Engineering Mathematics Miscellaneous
- Which one of the following equations is a correct identity for arbitrary 3 × 3 real matrices P, Q and R?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
This is a standard relation.
(P + Q)² = P² + PQ + QP + Q²Correct Option: D
This is a standard relation.
(P + Q)² = P² + PQ + QP + Q²
- For a matrix [M] =
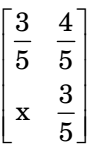
, the transpose of the matrix is equal to the inverse of the matrix,[M]T = [M]–1. The value of x is given by
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
AT = A-1
so, orthogonal matrix
Now AA-1 = I = AAT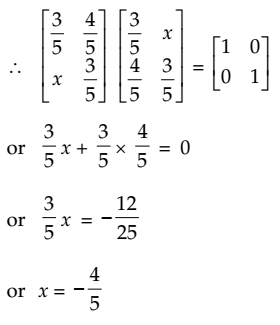
Correct Option: A
AT = A-1
so, orthogonal matrix
Now AA-1 = I = AAT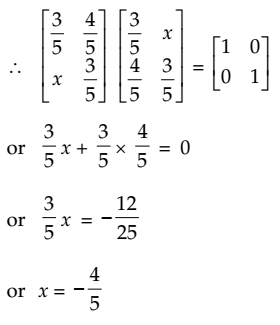
- Multiplication of matrices E and F is G. Matrices E and G are
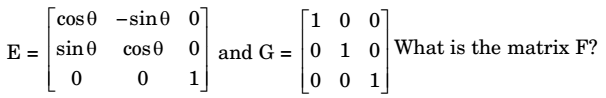
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

We know that product of (E × F) is unit matrix 50 F will be the inverse of E.
Now E × F = G
∴ F = E-1Correct Option: C

We know that product of (E × F) is unit matrix 50 F will be the inverse of E.
Now E × F = G
∴ F = E-1
- Match the items in columns I and II
Column I
P. Singular matrix
Q. Non-square matrix
R. Real symmetric
S. Orthogonal matrix
Column II
1. Determinant is not defined
2. Determinant is always one
3. Determinant is zero
4. Eigenvalues are always real
5. Eigenvalues are not defined
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: A
NA
- The Fourier cosine series for an even function f(x) is given by

The value of the coefficient a2 for the function f(x) = cos2(x) in [0, π] is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
cos2x = 1 + cos2x 2 f(x) = 1 + cos2x 2 2 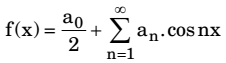
a0 = 1
a1 = 0
a2 = 1/2Correct Option: C
cos2x = 1 + cos2x 2 f(x) = 1 + cos2x 2 2 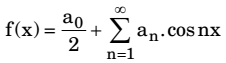
a0 = 1
a1 = 0
a2 = 1/2

