Signal and systems miscellaneous
- The function x(t) is shown in the given figure. If X(jω) is the Fourier transform of the x(t), then |X(jω)| at ω = 0 will be—

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
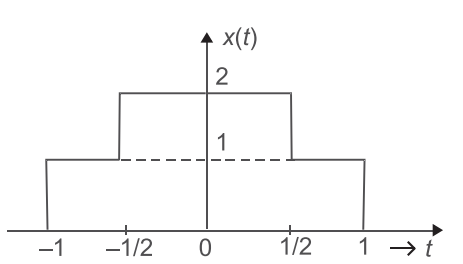
Given waveform of x(t) is a combination of four shifted step function i.e.,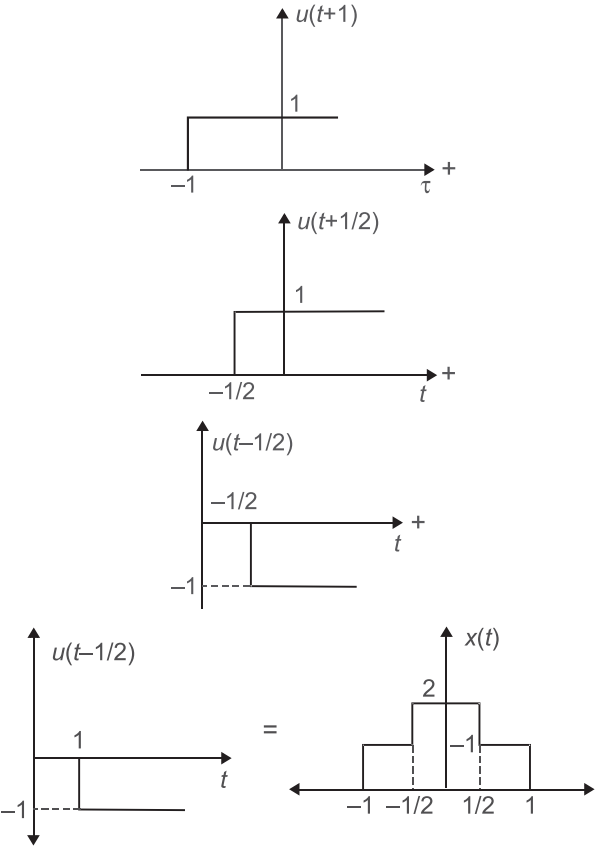
i.e., x(t) = u 
t + 1 
+ u 
t + 1 
- u 
t - 1 
-u (t - 1).......A 2 2 2 F[x(t)] = ejω + ejω/2 − e−jω/2 − e−jω jω jω jω jω X(jω) = 
ejω − jω/2 
+ 
ejω/2 − e jω/2 
jω jω X(jω) = 2 sin ω + 2 sin ω ω ω 2 |X(jω)|at ω = 0 = limω → 0 
2 sin ω + 2 sin ω 
ω ω 2 = limω → 0 
2.cos ω + 2 cos ω . 1 
1 2 2
= 2 + 1 = 3.
Hence, alternative (D) is the correct choice.Correct Option: D

Given waveform of x(t) is a combination of four shifted step function i.e.,
i.e., x(t) = u 
t + 1 
+ u 
t + 1 
- u 
t - 1 
-u (t - 1).......A 2 2 2 F[x(t)] = ejω + ejω/2 − e−jω/2 − e−jω jω jω jω jω X(jω) = 
ejω − jω/2 
+ 
ejω/2 − e jω/2 
jω jω X(jω) = 2 sin ω + 2 sin ω ω ω 2 |X(jω)|at ω = 0 = limω → 0 
2 sin ω + 2 sin ω 
ω ω 2 = limω → 0 
2.cos ω + 2 cos ω . 1 
1 2 2
= 2 + 1 = 3.
Hence, alternative (D) is the correct choice.
- System represented by equation
y(t + 4) + 2y(t) = x(t + 2) is:
(i) causal
(ii) linear
(iii) time invariant
The correct statements are—
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given equation y(t + 4) + 2y(t) = x(t + 2)
● is causal since output at any instant of time depends only on present and past values of there input signal.
● is linear since there is no constant term in the given equation.
● is time invariant since there is no any time factor in the given equation.
Hence, alternative (D) is the correct choice.Correct Option: D
Given equation y(t + 4) + 2y(t) = x(t + 2)
● is causal since output at any instant of time depends only on present and past values of there input signal.
● is linear since there is no constant term in the given equation.
● is time invariant since there is no any time factor in the given equation.
Hence, alternative (D) is the correct choice.
- The given system equation
y(t) = x(t + 2) is—
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The given system equation y(t) = x(t + 2) is—
● non-causal
● time invariant
● dynamic because input and output argument are not same i.e.,
different. Hence, alternative (C) is the correct choice.Correct Option: C
The given system equation y(t) = x(t + 2) is—
● non-causal
● time invariant
● dynamic because input and output argument are not same i.e.,
different. Hence, alternative (C) is the correct choice.
- The true statements for the system given below
y′(t + 4) + 2y(t) = x(t + 2)
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given system y′(t + 4) + 2y(t) = x(t + 2) is causal and dynamic.
Causal: Since, output dependes upon the present and past input only.
Dynamic: Because input and output arguments are different.Correct Option: A
Given system y′(t + 4) + 2y(t) = x(t + 2) is causal and dynamic.
Causal: Since, output dependes upon the present and past input only.
Dynamic: Because input and output arguments are different.
- The true statement for the system equation given below
y(t)=2x(at)
(i) If a = 1, y(t) is static causal.
(ii) If a < 1, y(t) is dynamic causal.
(iii) If a > 1, y(t) is dynamic and non-causal.
(iv) If a > 1, y(t) is dynamic and causal.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given equation
y(t)=2x(at) …(I)
Case I: When a = 1, equation (I) becomes
y(t)=2x(t) …(A)
Equation (A) is static and causal.
Case II: When a < 1 say 1/2 Equation (I) becomesy(t) = 2x 
1 t 
...........(B) 2
Equation (B) is causal and dynamic.
Case III: If a > 1, say a = 2
Equation (I) becomes
y(t)=2x(2t) …(C)
Equation (C) becomes non-causal and dynamic.
Hence, alternative (C) is the correct choice.Correct Option: C
Given equation
y(t)=2x(at) …(I)
Case I: When a = 1, equation (I) becomes
y(t)=2x(t) …(A)
Equation (A) is static and causal.
Case II: When a < 1 say 1/2 Equation (I) becomesy(t) = 2x 
1 t 
...........(B) 2
Equation (B) is causal and dynamic.
Case III: If a > 1, say a = 2
Equation (I) becomes
y(t)=2x(2t) …(C)
Equation (C) becomes non-causal and dynamic.
Hence, alternative (C) is the correct choice.

