Power systems miscellaneous
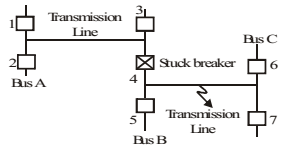
- Consider the protection system shown in the figure below. The circuit breakers, numbered from 1 to 7 are of identical type. A single line to ground fault with zero fault impedance occurs at the midpoint of the line (at point F), but circuit breaker 4 fails to operate (“stuck br eaker”). I f the relays are coordinated correctly, a valid sequence of circuit breaker operations is
(a)
(b)
(c)
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
If the relays are coordinated correctly, due to fault in a particular section, relay in that section must operate first, then relays in near by section if first relay fails. It is back up protection. Thus, the sequence is 5, 6, 7, 3, 1, 2.
Correct Option: C
If the relays are coordinated correctly, due to fault in a particular section, relay in that section must operate first, then relays in near by section if first relay fails. It is back up protection. Thus, the sequence is 5, 6, 7, 3, 1, 2.
- The total reactance and total susceptance of a lossless overhead EHV line, operating at 50 Hz, are given by 0.045 pu and 1.2 pu respectively. If the velocity of wave propagation is 3 × 105 km/s, then approximate length of the line is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Assume that ZB is the base impedance,
then, X(in Ω) 0.045 ZB
and, Y(inΩ) = 1.2/ZB
If l is length of line, then, = ωLl and Y = ωClor L = X = 0.045ZB ..............(A) ωl ωl and C = Y = 1.2 ..............(B) ωl ωlZB
Now, velocity of propagation= 1 √LC ⇒ vc = 1 = ωl √(0.045ZB/ωl)(1.2/ωlZB) √0.045 × 1.2 ⇒ 3 × 108 = (314)l √0.045 × 1.2
⇒ l ≌ 222 × 10³m = 222 km.Correct Option: B
Assume that ZB is the base impedance,
then, X(in Ω) 0.045 ZB
and, Y(inΩ) = 1.2/ZB
If l is length of line, then, = ωLl and Y = ωClor L = X = 0.045ZB ..............(A) ωl ωl and C = Y = 1.2 ..............(B) ωl ωlZB
Now, velocity of propagation= 1 √LC ⇒ vc = 1 = ωl √(0.045ZB/ωl)(1.2/ωlZB) √0.045 × 1.2 ⇒ 3 × 108 = (314)l √0.045 × 1.2
⇒ l ≌ 222 × 10³m = 222 km.
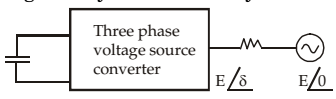
- The figure given below shows a three phase selfcommutated voltage source converter connected to a power system. The converter's dc bus capacitor is marked as C in the figure. The circuit is initially operating in steady state with δ = 0 and the capacitor dc voltage is equal to Vdc0. You may neglect all losses and harmonics. What action should be taken to increase the capacitor dc voltage slowly to a new steady state value?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
To increase the capacitor dc voltage slowly to a new steady state value, make δ negative and return it to its original valve.
Correct Option: D
To increase the capacitor dc voltage slowly to a new steady state value, make δ negative and return it to its original valve.
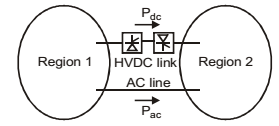
- Two regional systems, each having several synchr onous generators and loads are interconnected by an ac line and a HVDC link as shown in the figure given below. Which of the following statements is true in the steady state?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
By changing the grid angle, we can change the power sharing between the AC line and HVDC link.
Correct Option: C
By changing the grid angle, we can change the power sharing between the AC line and HVDC link.
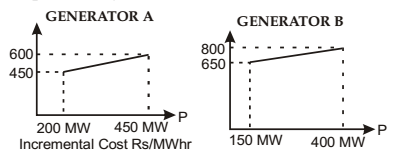
- The incremental cost curves in Rs/ MW hr for two generators supplying a common load of 700 MW are shown in the figures. The maximum and minimum generation limits are also indicated. The optimum generation schedule is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Maximum incremental cost in Rs/M Whr for generator A = 600 (at 450 MW)
Minimum incremental cost in Rs/MWhr for generator B = 650 (at 150 MW)
As maximum value of increamental cost of A is less than minimum value of B,
∴ Generator A will operate at its maximum output 450 MW and B at (700 – 450) MW = 250 MWCorrect Option: C
Maximum incremental cost in Rs/M Whr for generator A = 600 (at 450 MW)
Minimum incremental cost in Rs/MWhr for generator B = 650 (at 150 MW)
As maximum value of increamental cost of A is less than minimum value of B,
∴ Generator A will operate at its maximum output 450 MW and B at (700 – 450) MW = 250 MW

