-
In ∆ABC, ∠C is an obtuse angle. The bisectors of the exterior angles at A and B meet BC and AC produced at D and E respectively. If AB = AD = BE, then ∠ACB =
-
- 105°
- 108°
- 110°
- 135°
- 105°
Correct Option: B
As per the given in question , we draw a figure of triangle ABC 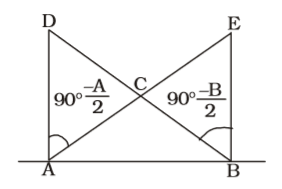
| ∠DAC = | (180° - A) | = 90° – | 2 | 2 |
In ∆ADB,
∠DAB + ∠ADB + ∠DBA = 180°
| ⇒90° – ∠ | + ∠A + 2 ∠B = 180° | 2 |
[∵ AD = AB ⇒ ∠ADB = ∠DBA = ∠B]
| ⇒90° + ∠ | + 2 ∠B = 180° | 2 |
⇒ ∠A + 4∠B = 180° ....(i)
In ∆ABE,
AB = BE
∴ ∠BAE = ∠AEB
∴ ∠ABE + ∠BAE + ∠BEA = 180°
| ⇒90° - | + ∠B + 2∠A = 180° | 2 |
| ⇒90° + | + 2 ∠A = 180° | 2 |
⇒ ∠B + 4∠A = 180° ....(ii)
From equations (i) and (ii),
∠A + 4∠B = 4∠A + ∠B
⇒ 3∠A = 3∠B
⇒ ∠A = ∠B
∴ ∠A + 4∠B = 180°
⇒ 5∠B = 180°
| ⇒ ∠B = | = 36° = ∠A | 5 |
∴ ∠ACB = 180° – 36° – 36°
∠ACB = 180° – 72° = 108°

