Heat Transfer Miscellaneous
- For the three-dimensional object shown in the figure below, five faces are insulated. The sixth face (PQRS), which is not insulated, interacts thermally with the ambient, with a convective heat transfer coefficient of 10W/m2K. The ambient temperature is 30°C. Heat is uniformly generated inside the object at the rate of 100 W/m3. Assuming the face PQRS to be at uniform temperature, its steady state temperature is

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given data;
ho = W/m2K
ho = 30 °C
qG = 100 W/m3
Volume, V = 2×1×2=4 m3
Heat generated, Q = qG × V = 100 × 4 = 400 W
Convection heat transfer from face PQRS,
Q = ho A (Ts – To)
400 = 10 × 2 × 2 (Ts – 30)
Ts = 40°CCorrect Option: D
Given data;
ho = W/m2K
ho = 30 °C
qG = 100 W/m3
Volume, V = 2×1×2=4 m3
Heat generated, Q = qG × V = 100 × 4 = 400 W
Convection heat transfer from face PQRS,
Q = ho A (Ts – To)
400 = 10 × 2 × 2 (Ts – 30)
Ts = 40°C
- A stainless steel tube (ks = 19 W/mK) of 2 cm ID and 5 cm OD is insulated with 3 cm thick asbestos (ka = 0.2 W/mK). If the temperature difference between the inner most and outermost surfaces is 600°C, the heat transfer rate per unit length is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given: d1 = 2 cm
r1 = 1 cm
d2 = 5 cm
r2 = 2.5 cm
d3 = 5 + 2 × 3 = 11
r3 = 5.5 cm
Equivalent thermal resistance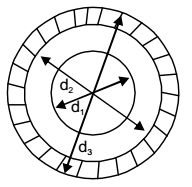
Rt = 1 In r2 + 1 In r3 2πkst r1 2πka r2 = 1 In 2.5 + 1 In 5.5 2π × 19 1 2π × 0.2 2.5
= 7.67 × 10–3 + 0.627 = 0.635
∴ Heat transfer rate per unit lengtht1 - t2 = 600 = 944.88 W/m Rt 0.635 Correct Option: C
Given: d1 = 2 cm
r1 = 1 cm
d2 = 5 cm
r2 = 2.5 cm
d3 = 5 + 2 × 3 = 11
r3 = 5.5 cm
Equivalent thermal resistance
Rt = 1 In r2 + 1 In r3 2πkst r1 2πka r2 = 1 In 2.5 + 1 In 5.5 2π × 19 1 2π × 0.2 2.5
= 7.67 × 10–3 + 0.627 = 0.635
∴ Heat transfer rate per unit lengtht1 - t2 = 600 = 944.88 W/m Rt 0.635
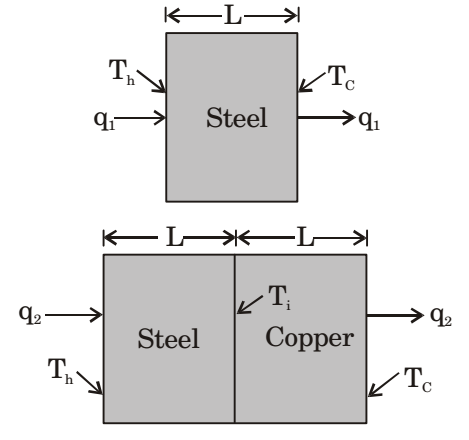
- A well machined steel plate of thickness L is kept such that the wall temperature are Th and Tc as seen in the figure below. A smooth copper plate of the same thickness L is now attached to the steel plate without any gap as indicated in the figure below. The temperature at the interface is Tt. The temperatures of the outer walls are still the same at Th and Tc. The heat transfer rates are q1 and q2 per unit area in the two cases respectively in the direction shown. Which of the following statements is correct?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
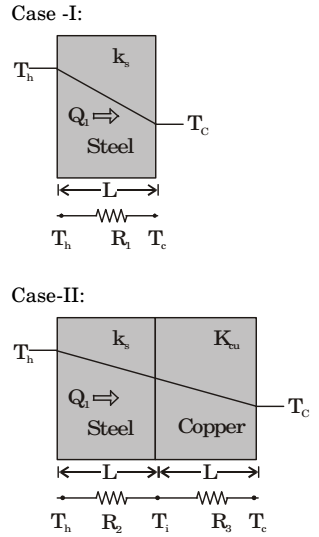
For caseI-:Q1 = Th - Tc R1 where R1 = L KSA
For Case-II:Q2 = Th - Tc R2 + R3 where R2 = L and R3 = L KsA KcuA
As R2 + R3 > R1 at constant temperature difference in both cases.Then q1 
or Q1 
> q2 
or Q2 
A A
For Case-II:
R2 > R3
∵ kcu > ksQ2 = Th - T1 R2 or R2 = Th - T1 Q2 also Q2 = Ti - Tc R3 or R3 = Ti - Tc Q2 ∴ Th - Ti > Ti - Tc Q2 Q2
or Th – Ti > Ti – Tc
or Th + Tc > 2Tior Ti < Th + Tc 2 Correct Option: D

For caseI-:Q1 = Th - Tc R1 where R1 = L KSA
For Case-II:Q2 = Th - Tc R2 + R3 where R2 = L and R3 = L KsA KcuA
As R2 + R3 > R1 at constant temperature difference in both cases.Then q1 
or Q1 
> q2 
or Q2 
A A
For Case-II:
R2 > R3
∵ kcu > ksQ2 = Th - T1 R2 or R2 = Th - T1 Q2 also Q2 = Ti - Tc R3 or R3 = Ti - Tc Q2 ∴ Th - Ti > Ti - Tc Q2 Q2
or Th – Ti > Ti – Tc
or Th + Tc > 2Tior Ti < Th + Tc 2
- In a case of one dimensional heat conduction in a medium with constant properties, T is the temperature at position x, at time t.
Then δT is proportional to δt
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
One dimensional heat conduction equation is,
δ2T = 1 δT δx2 α δt ∴ δ2T ∝ δT δx2 δt Correct Option: D
One dimensional heat conduction equation is,
δ2T = 1 δT δx2 α δt ∴ δ2T ∝ δT δx2 δt
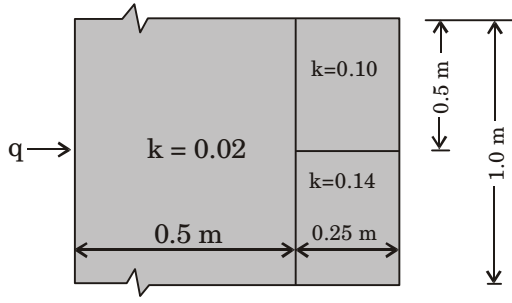
- Heat flows through a composite slab, as shown below. The depth of the slab is 1 m. The k values are in W/mK. The overall thermal resistance in K/W is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
L1 = 0.5 = 25 k1 0.02 2L2 = 5 k2 2L3 = 12.5 k3
Rtotal = 25 + 3.6 = 28.6 K/WCorrect Option: C
L1 = 0.5 = 25 k1 0.02 2L2 = 5 k2 2L3 = 12.5 k3
Rtotal = 25 + 3.6 = 28.6 K/W

