited. The coefficient of coupling would be
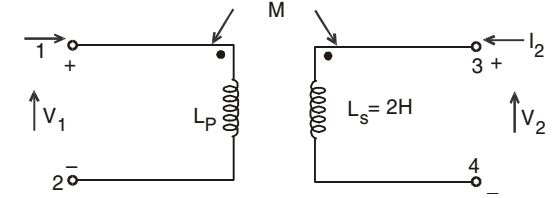
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: D
NA
- The value of the capacitance C in the given ac circuit to make it a constant resistance circuit OR for the supply current to be independent of its frequency is
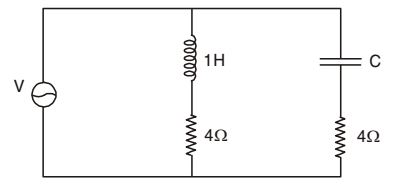
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
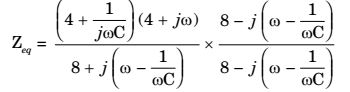
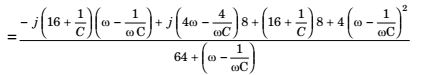
For constant resistance, equating imaginary term to zero,
16 + 1 

ω - 1 
= 32 
ω - 1 
C ωC ωC ∴ C = 1 F 16 Correct Option: A
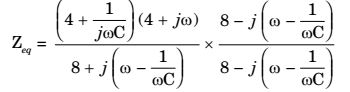
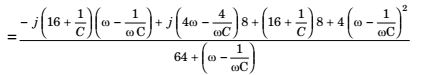
For constant resistance, equating imaginary term to zero,
16 + 1 

ω - 1 
= 32 
ω - 1 
C ωC ωC ∴ C = 1 F 16
- A network contains linear resistors and ideal voltage sources. If values of all the resistors are doubled, then the voltage across each resistor is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
First Method :
V ratio is a constant R. If R is doubled current will become half. I V = 2R I = RI 2
Second Method :VR1 = V × R1 R1 + R2 VR2 = V × R2 R1 + R2
If R1 and R2 are doubled, thenV'R1 = V × 2R1 = VR1 2(R1 + R2) V'R2 = V × 2R1 = VR2 2(R1 + R2)
Correct Option: D
First Method :
V ratio is a constant R. If R is doubled current will become half. I V = 2R I = RI 2
Second Method :VR1 = V × R1 R1 + R2 VR2 = V × R2 R1 + R2
If R1 and R2 are doubled, thenV'R1 = V × 2R1 = VR1 2(R1 + R2) V'R2 = V × 2R1 = VR2 2(R1 + R2)
- Current I1, I2 and I3 meet at a junction (node) in a circuit. All currents are marked as entering the node. If I1 = – 6 sin (ω t) mA and I2 = 8 cos (ω t) mA, then I 3 will be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: D
NA

