Architecture and Planning Miscellaneous-topic
- Liquidated damage refers to the
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Liquidated damages (also referred to as liquidated and ascertained damages) are damages whose amount the parties designate during the formation of a contract for the injured party to collect as compensation upon a specific breach (e.g., late performance).
Correct Option: B
Liquidated damages (also referred to as liquidated and ascertained damages) are damages whose amount the parties designate during the formation of a contract for the injured party to collect as compensation upon a specific breach (e.g., late performance).
- Which of the following processes is NOT used for corrosion resistance of cast iron?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface. The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and airbrushes, can be used. Epoxy is either any of the basic components or the cured end products of epoxy resins, as well as a colloquial name for the epoxide functional group. In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, oil or air to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low temperature processes, such as phase transformations, from occurring. Galvanization or galvanizing is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting. The most common method is hot -dip galvanizing, in which the parts are submerged in a bath of molten zinc.
Correct Option: C
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface. The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and airbrushes, can be used. Epoxy is either any of the basic components or the cured end products of epoxy resins, as well as a colloquial name for the epoxide functional group. In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, oil or air to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low temperature processes, such as phase transformations, from occurring. Galvanization or galvanizing is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting. The most common method is hot -dip galvanizing, in which the parts are submerged in a bath of molten zinc.
- Data on ‘households with one or more married couples sharing room with a person aged 12 years or more’, is used for computing
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Housing Shortage is defined as insufficient housing/ lack of housing to accommodate the existing population. The standard household size depends upon the existing infrastructure available in the area, location of the area, etc. If the household size exceeds this standard size, it shows sharing of single dwelling unit by one or more households.
Correct Option: B
Housing Shortage is defined as insufficient housing/ lack of housing to accommodate the existing population. The standard household size depends upon the existing infrastructure available in the area, location of the area, etc. If the household size exceeds this standard size, it shows sharing of single dwelling unit by one or more households.
- The grade-separated interchange suitable for 3- legged road intersection is :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
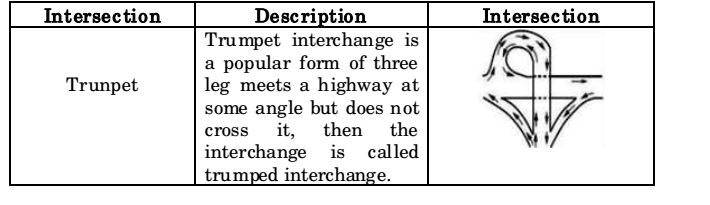
Correct Option: A

- The design element provided to ensure safety of a vehicle travelling at a prescribed design speed along the curved segment of a highway is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Super elevation is the amount by which the outer edge of a curve on a road or railway is banked above the inner edge. It helps to offset centripetal forces developed as the vehicle goes around a given curve. Along with the friction, on the road, super-elevation keeps vehicle from going off the road.
Correct Option: B
Super elevation is the amount by which the outer edge of a curve on a road or railway is banked above the inner edge. It helps to offset centripetal forces developed as the vehicle goes around a given curve. Along with the friction, on the road, super-elevation keeps vehicle from going off the road.

