Signal and systems miscellaneous
- Which one the following is the response y(t) of a causal LTI system described by
H(s) = (s + 1) s2 + 2s + 2
for a given input x(t) = e– t .u(t)?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given
H (s) = (s + 1) s2 + 25 + 2
if x(t) = e–tu(t)
thenX(s) = 1 s + 1
Now,
Y(s) = H(s).X(s)or Y(s) = (s + 1) . (s + 1) s2 + 25 + 2 (s + 1)
or Y(s) = 1 (s + 1)2 + 1
y(t) = e–t.sin t.u(t)
Hence, alternative (A) is the correct choice.Correct Option: A
Given
H (s) = (s + 1) s2 + 25 + 2
if x(t) = e–tu(t)
thenX(s) = 1 s + 1
Now,
Y(s) = H(s).X(s)or Y(s) = (s + 1) . (s + 1) s2 + 25 + 2 (s + 1)
or Y(s) = 1 (s + 1)2 + 1
y(t) = e–t.sin t.u(t)
Hence, alternative (A) is the correct choice.
-
If y(t) + 
∞ y(τ) x(t – τ )dτ = S(t) + x(t) then y(t) is— 0
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
y(t) + 
∞ y(τ) x(t – τ )dτ = δ(t) + x(t) …(A) 0 L.H.S. = y(t) + 
∞ y(τ) x(t – τ )dτ 0
= y(t) + y(t) * x(t)
If we compare the equation with R.H.S part of equation (A), we conclude that
y(t) = δ(t) {∵ x(t) * δ(t) = x(0)}Correct Option: B
y(t) + 
∞ y(τ) x(t – τ )dτ = δ(t) + x(t) …(A) 0 L.H.S. = y(t) + 
∞ y(τ) x(t – τ )dτ 0
= y(t) + y(t) * x(t)
If we compare the equation with R.H.S part of equation (A), we conclude that
y(t) = δ(t) {∵ x(t) * δ(t) = x(0)}
- The impulse response of a system consists of two delta function as shown in the given figure.
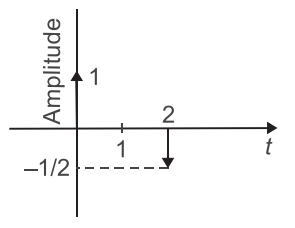
The input to the system is a unit amplitude square pulse of one unit time duration. Which one of the following depicts the correct output?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given that impulse response i.e.
h(t) = 1.δ(t) – 1 δ(t – 1) 2
or H(s) = 1 – 1 e–s 2 
Also, given x(t) = unit amplitude pulse of one unit time duration i.e.
or x(t) = u(t) – u(t – 1)
or X(s) = 1 - 1 e–s s s 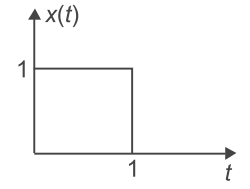
Now, Y(s) = H(s).X(s)
or Y(s) = 
1 - 1 e–s 

1 - 1 e–s 
s s s
or Y(s) = 1 - 1 . 1 e–s + 1 1 e–s s 2 s 2 s or Y(s) = 1 - 1 - e–s - 1 1 e–s + 1 1 e–2s s s 2 s 2 s
Taking inverse Laplace transform
or y(t) = u(t) – u(t – 1) – 1/2 · u(t – 1) + 1/2 u(t – 2)
or y(t) = u(t) – 3/2 u(t – 1) + 1/2 u(t – 2)
Hence, alternative (B) is the correct choice.Correct Option: B
Given that impulse response i.e.
h(t) = 1.δ(t) – 1 δ(t – 1) 2
or H(s) = 1 – 1 e–s 2 
Also, given x(t) = unit amplitude pulse of one unit time duration i.e.
or x(t) = u(t) – u(t – 1)
or X(s) = 1 - 1 e–s s s 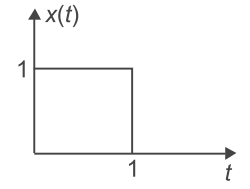
Now, Y(s) = H(s).X(s)
or Y(s) = 
1 - 1 e–s 

1 - 1 e–s 
s s s
or Y(s) = 1 - 1 . 1 e–s + 1 1 e–s s 2 s 2 s or Y(s) = 1 - 1 - e–s - 1 1 e–s + 1 1 e–2s s s 2 s 2 s
Taking inverse Laplace transform
or y(t) = u(t) – u(t – 1) – 1/2 · u(t – 1) + 1/2 u(t – 2)
or y(t) = u(t) – 3/2 u(t – 1) + 1/2 u(t – 2)
Hence, alternative (B) is the correct choice.
- The amplitude response of a discrete system with a simple pole is shown in the given figure.
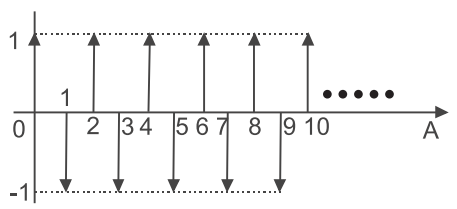
The must be located—
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
From given figure Function say x(n) represented as
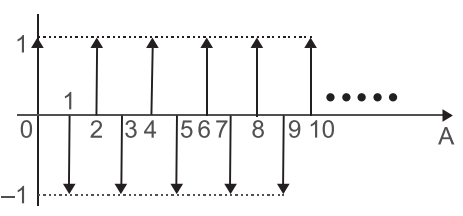
x(n) = (– 1)n u(n) Now, X(z)∞ X(z) = 
x(n)·z–n n = – ∞
or∞ X(z) = 
(– 1)n·z–n n = – ∞
or
X(z) = 1 + (– 1)z–1 + z–2 + (– 1)–3 + …
orX(z) = 1 1 + z–1
orX(z) = z z + 1
Here, pole at z + 1 = 0
i.e., z = – 1
Hence, alternative (B) is the correct choice.Correct Option: B
From given figure Function say x(n) represented as

x(n) = (– 1)n u(n) Now, X(z)∞ X(z) = 
x(n)·z–n n = – ∞
or∞ X(z) = 
(– 1)n·z–n n = – ∞
or
X(z) = 1 + (– 1)z–1 + z–2 + (– 1)–3 + …
orX(z) = 1 1 + z–1
orX(z) = z z + 1
Here, pole at z + 1 = 0
i.e., z = – 1
Hence, alternative (B) is the correct choice.
- The discrete time system described by y[n] = x(n2) is—
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The given discrete-time system is y[n] = x[n2]
● is linear since there is no constant term as well as square terms in input and output.
● non-causal since for any value of n except 0 and 1, output depends upon the future value of the input for example at n = – 1y[– 1] = x[12] = x[1] 
y[2] = x[22] = x[4]
i.e., output depends upon the future input.
● System is time-invariant since there is no time factor term i.e., n in the given equation.
Hence, alternative (C) is the correct choice.Correct Option: C
The given discrete-time system is y[n] = x[n2]
● is linear since there is no constant term as well as square terms in input and output.
● non-causal since for any value of n except 0 and 1, output depends upon the future value of the input for example at n = – 1y[– 1] = x[12] = x[1] 
y[2] = x[22] = x[4]
i.e., output depends upon the future input.
● System is time-invariant since there is no time factor term i.e., n in the given equation.
Hence, alternative (C) is the correct choice.

