Architecture and Planning Miscellaneous-topic
- Match the characteristics of settlement systems in Column I with their corresponding theory/ rules in column II and select appropriate option.
Column I Column II P. Primacy of settlements 1. Central place theory Q. Settlement size and 2. Gravity model location R. Random component 3. Rank size rule in location of settlement S. Interactions between 4. Entropy of settlements settlements 5. Core periphery model
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Central Place Theory (Christaller, 1933)
Christaller’s model is based on the following assumptions that every part of the plain is served by a central place and the circles of influence of these central places fills the plain. A central place is a place offering a variety of goods in the centre of the market area, such as a village, town or city. In the K = 3 system or market principle optimises the markets of each central place. Supposing a region has three cities, then it will have 9 towns and 27 villages, and so on.
Core Periphery Model, is a concept where Core regions are based on comparative advantages-resource endowment and location. Periphery is inaccessible, under populated and has poor resources. Favourable effects flow from center to periphery.
The Rank size rule is an empirical regularity. The settlements within a defined area are ranked in descending order according to the size of their population. Urban primacy indicates the ratio of the largest city to the next largest i.e the second largest in a country.
Gravity model, as social scientists refer to the modified law of gravitation, takes into account the population size of two places and their distance. The gravity model of migration is a model in urban geography derived from Newton’s law of gravity, and used to predict the degree of migration interaction between two places.
Entropy is an important concept in the studies on complex systems such as cities. Spatial patterns and processes can be described with varied entropy functions. This model is a criterion to measure urban population distribution and the distribution of cities at urban classes in the region.Correct Option: D
Central Place Theory (Christaller, 1933)
Christaller’s model is based on the following assumptions that every part of the plain is served by a central place and the circles of influence of these central places fills the plain. A central place is a place offering a variety of goods in the centre of the market area, such as a village, town or city. In the K = 3 system or market principle optimises the markets of each central place. Supposing a region has three cities, then it will have 9 towns and 27 villages, and so on.
Core Periphery Model, is a concept where Core regions are based on comparative advantages-resource endowment and location. Periphery is inaccessible, under populated and has poor resources. Favourable effects flow from center to periphery.
The Rank size rule is an empirical regularity. The settlements within a defined area are ranked in descending order according to the size of their population. Urban primacy indicates the ratio of the largest city to the next largest i.e the second largest in a country.
Gravity model, as social scientists refer to the modified law of gravitation, takes into account the population size of two places and their distance. The gravity model of migration is a model in urban geography derived from Newton’s law of gravity, and used to predict the degree of migration interaction between two places.
Entropy is an important concept in the studies on complex systems such as cities. Spatial patterns and processes can be described with varied entropy functions. This model is a criterion to measure urban population distribution and the distribution of cities at urban classes in the region.
- A residential area of 20 hectares is planned for three different types of plots of 500 m2, 300 m2 and 200 m2 with numbers of plot in each category are 100, 120, 150 respectively. The rest of the area is allowed for roads and facilities such as school, shops and par ks. Each plot has one dwelling unit and the average household size is 5 persons. The net residential density of the area in person per hectare is ______.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
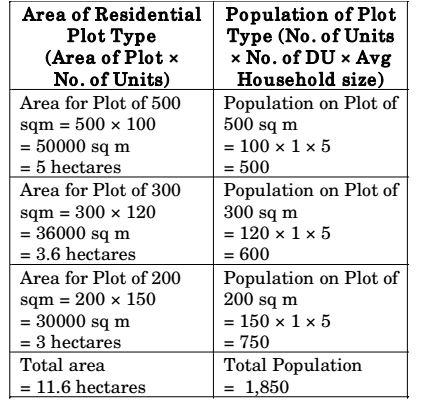
Net Residential Density = Population Area under residential plots = 
1860 
persons per hectare 11.6
= 160.3 persons per hectare
Correct Option: B

Net Residential Density = Population Area under residential plots = 
1860 
persons per hectare 11.6
= 160.3 persons per hectare
- A room having dimension 12m × 10m × 3.5m is required to be mechanically ventilated by airconditioner. The temperature difference outdoor ambient air and the supply air is 12°C. Consider three air exchanges per hour. The volumetric specific heat of the air is 1250 J/m3 °C. Assume one ton of refrigeration (TR) is equal to 3.5kW. The capacity of the air-conditioner for the room in TR will be _______.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Rate of ventilation = (12 × 10 × 3.5 × 3) = 0.35 3600
Cooling load = 1250 × 0.35 × 12 = 5.25 kW = 1.5 TRCorrect Option: B
Rate of ventilation = (12 × 10 × 3.5 × 3) = 0.35 3600
Cooling load = 1250 × 0.35 × 12 = 5.25 kW = 1.5 TR
- A cone, with a base of 10 cm diameter and axis of 12 cm, is lying on Horizontal Plane (HP) along its generator. The internal angle which is the base of the cone makes with HP is _____ degrees.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
tan θ = height = 12 base 5
θ = 67.6 °
Alternatively, using Pythogorean theorem, hypotenuse i.e. the length of the cone is calculated to be 13 cm.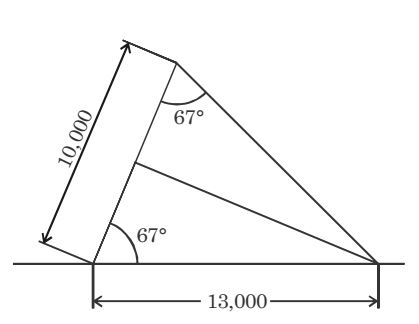
cos θ = base = 5 hypotaneous 13
cos θ = 0.38
θ = 67.6 °Correct Option: C
tan θ = height = 12 base 5
θ = 67.6 °
Alternatively, using Pythogorean theorem, hypotenuse i.e. the length of the cone is calculated to be 13 cm.
cos θ = base = 5 hypotaneous 13
cos θ = 0.38
θ = 67.6 °
- A power shovel is having 1.8 m2 excavation output per batch of operation. The average cycle time of the batch operation is 45 seconds. The lost time per hour of the excavation activity is 10 minutes. Assume six working hours of operation per day. The amount of soil excavated by the power shovel per day is ________ m3 (rounded of to one decimal place).
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Considering 10 min loss per hour,
Effective operating time per day = 50 × 6 = 300 minVolume of soil excavated = (300 × 60 × 1.8) = 720 cum 45
Correct Option: A
Considering 10 min loss per hour,
Effective operating time per day = 50 × 6 = 300 minVolume of soil excavated = (300 × 60 × 1.8) = 720 cum 45

