Signals and systems electrical engineering miscellaneous
-
Let X(z) = 1 1 - z-3
be the Z-transform of a causal signal x[n]. Then, the values of x[2] and x[3] are
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given x(z) = 1 1 - z–3
x(z) can be written as = 1 + z–3 + z–6 + 2–9
Now x[2] correspond to coefficient z–2 = 0
and x [3] correspond to coefficient of z–3 = 1Correct Option: B
Given x(z) = 1 1 - z–3
x(z) can be written as = 1 + z–3 + z–6 + 2–9
Now x[2] correspond to coefficient z–2 = 0
and x [3] correspond to coefficient of z–3 = 1
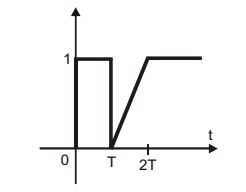
- The functi on shown in the figure can be represented as
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: A
NA
- For a periodic square wave, which one of the following statements is TRUE?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
For a Periodic square wave, the fourier series coefficients exist and reconstruction converges at most points.
Correct Option: C
For a Periodic square wave, the fourier series coefficients exist and reconstruction converges at most points.
- x(t) is nonzero only for Tx < t < T'x, and similarly, y(t) is nonzero only for Ty < t < T'y. Let z(t) be convolution of x(t) and y(t). Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given that z(t) is x(t)* y(t)
Range of z(t) is [sum of lower limits of x(t) and y(t) to sum of upper limit of x(t) and y(t)].
Tx + Ty < t < Tx + TyCorrect Option: C
Given that z(t) is x(t)* y(t)
Range of z(t) is [sum of lower limits of x(t) and y(t) to sum of upper limit of x(t) and y(t)].
Tx + Ty < t < Tx + Ty
- Let S be the set of points in the complex plane corresponding to the unit circle. (That i s, S = {z: | z| = 1}. Consider the function f(z) = zz* where z* denotes the complex conjugate of z. The f(z) maps S to which one of the following in the complex plane
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
ƒ(Z) = Z.Z*
where Z* is conjugate of Z
∴ ƒ(Z) = | Z|²
= 1 + i.0
∴ ƒ(Z) maps S to the point (1, 0) in the complex planeCorrect Option: C
ƒ(Z) = Z.Z*
where Z* is conjugate of Z
∴ ƒ(Z) = | Z|²
= 1 + i.0
∴ ƒ(Z) maps S to the point (1, 0) in the complex plane

