Signals and systems electrical engineering miscellaneous
- The raised cosine pulse x(t) is defined as
x(t) = 
1/2(cos ωt + 1), - π/ω ≤ t ≤ π/ω 
0, otherwise
The total energy of x(t) is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
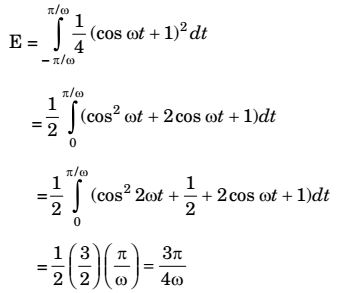
Correct Option: A
- The relationship between the input x(t) and output y(t)of a causal system is defined as
d²y(t) - dy(t) - 2y(t) = 4x(t) + 5 dx(t) dt² dt dt
The impulse response of system is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Y(s) (s² – s – 2) = X (s) (5s – 4)
H(s) = Y(s) = 5s - 4 X(s) s ² - s - 2 = 3 + 2 s + 1 s - 2
h(t) = 3e– t u(t) + 2e2t u(t).Correct Option: B
Y(s) (s² – s – 2) = X (s) (5s – 4)
H(s) = Y(s) = 5s - 4 X(s) s ² - s - 2 = 3 + 2 s + 1 s - 2
h(t) = 3e– t u(t) + 2e2t u(t).
- The two inputs to an analogue multiplier are x(t) and y(t) with Fourier transform X(ƒ) and Y(ƒ) respectively. The output z(t) will have a transform Z(ƒ) given by
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Multiplication of two signals in frequency domain is equivalent to their convolution in time domain.
Correct Option: D
Multiplication of two signals in frequency domain is equivalent to their convolution in time domain.
- Consider a continuous-time signal x(t) whose magnitude and phase spectra are as follows:
| X (jω)| = 2{u(ω + 3) – u(ω – 3)},∠X (jω) = - 3ω + π 2
The value of t, for which x(t) = 0, is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
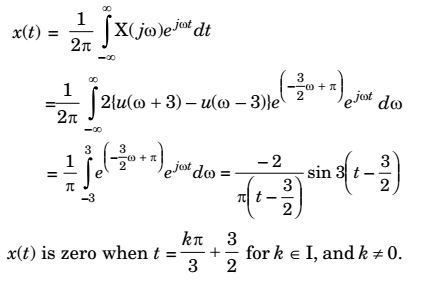
Correct Option: B
- A real and non-negative signal x(t) has Fourier transform X(jω). The following facts are given 1. F– 1{(1 + jω) X(jω)} = Ae– 2tu(t), where A is constant
2.
The signal x(t) may be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Y(jω) = 1 - 1 = 1 3 + jω 4 + jω (3 + jω)(4 + jω) X(jω) = Y(jω) = 1 H(jω) 4 + jω
⇒ x(t) = e– 4tu(t)Correct Option: B
Y(jω) = 1 - 1 = 1 3 + jω 4 + jω (3 + jω)(4 + jω) X(jω) = Y(jω) = 1 H(jω) 4 + jω
⇒ x(t) = e– 4tu(t)

