Signals and systems electrical engineering miscellaneous
- x [n] = 0; n < – 1, n > 0, x [– 1] = – 1, x[0] = 2 is the input and y [n] = 0; n < – 1, n > 2, y[– 1] = – 1 = y[1], y [0] = 3, y [2] = – 2 is the output of a discret e-time LTI system. The system impulse response h[n] will be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: A
NA
- x (t) is a real valued function of a real variable with period T. Its trigonometric Fourier Series expansion contains no terms of frequency
ω = 2π (2k)/T; k = 1, 2,.... Also, no sine terms are present. Then x (t) satisfies the equation
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Since, the fourier expansion of x(t) contains no sine terms, therefore,
x(t) = x(–t)
or, x(t) = x(T – t)
as x(t) is periodic with T
Now, as signal x(t) contains odd harmonics.Then x(t) = -x 
t - T 
2 Thus x(t) = x(T - t) = -x 
t - T 
2 Correct Option: D
Since, the fourier expansion of x(t) contains no sine terms, therefore,
x(t) = x(–t)
or, x(t) = x(T – t)
as x(t) is periodic with T
Now, as signal x(t) contains odd harmonics.Then x(t) = -x 
t - T 
2 Thus x(t) = x(T - t) = -x 
t - T 
2
- Which of the following is true?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
A signal having amplitude within finite boundaries called bounded signal and it can have finite energy or infinite energy. If this signal is power signal, then it possess infinite energy. But in any case, this bounded signal will be finite for all the values of time.
Correct Option: B
A signal having amplitude within finite boundaries called bounded signal and it can have finite energy or infinite energy. If this signal is power signal, then it possess infinite energy. But in any case, this bounded signal will be finite for all the values of time.
- X(z) = 1 – 3z– 1, Y (z) = 1 + 2z–2 are Z- transforms of two signals x[n], y[n] respectively. A linear time invariant system has the impulse response h[n] defined by these two signals as h[n] = x[n– 1]*y[n] where * denotes discrete time convolution. Then the output of the system for the input δ [n – 1]
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: B
NA
- The frequency spectrum of a signal is shown in the figure. If this signal is ideally sampled at intervals of 1 ms, then frequency spectrum of the sampled signal will be
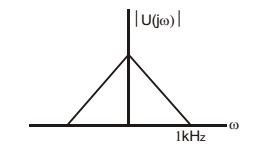
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Here, frequency of signal, ωc = 1 kHz
Sampling frequency, ωs = 1 = 1kHz 1ms
For an ideal sampler, ωs > 2ωc
But here ωs = ωc
so, at ωs/2, next sampling will start resulting sampled signal will be as follows: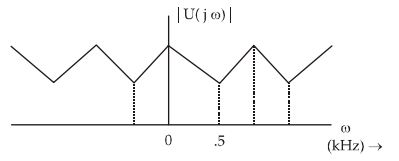
Correct Option: D
Here, frequency of signal, ωc = 1 kHz
Sampling frequency, ωs = 1 = 1kHz 1ms
For an ideal sampler, ωs > 2ωc
But here ωs = ωc
so, at ωs/2, next sampling will start resulting sampled signal will be as follows:

