Industrial Engineering Miscellaneous
- The net requirements of an item over 5 consecutive weeks are 50-0-15-20-20. The inventory carrying cost and ordering cost are Rs. 1 per item per week and Rs. 100 per order respectively. Starting inventory is zero. Use "Least Unit Cost Technique" for developing the plan. The cost of the plan (in Rs.) is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Ch = 1 per unit per week
Co = 100/orderCorrect Option: B
Ch = 1 per unit per week
Co = 100/order
- In machine shop, pins of 15 mm diameter are produced at a rate of 1000 per month and the same is consumed at a rate of 500 per month. The production and consumption continue simultaneously till the maximum inventory is reached. Then inventory is allowed to reduce to zero due to consumption. The lot size of production is 1000. If backlog is not allowed, the maximum inventory level is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
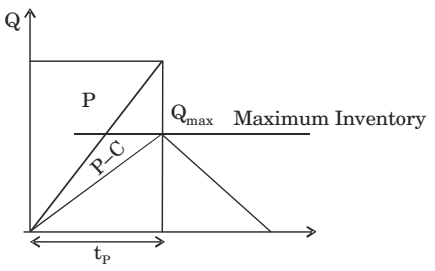
Qmax = tp (P - C) = Q (P - C) P ⇒ Q 
1 - C 
P Qmax = 1000 
1 - 500 
1000 ⇒ 1000 
1 
= 500 2
So the maximum inventory level is 500Correct Option: B

Qmax = tp (P - C) = Q (P - C) P ⇒ Q 
1 - C 
P Qmax = 1000 
1 - 500 
1000 ⇒ 1000 
1 
= 500 2
So the maximum inventory level is 500
- The maximum level of inventory of an item is 100 and it is achieved with infinite replenishment rate. The inventory becomes zero over one and half month due to consumption at a uniform rate. This cycle continues through out the year. Ordering cost is Rs. 100 per order and inventory carrying cost is Rs. 10 per item per month. Annual cost (in Rs.) of the plan, neglecting material cost, is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Maximum Inventory = 100
Inventory Cycle = 1.5 months
Number of cycle required per year= 12 = 8cycle 1.5
Co = 8 × 100 = 800/year
Ch = 8 × 10 = 80/year/unitTAC = Q Ch + D Co 2 Q ⇒ 100 (80) + 100 (800) ⇒ 4800 2 100 Correct Option: C
Maximum Inventory = 100
Inventory Cycle = 1.5 months
Number of cycle required per year= 12 = 8cycle 1.5
Co = 8 × 100 = 800/year
Ch = 8 × 10 = 80/year/unitTAC = Q Ch + D Co 2 Q ⇒ 100 (80) + 100 (800) ⇒ 4800 2 100
- A stockist wishes to optimize the number of perishable items he needs to stock in any month in his store. The demand distribution for this perishable item is

The stockist pays Rs. 70 for each item and he sells each at Rs. 90. If the stock is left unsold in any month, he can sell the item at Rs. 50 each. There is no penalty for unfulfilled demand. To maximize the expected profit, the optimal stock level is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: C
NA
- Consider the following data for an item. Annual demand: 2500 units per year Ordering cost: Rs. 100 per order, Inventory holding rate: 25% of unit price
Price quoted by a supplier
The optimum order quantity (in units) is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
D = 2500 units/years
Co = Rs. 100/order
Ch = (0.25) Unit + Price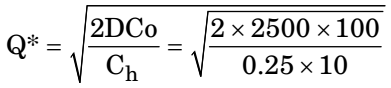
Q* &rArrr; 447.2 ±
TAC (O*) = D × C + √2DCoCh
⇒ 2500 × 10 + √2 × 2500 × 10 × 2.5⇒ 2500 × 9 + 2500 × 100 500 = 500 (23.25 × 9) 2
⇒ 23562.5
Since Total cost minimum at Q = 500 units
∴ the optimal order quality is Q = 500 unitsCorrect Option: C
D = 2500 units/years
Co = Rs. 100/order
Ch = (0.25) Unit + Price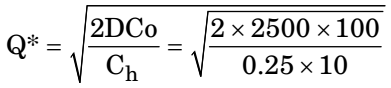
Q* &rArrr; 447.2 ±
TAC (O*) = D × C + √2DCoCh
⇒ 2500 × 10 + √2 × 2500 × 10 × 2.5⇒ 2500 × 9 + 2500 × 100 500 = 500 (23.25 × 9) 2
⇒ 23562.5
Since Total cost minimum at Q = 500 units
∴ the optimal order quality is Q = 500 units

