Architecture and Planning Miscellaneous-topic
- A town with a population of 50000 has an average household size of 5.0. The number of occupied dwelling units is 8400 of which 10% are in dilapidated condition. The housing demand of the town is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Number of units required = 50000 = 10000 units 5
Number of units available = 8400
Due to dilapidation (10%)
= 9 × 8400 = 7560 units
Requirement = 1000 – 7560
= 2440 unitsCorrect Option: C
Number of units required = 50000 = 10000 units 5
Number of units available = 8400
Due to dilapidation (10%)
= 9 × 8400 = 7560 units
Requirement = 1000 – 7560
= 2440 units
- Match the high-rise tube structural systems in Group 1 with their corresponding terms in Group II:
Group I Group II 
1. Framed tube 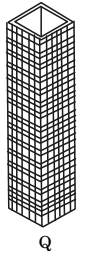
2. Bundled tubes 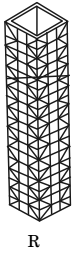
3. Braced tube 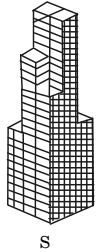
4. Perforated shell tube
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
1. Tube system
⇒ Concept is based on the idea that a building can be designed to resist lateral loads by desi gning it as a hollow cantilever perpendicular to the ground.
⇒ In the simplest incarnation of the tube, the exterior consists of closely spaced columns that are tied together with deep spandrel beams through moment connections.
⇒ This assembly of columns and beams forms a rigid frame that amounts to a dense and strong structural wall along the exterior of the building.
The different tubular systems are-
➤ Framed tube
➤ Braced tube
➤ Bundled tube
➤ Tube in tube
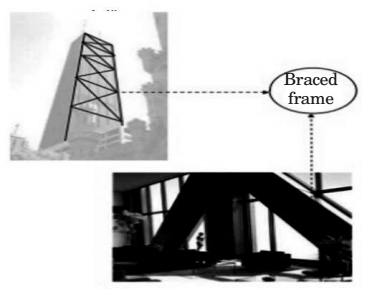
BRACED TUBE
∙ A braced tube overcomes this problem by stiffening the perimeter frames in their own planes.
∙ This concept stems from the fact instead of using closely spaced perimeter columns, it is possible to stiffen the widely spaced columns by diagonal braces to create wall -like characteristics.
∙ The braces also collect gravity loads from floors and act as inclined columns.
∙ The diagonals of a trussed tube connected to columns at each joint effectively eliminate the effects of shear lag throughout the tubular framwork.
∙ Therefore, the columns can be more widely spaced and the sizes of spandrels and columns can be smaller than those needed for framed tubes, allowing for larger window openings than in the framed tubes (Khan, 1967).
FRAMED TUBE
∙ In a framed tube system, which is the basic tubular form, the building has closely spaced columns and deep spandrel beams rigidly connected together throughout the exterior frames.
∙ Exterior column spacing should be from 5 to 15ft (1.5 to 4.5m) on centers. Practical spandrel beam depths should vary from 24 to 48 in (600 to 1200 mm)
∙ The axial forces in the corner columns are the greatest and the distribution is non-linear for both the web frame (i.e, frame parallel to wi nd), and the flange frame (i .e., fr ame perpendicular to wind).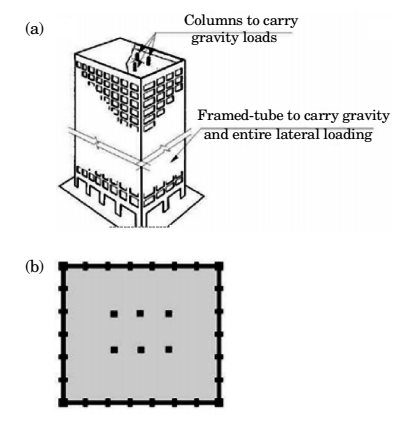
BUNDLED TUBE
∙ A bundled tube is a cluster of individual tubes connected together to act as a single unit.
∙ For such a structure, the three-dimensional response of the structure could be improved for strength and stiffness by providing cross walls or cross frames in the building.
∙ Also allowed for wider column spacing in the tubular walls, which made it possible to place interior frame lines without seriously compromising interior space planning of the building.
∙ It is possible to add diagonals to them to increase the efficient height limit.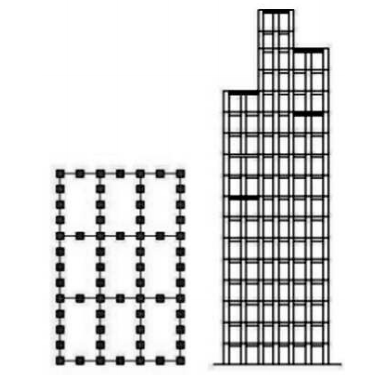
Correct Option: B
1. Tube system
⇒ Concept is based on the idea that a building can be designed to resist lateral loads by desi gning it as a hollow cantilever perpendicular to the ground.
⇒ In the simplest incarnation of the tube, the exterior consists of closely spaced columns that are tied together with deep spandrel beams through moment connections.
⇒ This assembly of columns and beams forms a rigid frame that amounts to a dense and strong structural wall along the exterior of the building.
The different tubular systems are-
➤ Framed tube
➤ Braced tube
➤ Bundled tube
➤ Tube in tube
BRACED TUBE
∙ A braced tube overcomes this problem by stiffening the perimeter frames in their own planes.
∙ This concept stems from the fact instead of using closely spaced perimeter columns, it is possible to stiffen the widely spaced columns by diagonal braces to create wall -like characteristics.
∙ The braces also collect gravity loads from floors and act as inclined columns.
∙ The diagonals of a trussed tube connected to columns at each joint effectively eliminate the effects of shear lag throughout the tubular framwork.
∙ Therefore, the columns can be more widely spaced and the sizes of spandrels and columns can be smaller than those needed for framed tubes, allowing for larger window openings than in the framed tubes (Khan, 1967).
FRAMED TUBE
∙ In a framed tube system, which is the basic tubular form, the building has closely spaced columns and deep spandrel beams rigidly connected together throughout the exterior frames.
∙ Exterior column spacing should be from 5 to 15ft (1.5 to 4.5m) on centers. Practical spandrel beam depths should vary from 24 to 48 in (600 to 1200 mm)
∙ The axial forces in the corner columns are the greatest and the distribution is non-linear for both the web frame (i.e, frame parallel to wi nd), and the flange frame (i .e., fr ame perpendicular to wind).

BUNDLED TUBE
∙ A bundled tube is a cluster of individual tubes connected together to act as a single unit.
∙ For such a structure, the three-dimensional response of the structure could be improved for strength and stiffness by providing cross walls or cross frames in the building.
∙ Also allowed for wider column spacing in the tubular walls, which made it possible to place interior frame lines without seriously compromising interior space planning of the building.
∙ It is possible to add diagonals to them to increase the efficient height limit.
- Identify the urban functions that are included under Social Infrastructure:
P. Schools and colleges
Q. Hospitals and clinics
R. Roads and footpaths
S. Parks and plazas
T. Malls and markets
U. Community centres
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Markets and Malls are commercial land use
Correct Option: A
Markets and Malls are commercial land use
- Match the I nstitutions in Group I with their Architects in Group IT
Group I Group II P. National Dairy Development Board, New Delhi 1. B.V. Doshi Q. National Institute of Immunology, New Delhi 2. Charles Correa R. Indian Institute of Management. Bangalore 3. A.P. Kanvinde S. Jodhpur University, Jodhpur 4. J.A. Stein 5. Raj Rewal 6. U.C. Jain
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: A
NA
- Match the domes in Group I with their examples in Group II:
Group I Group II P. Dome with a huge central cut-out at the top 1. Pisa Cathedral Q. Dome with slit windows at the springing level 2. St. Peter's Cathedral R. Dome with an elliptical base 3. Pantheon S. Dome on a drum with a lantern on top 4. Hagia Sophia
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
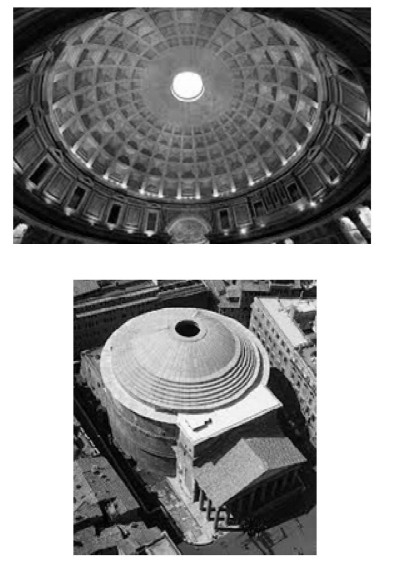



Correct Option: D





