Computer organization and architecture miscellaneous
- For computers based on three-address instruction formats, each address field can be used to specify which of the following.
S1: A memory operand
S2: A processor register
S3: An implied accumulator register
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: A
NA
- The width of the physical address on a machine is 40 bits. The width of the tag field in a 512 KB 8-way set associative cache is________bits.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

Tag bits = 40 – (19 – 3) = 24 bitsCorrect Option: C

Tag bits = 40 – (19 – 3) = 24 bits
- Consider a processor with 64 registers and an instruction set of size twelve. Each instruction has five distinct fields, namely, opcode, two source register identifiers, one destination register identifier, and a twelve-bit immediate value. Each instruction must be stored in memory in a byte-aligned fashion. If a program has 100 instructions, the amount of memory (in bytes) consumed by the program text is ________.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given No. of registers = 64
Required No. of bits to address registers = log2 64 = 6
Given No. of instructions = 12
∴ Opcode size = log2 12 = 4
Opcode + 3 reg address + 12 bit immediate value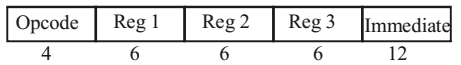
Total bits per instruction = 34
Total bytes per instruction = 4.25
Due to byte alignment 0.75 byte will waste while storing 4.25 bytes.
Total no. of bytes per instruction = 5
Total no. of instructions = 100
Total size = No. of Instructions × Size of Instruction = 100 × 5 = 500 BytesCorrect Option: A
Given No. of registers = 64
Required No. of bits to address registers = log2 64 = 6
Given No. of instructions = 12
∴ Opcode size = log2 12 = 4
Opcode + 3 reg address + 12 bit immediate value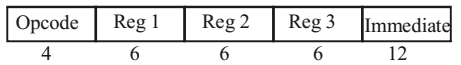
Total bits per instruction = 34
Total bytes per instruction = 4.25
Due to byte alignment 0.75 byte will waste while storing 4.25 bytes.
Total no. of bytes per instruction = 5
Total no. of instructions = 100
Total size = No. of Instructions × Size of Instruction = 100 × 5 = 500 Bytes
- A processor has 40 distinct instructions and 24 general purpose registers. A 32-bit instruction word has an opcode, two register operands and an immediate operand. The number of bits available for the immediate operand field is ________.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
6 bits are needed for 40 distinct instructions (because, 32 < 40 < 64) 5 bits are needed for 24 general purpose registers (because, 16 < 24 < 32) 32-bit instruction word has an opcode(6 bit), two register operands(total 10 bits) and an immediate operand (x bits). The number of bits available for the immediate operand field => x = 32 – (6 + 10) = 16 bits
Correct Option: B
6 bits are needed for 40 distinct instructions (because, 32 < 40 < 64) 5 bits are needed for 24 general purpose registers (because, 16 < 24 < 32) 32-bit instruction word has an opcode(6 bit), two register operands(total 10 bits) and an immediate operand (x bits). The number of bits available for the immediate operand field => x = 32 – (6 + 10) = 16 bits
- Consider the expression (a – 1) * (((b + c)/ 3) + d)), Let X be the minimum number of registers required by an optimal code generation (without any register spill) algorithm tor a load/store architecture, in which
(i) only load and store instructions can have memory operands and
(ii) arithmetic instructions can have only register or immediate operands.
The value of X is______.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The given expression is (1) * 

b + c 
+ d 
3 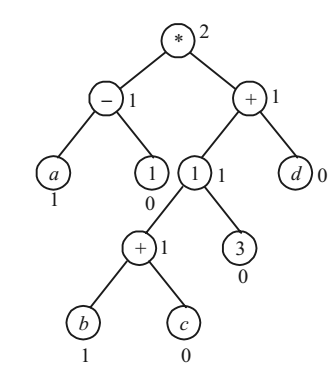
Let R1 and R2 be two registers
Load R1 ← b
Load R2 ← c
Add R1 ← (R1 + R2)
Div. R1 ← R1 / 3
Load R2 ← d
Add R1 ← R1 + R2
Load R2 ← a
Sub. R2 ← R2 - 1
Mul. R1 ← R1 * R2
Hence, only two registers are required.Correct Option: C
The given expression is (1) * 

b + c 
+ d 
3 
Let R1 and R2 be two registers
Load R1 ← b
Load R2 ← c
Add R1 ← (R1 + R2)
Div. R1 ← R1 / 3
Load R2 ← d
Add R1 ← R1 + R2
Load R2 ← a
Sub. R2 ← R2 - 1
Mul. R1 ← R1 * R2
Hence, only two registers are required.

