Analogy
The meaning of analogy is similar properties or similarity. If an object or word or digit or activity shows any similarity with another object or word or digit or activity in terms of properties, type, shape, size etc., then the particular similarity will be called analogy.
The relationship of analogy can be established in two ways:
Types of Analogy
1.Word Analogy
2. Letter Analogy
3. Number Analogy
4. Mixed Analogy
Word Analogy
In word analogy, candidates have to find the relationship between given words in a pair.
Tool and Object Based Analogy
This establishes a relationship between a tool and the object in which it works.
For example- Scissors : Cloth
Synonym Based Analogy
In this type of analogy two words have similar meaning.
For example- Huge : Gigantic
Worker and Tool Based Analogy
This establishes a relationship between a particular tool and the person of that particular profession who uses that tool.
For example- Writer : Pen
Worker And Product Based Analogy
This type of analogy gives a relationship between a person of particular profession and his/her creations.
For example- Writer : Book
Causes And Effect Based Analogy
In Such type of analogy 1st word acts and 2nd word is the effect of that action.
For example- Work : Tiredness
Antonym Based Analogy
In such type of analogy the two words of the question pair are opposite in meaning.
For example- Poor : Rich
Gender Based Analogy
In this type of analogy, one word is masculine and another word is feminine of it is a male and female or sex relationship.
For example- Man : Woman Cock : Hen Dog : Bitch
Classification Based Analogy
In this type of analogy is based on biological, physical, chemical or any other classification. In such problems the 1st word may be classified by the 2nd word and vice-versa.
For example- Oxygen : Gas
Function Based Analogy
In such type of analogy, 2nd word describes the function of the 1st word.
For example- Singer : Sings
Quantity and Unit Based Analogy
In such type of analogy 2nd word is the unit of the first word and vice-versa.
For example- Distance : Mile
Finished Product and Raw Material Based Analogy
In such type of analogy the 1st word is the raw material and 2nd word is the end product of that raw material and vice-versa.
For example- Yarn : Fabric
Milk : Curd
Ex- Milk : Curd :: Fruit : ?
Solution:- Juice, Because 1st word is the raw material of the 2nd word.
Utility Based Analogy
In such type of analogy the 2nd word shows the purpose of the 1st word or vice-versa.
For example- Pen : Writing
Bed : Sleeping
Food : Eating
Ex- Chair : Sitting :: Bat : ?
Solution:- Playing, Because 2nd word shoe the purpose of the 1st word.
Symbolic Relationship Based Analogy
In such type of analogy, the 1st word is the symbol of the 2nd word and vice-versa.
For example-White : Peace
Black : Sorrow
Red : Danger
Ex- Red Cross : Hospital :: Yellow :
Solution:- Flood, Because 1st word is the symbol of the 2nd word.
Adult and Young One Based Analogy
In such type of analogy, the 1st word is the adult one and 2nd word is the young one of the 1st word or vice-versa.
For example- Cow : Calf
Ex- Cow : Calf :: Cat : ?
Solution:- Kitten, Because 2nd word is the young one of the 1st word.
Subject and Specialist Based Analogy
In such type of analogy the 2nd word is the specialist of 1st word or vice-versa.
For example- Heart : Cardiologist
Skin : Dermatologist
Ex- Geologist : Earth Science :: Ophthalmologist : ?
Solution:- Eye, Because 1st word is the specialist of the 2nd word.
Habit Based Analogy
In this type of analogy 2nd word is the habit of 1st word and vice versa.
For example- Cat : Omnivorous
Cow : Herbivorous
Ex- Cat : Omnivorous :: Tiger : ?
Solution:- Carnivorous, Because 2nd word is the habit of the 1st word.
Instrument and Measurement Based Analogy
In this type of analogy, the 1st word is the instrument to measure the 2nd word and vice-versa:
For example- Hygrometer : Humidity
Odometer : Speed
Anemometer : Wind
Ex- Barometer : Pressure ::Thermometer : ?
Solution:- Temperature, Because 1st word is the instrument to measure the 2nd word.
Individual and Group Based Analogy
In this type of analogy second word is the group of 1st word and vice-versa.
For example- Cow : Herd
Sailors : Crew
Sheep : Flock
Ex- Ministers : Council :: Flowers : ?
Solution:- Bouquet, Because 2nd word is the group of 1st word.
State and Capital Based Analogy
In this type of analogy 1st word is the state and 2nd word is the capital of that state and vice-versa.
For example- West Bengal : Kolkata
U.P : Lucknow
Nagaland : Mizoram
Ex- Bihar : Patna :: Assam : ?
Solution:- Dishpur, Because 2nd word is the capital of the first word.
Analogy Based on Individual and Dwelling Place
In such type of analogy 1st word is the individual and 2nd word is the dwelling place of that individual and vice-versa.
For example- Horse : Stable
Pig : Sty
Bird : Nest
Ex- King : Palace :: Mouse : ?
Solution:- Hole, Because 2nd word is the living place of the 1st word.
Analogy Based on Worker and Working Place
In this type of analogy the 1st word represents a person of particular profession and 2nd word represents the working place of that person and vise-versa.
For example- Doctor : Hospital
Ex- Doctor : Hospital :: Teacher : ?
Solution:- School, Because 2nd word is the work place of 1st word.
Analogy Based on Topic Study
In this type of analogy 1st word is the study of the 2nd word and vice-versa.
For example- Birds : Ornithology
Botany- Plants
Zoology- Animals
Ex- Birds : Ornithology :: Histology : ?
Solution:- Tissues, Because 1st word is the study of 2nd word.
Letter Analogy
In this type of analogy candidate has to find out the relationship between given letters or group of letters.
Analogy Based on Letters or Meaningless Words
Case-1- Forward alphabetical sequence
Example- EF : HI :: TU : WX
Here, EF and HI are in the natural alphabetical sequence. Similarly, TU and WX are in the natural alphabetical sequence.
Ex- KL : OP :: PQ : ?
Solution:- Here, EF and OP are in the natural alphabetical sequence. Similarly PQ and TU are in the natural alphabetical sequence.
Case-2- Backward or Opposite alphabetical sequence
Example- FE : IH :: UT : XW
In fact this case is opposite of case 1.
Case-3- Vowel-Consonant Relation
Example- ATL : EVX :: IPR : ORS
Here, the 1st two words start with the 1st two vowels A & E and next two words start with the next two vowels I & O. Last two letters of every word are consonants.
Case-4- Skip letter relation
Example- ABC : FGH :: IJK : NOP
Here, between ABC & FGH two skip and they are D & E. Similarly, between IJK & NOP two letters skip and they are L & M.
Case-5- Jumbled letters relation
Example- LAIN : NAIL :: EVOL : LOVE
Here, the 1st term gets reversed to product the 2nd term and similar relation show in between 3rd and 4th term.
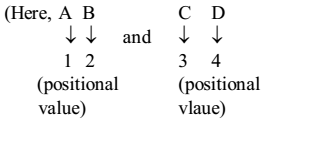
Shortcut Approach

Number Analogy
In this, candidate has to find out the relationship the number or group of numbers.
Prime number
Example- 13 : 17 :: 19 : 23
Here, 13 & 17 are consecutive prime number and 19 and 23 are consecutive prime number.
Ex- 23 : 29 :: 43 : ?
Solution:- 23 and 29 are consecutive number.
∴ Required Prime number = 47.
Square number/Cube number
Example- 3 : 9 :: 5 : 25
Here, 32 = 9 and 52 = 25
Ex- 7 : 49 :: 11 : ?
Solution:- Here, 72 = 49
∴ 112 = 121.
Ex- 3 : 27 :: 5 : ?
Solution:- Here, 33 = 27
∴ Required number = 53 = 125.
Mathematical Operation ( BODMAS )
Example- 4 : 20 :: 6 : 30
Here, 4 × 5 = 20 and 6 × 5 = 30.
Ex- 13 : 91 :: 15 : ?
Solution:- Here, 13 × 7 = 91
∴ Required number = 15 × 7 = 105.
Example- 125 : 5 :: 250 : 10
Here, 125 ÷ 25 = 5 and 250 ÷ 25 = 10.
Ex- 72 : 9 :: 144 : ?
Solution:- Here, 72/8 = 9
∴ Required number = 144/8 = 18.
Combination of digits
Example- 135 : 9 :: 435 : 12
Here, 135 = 1 + 3 + 5 = 9 and
435 = 4 + 3 + 5 = 12.
Ex- 436 : 13 :: 567 :?
Solution:- 436 = 4 + 3 + 6 = 13
∴ Required number = 567 = 5 + 6 + 7 = 18.
MIXED ANALOGY
In this, candidate has to find out the relationship between the given group of letters and a number on one side.
Example- AB: 12:: CD:: 34