Engineering Mathematics Miscellaneous
-
Assuming i = √-1 and t is a real number 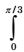
eit dt is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

= 1 
1 + i√3 - 1 
2 2 2 = 
-1 + √3 
= 
√3 + i 
2i 2 2 2 Correct Option: A

= 1 
1 + i√3 - 1 
2 2 2 = 
-1 + √3 
= 
√3 + i 
2i 2 2 2
- Given that x¨ + 3x = 0 , and x(0) = 1, ẋ(0) what is x(1)?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
x¨ + 3x = 0
⇒ (D2 + 3)x = 0P.I. = 
1 
(0) = 0 D2 + 3
Now C.F. is given by,
C1em1t + C2em2t
∴ m2 + 3 = 0
⇒ m = ± i √3
Hence the solution is C.F. + P.I.
i.e. C1ei √3t + C2e-i √3t
But x(0) = 1
⇒ C1 + C2 = 1
and x(0) = 0, x = i √3 C1 ei √3t - i √3 C2 e-i √3t
⇒ x(0) = 0
⇒ C1 = C2 = 1 2 ∴ x = 1 [ ei √3t + e-i √3t ] 2 ⇒ x(1) = 1 [ ei √3 + e(1 / i √3) ] 2
cos √3 = −0.16
Correct Option: B
x¨ + 3x = 0
⇒ (D2 + 3)x = 0P.I. = 
1 
(0) = 0 D2 + 3
Now C.F. is given by,
C1em1t + C2em2t
∴ m2 + 3 = 0
⇒ m = ± i √3
Hence the solution is C.F. + P.I.
i.e. C1ei √3t + C2e-i √3t
But x(0) = 1
⇒ C1 + C2 = 1
and x(0) = 0, x = i √3 C1 ei √3t - i √3 C2 e-i √3t
⇒ x(0) = 0
⇒ C1 = C2 = 1 2 ∴ x = 1 [ ei √3t + e-i √3t ] 2 ⇒ x(1) = 1 [ ei √3 + e(1 / i √3) ] 2
cos √3 = −0.16
-
For d2y + 4 dy + 3y = 3e2x the particular integral is dx2 dx
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The given differential equaiton may be written as
D2y + 4Dy + 3y = 3e2x∴ P.I. = 3e2x (D2 + 4D + 3)
Substituting D = 2, we getP.I. = 3e2x 1 = e2x 15 5
Correct Option: B
The given differential equaiton may be written as
D2y + 4Dy + 3y = 3e2x∴ P.I. = 3e2x (D2 + 4D + 3)
Substituting D = 2, we getP.I. = 3e2x 1 = e2x 15 5
Direction: The complete solution of the ordinary differential equation
| + p | + qy = 0 is | |||
| dx2 | dx |
y = c1e-x + c2e-3x
-
Which of the following is a solution of the differential equation d2y + p dy + (q + 1)y = 0 ? dx2 dx
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
d2y + p dy + (q + 1)y = 0 dx2 dx
∴ D2 + pD + (q + 1) = 0
⇒ D2 + 4D + 4 = 0
Since, p = 4, q = 3, therefore⇒ D = -4 ± √16 - 16 = -2 2
Hence, it's solution is, = xeDx = xe–2x
Correct Option: C
d2y + p dy + (q + 1)y = 0 dx2 dx
∴ D2 + pD + (q + 1) = 0
⇒ D2 + 4D + 4 = 0
Since, p = 4, q = 3, therefore⇒ D = -4 ± √16 - 16 = -2 2
Hence, it's solution is, = xeDx = xe–2x
- Then, p and q are
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
d2y + p dy + qy = 0 dx2 dx
D2 + pD + q = 0
It's solutions is y = c1e-x + c2e-3x
⇒ m = –1, n = –3
If m and n are two roots of the above equation, then
m + n = –p,
⇒ –1 – 3 = –p,
⇒ p = 4
and mn = q,
⇒ (–1) (–3) = q,
⇒ q = 3Correct Option: C
d2y + p dy + qy = 0 dx2 dx
D2 + pD + q = 0
It's solutions is y = c1e-x + c2e-3x
⇒ m = –1, n = –3
If m and n are two roots of the above equation, then
m + n = –p,
⇒ –1 – 3 = –p,
⇒ p = 4
and mn = q,
⇒ (–1) (–3) = q,
⇒ q = 3

