Engineering Mechanics Miscellaneous
- An annular disc has a mass m, inner radius R and outer radius 2R. The disc rolls on a flat surface without slipping. If the velocity of the center of mass is v, the kinetic energy of the disc is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
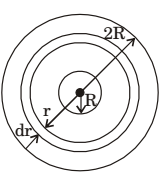
I = 5mr2 2
K.E. = (K.E.) translation + (K.E.) Rotation= 1 mv² + 1 Iω² 2 2
Where V = 2 R ω⇒ ω = V 2R ∴ K.E. = 1 mv² + 5mV² 2 16 K.F. = 13mV² 16
Correct Option: C

I = 5mr2 2
K.E. = (K.E.) translation + (K.E.) Rotation= 1 mv² + 1 Iω² 2 2
Where V = 2 R ω⇒ ω = V 2R ∴ K.E. = 1 mv² + 5mV² 2 16 K.F. = 13mV² 16
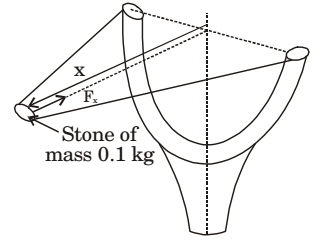
- A stone with mass of 0.1 kg is catapulted as shown in the figure. The total force Fx (in N) exerted by the rubber band as a function of distance x (in m) is given by Fx = 300x2. If the store is displaced by 0.1 m from the un-stretched position (x = 0) of the rubber band, the energy stored in the rubber band is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Energy stored in the bar
= Work done by the stone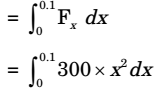
= 300 × x3 3
= 100 × 0.13
= 0.1JCorrect Option: B
Energy stored in the bar
= Work done by the stone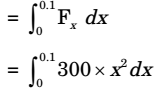
= 300 × x3 3
= 100 × 0.13
= 0.1J
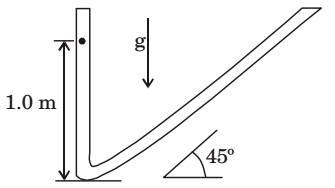
- A ball is dropped from rest from a height of 1 min a frictionless tube as shown in the figure. If the tube profile is approximated by two straight lines (ignoring the curved portion), the total distance travelled (in m) by the ball is (correct to two decimal places).
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
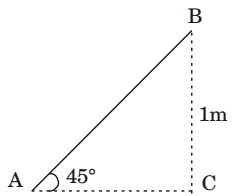
BC = sin 45° AB AB = BC = 1 = 1.414m sin 45° sin 45°
Total travel, OA + AB = 1+1.414 = 2.414 mCorrect Option: A

BC = sin 45° AB AB = BC = 1 = 1.414m sin 45° sin 45°
Total travel, OA + AB = 1+1.414 = 2.414 m
- An ejector mechanism consists of a helical compression spring having a spring constant of K = 981 × 103 N/m. It is pre-compressed by 100 mm from its free state. If it is used to eject a mass of 100 kg held on it, the mass will move up through a distance of
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
From the conservation of energy after precompression,
Initial energy = Final energyor 1 k(0.1)² = 1 + kx² + mg(x + 0.1) 2 2
or k(0.1)²= kx² + 2mg(x + 0.1)
or 981 × 103 × 10- 2 = 981 × 103 × x2 + 2 × 100 × 9.81(x + 0.1)
or 100x2 + 2x – 0.8 = 0∴ x = -2 ± √(2)² - 4 × 100 × 0.8 200
Taking + ve sign, x = 100 mmCorrect Option: A
From the conservation of energy after precompression,
Initial energy = Final energyor 1 k(0.1)² = 1 + kx² + mg(x + 0.1) 2 2
or k(0.1)²= kx² + 2mg(x + 0.1)
or 981 × 103 × 10- 2 = 981 × 103 × x2 + 2 × 100 × 9.81(x + 0.1)
or 100x2 + 2x – 0.8 = 0∴ x = -2 ± √(2)² - 4 × 100 × 0.8 200
Taking + ve sign, x = 100 mm
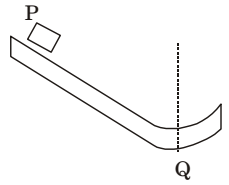
- Block P of mass 2 kg slides down the surface and has a speed 20 m/s at the lowest point, Q where the local radius of curvature is 2 m as shown in the figure. Assuming g = 10 m/s², the normal force (in N) at Q is _______ (correct to two decimal places).
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
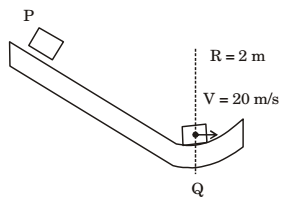
m = 2 kg, g = 10 m/s²
FBD of mass P at point Q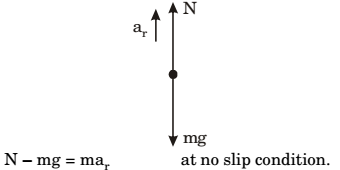
N = mg + mv² = 2 × 10 + 2 × 20 × 20 = 420 N R 2
Correct Option: A

m = 2 kg, g = 10 m/s²
FBD of mass P at point Q
N = mg + mv² = 2 × 10 + 2 × 20 × 20 = 420 N R 2

