Signals and systems electrical engineering miscellaneous
-
Let x(t) = rect 
t - 1 
(where rect (x) = 1 2 for - 1 ≤ x ≤ 1 and zero otherwise). 2 2 Then if since (x) = sin (πx) , πx
then Fourier Transform of x(t) + x(– t) will be given by
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
rect(x) =1 for - 1 ≤ x ≤ 1 .......(1) 2 2 Given x(t) = rect 
t - 1 
2
Simplifying x(t) with the help of equation (1).
∴ x(t) = 1, 0 ≤ t ≤ 1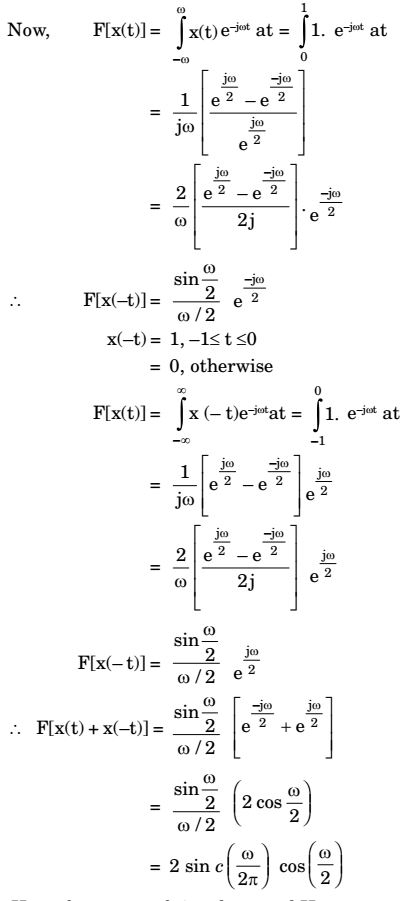
Correct Option: C
rect(x) =1 for - 1 ≤ x ≤ 1 .......(1) 2 2 Given x(t) = rect 
t - 1 
2
Simplifying x(t) with the help of equation (1).
∴ x(t) = 1, 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
-
If X(z) = z eith |z| > a, (z - a)²
then residue of X(z)zn – 1 at z = a for n ≥ 0 will be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
X(z) = z with |z| > a (z - a)² Let f(z) = X(z) zn – 1 = zn with |z| > a (z - a)² 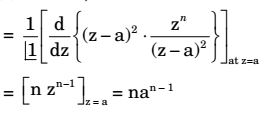
X(z) = z with |z| > a (z - a)² Let f(z) = X(z) zn – 1 = zn with |z| > a (z - a)² 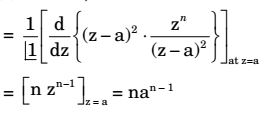
Correct Option: D
X(z) = z with |z| > a (z - a)² Let f(z) = X(z) zn – 1 = zn with |z| > a (z - a)² 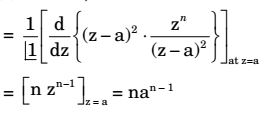
- H(z) is a transfer function of a real system. When a signal x[n] = (t + j)n is the input to such a system, the output is zero. Further, the Region Of Convergence (ROC) of

1 - 1 z-1 
2
H(z) is the entire Z-plane (except z = 0). It can then be inferred that H(z) can have a minimum of
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
It will have minimum 1 pole and 2 zeros.
ROC = 
1 - 1 z-1 
H(z) = (2z - 1) H(z) 2 2z ∴ H(z) will be in the form of zn , (2z - 1)
Hence for minimum realization, n = 2H(z) = z2 , (2z - 1) Correct Option: B
It will have minimum 1 pole and 2 zeros.
ROC = 
1 - 1 z-1 
H(z) = (2z - 1) H(z) 2 2z ∴ H(z) will be in the form of zn , (2z - 1)
Hence for minimum realization, n = 2H(z) = z2 , (2z - 1)
- Let x(t) be a periodic signal with time period T. Let y(t) = x(t – t0) + x(t + t0) for some t0.
The fourier Series coefficients of y(t) are denoted by b. If bk = 0 for all odd k, then t0 can be equal to
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
y(t)= x(t – t0) + x (t + t0)
Since y(t) is periodic with period T, then x(t – t0) and x(t + t0) will also be periodic with T
Now, bk = ake-jkω0t0 + akejkω0t0
Where, ak is fourier series coefficient of equal x(t),
bk = ak[e-jkω0t0 + ejkω0t0]
= 2ak cos kω0t0
Given that, bk = 0 for odd k
then, kω0t0 = k(π/2),
where k = 2m + 1, m is an integer⇒ t0 = T 
ω0 = 2π 
4 T Correct Option: B
y(t)= x(t – t0) + x (t + t0)
Since y(t) is periodic with period T, then x(t – t0) and x(t + t0) will also be periodic with T
Now, bk = ake-jkω0t0 + akejkω0t0
Where, ak is fourier series coefficient of equal x(t),
bk = ak[e-jkω0t0 + ejkω0t0]
= 2ak cos kω0t0
Given that, bk = 0 for odd k
then, kω0t0 = k(π/2),
where k = 2m + 1, m is an integer⇒ t0 = T 
ω0 = 2π 
4 T
- A system with input x(t) and output y(t) is defined by the input-output relation
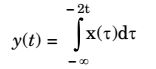
The system will be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
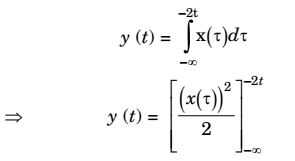
It is obvious that system will be time variant, unstable and non-causal.Correct Option: D
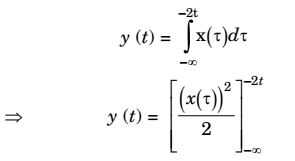
It is obvious that system will be time variant, unstable and non-causal.

