Signals and systems electrical engineering miscellaneous
- For the system governed by the set of equations:
dx1/dt = 2x1 + x2 + 4
dx2 /dt = – 2x1 + 4
y = 3x1
the transfer function Y(s)/U(s) is given by
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
dx1 = 2x1 + x2 + 4 dt dx2 = - 2x1 + 4 dt
y = 3x1
Now from the standard equation xi = Ax + BU
y = Cx + DU
x1 
= 
2 1 

x1 
+ 
1 
[4] x2 - 2 2 x2 1 y = [3 0] 
x1 
x2 Transfer function y(s) C(SI - A)-1 B u(s) 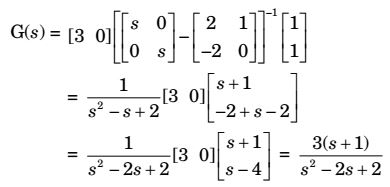
Correct Option: A
dx1 = 2x1 + x2 + 4 dt dx2 = - 2x1 + 4 dt
y = 3x1
Now from the standard equation xi = Ax + BU
y = Cx + DU
x1 
= 
2 1 

x1 
+ 
1 
[4] x2 - 2 2 x2 1 y = [3 0] 
x1 
x2 Transfer function y(s) C(SI - A)-1 B u(s) 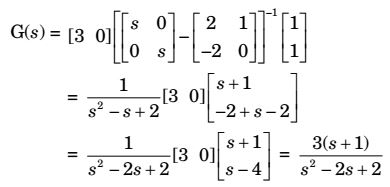
- The Laplace transform of f(t) = 2√t/π is s–3/2 . The Laplace transform of g(t) = √1/xt is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
It is given that laplace transform of ƒ(t)
i.e. ∫ 
2√ t 
= s-3/2 π Given as g(t) = 1 √πt 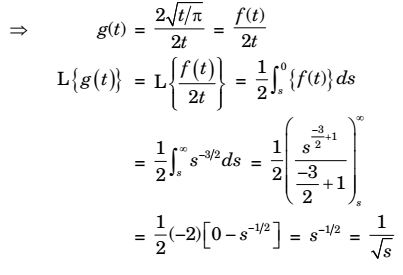
Correct Option: B
It is given that laplace transform of ƒ(t)
i.e. ∫ 
2√ t 
= s-3/2 π Given as g(t) = 1 √πt 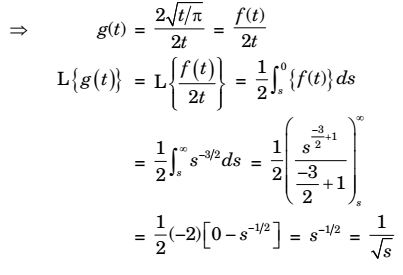
- The signum function is given by
sgn(x) = 
x/|x|, x≠0 0 x = 0
The fourier series expansion of sgn(cos(t)) has
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The signum function is given by,
sgn(x) = 
x/|x|; x ≠ 0 0; x = 0
Similarly,sgn(cos t) = 
cos/|cos t|; cos t ≠ 0 - 1; cos t = 0 cos t / |cos t| = 
1, cos t > 0 - 1; cos t < 0 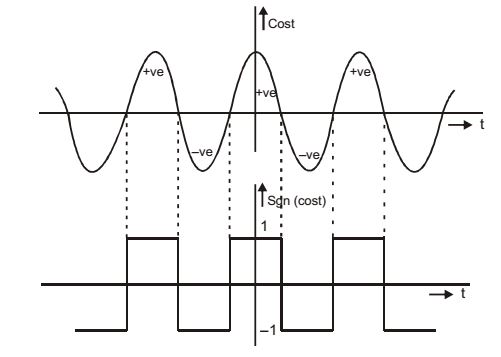
It is even function and show half wave symmetry. It contains only cosine term with odd numbered harmonics. a0 = 0
bn = 0an = 
0; n = even ≠0; n = odd
Sgn(Cost) = a1 cosωt + a3 cos3ωt + a5cos5ωt +...Correct Option: D
The signum function is given by,
sgn(x) = 
x/|x|; x ≠ 0 0; x = 0
Similarly,sgn(cos t) = 
cos/|cos t|; cos t ≠ 0 - 1; cos t = 0 cos t / |cos t| = 
1, cos t > 0 - 1; cos t < 0 
It is even function and show half wave symmetry. It contains only cosine term with odd numbered harmonics. a0 = 0
bn = 0an = 
0; n = even ≠0; n = odd
Sgn(Cost) = a1 cosωt + a3 cos3ωt + a5cos5ωt +...
- Consider a discrete time signal given by
x[n] = (– 0.25)n u[n] + (0.5)n u[ – n – 1]
The region of convergence of its Z-transform would be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
x[n] = (– 0.25)n u[n] + (0.5)n u[– n – 1] = x1 [n] + x2[n]
x1 [n] = (– 0.25)n u[n] (+ve sided sequence)x1[z] = z = z z - ( -0.25) z + 0.25 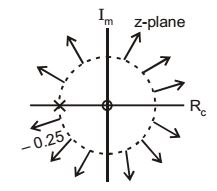
ROC1 : |z| > |– 0.25|
|z| > 0.25
x2 [n] = (0.5)n u[– n – 1] (– ve sided sequence)x2(z) = z z - 0.5 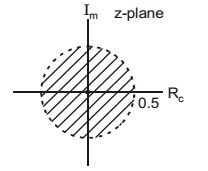
ROC2 :
| z| < | 0.5|
| z| < 0.5
Therefore required ROC for given signal
0.5 > | | > 0.25Correct Option: C
x[n] = (– 0.25)n u[n] + (0.5)n u[– n – 1] = x1 [n] + x2[n]
x1 [n] = (– 0.25)n u[n] (+ve sided sequence)x1[z] = z = z z - ( -0.25) z + 0.25 
ROC1 : |z| > |– 0.25|
|z| > 0.25
x2 [n] = (0.5)n u[– n – 1] (– ve sided sequence)x2(z) = z z - 0.5 
ROC2 :
| z| < | 0.5|
| z| < 0.5
Therefore required ROC for given signal
0.5 > | | > 0.25
- The impulse response g(t) of a system, G, is as shown in Figure (a). What is the maximum value attained by the impulse response of two cascaded blocks of Gas shown in Figure (b)?
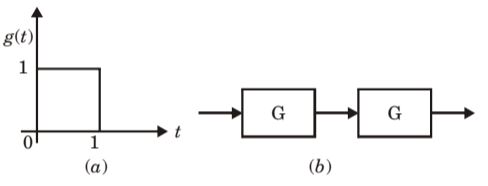
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
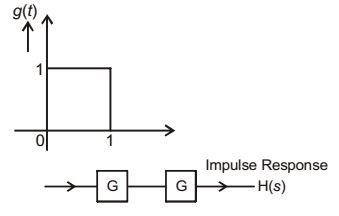
Impulse Response,
H(s) = G(s) · G(s) ...(i)
Taking Inverse Laplace transform both sides,
h(t) = g(t) * g(t) ...(ii)
where g(t) = u(t) – u(t – 1)
h(t) =
= u(t) * u(t) – u(t) * u(t – 1) – u(t) * u (t – 1) + u(t – 1) * u(t – 1)
= r(t) – r(t – 1) – r(t – 1) + r(t – 2)
h(t) = r(t) – 2r (t – 1) + r(t – 2)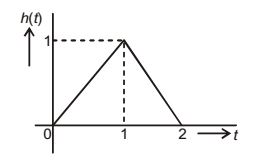
Therefore, Maxm value of Impulse Response
h(t)max = 1Correct Option: D

Impulse Response,
H(s) = G(s) · G(s) ...(i)
Taking Inverse Laplace transform both sides,
h(t) = g(t) * g(t) ...(ii)
where g(t) = u(t) – u(t – 1)
h(t) =
= u(t) * u(t) – u(t) * u(t – 1) – u(t) * u (t – 1) + u(t – 1) * u(t – 1)
= r(t) – r(t – 1) – r(t – 1) + r(t – 2)
h(t) = r(t) – 2r (t – 1) + r(t – 2)
Therefore, Maxm value of Impulse Response
h(t)max = 1

