Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Monochromatic radiation emitted when electron on hydrogen atom jumps from first excited to the ground state irradiates a photosensitive material. The stopping potential is measured to be 3.57 V. The threshold frequency of the materials is :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
n → 2 – 1
E = 10.2 eV
kE = E – φ
Q = 10.20 – 3.57
h υ0 = 6.63 eVυ0 = 6.63 × 1.6 × 10-19 1.6 × 1015 6.67 × 10-34 Correct Option: C
n → 2 – 1
E = 10.2 eV
kE = E – φ
Q = 10.20 – 3.57
h υ0 = 6.63 eVυ0 = 6.63 × 1.6 × 10-19 1.6 × 1015 6.67 × 10-34
- A source of light is placed at a distance of 50 cm from a photocell and the stopping potential is found to be V0. If the distance between the light source and photocell is made 25 cm, the new stopping potential will be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Since, stopping potential is independent of distance hence new stopping potential will remain unchanged i.e., new stopping potential = V0.
Correct Option: C
Since, stopping potential is independent of distance hence new stopping potential will remain unchanged i.e., new stopping potential = V0.
- A 200 W sodium street lamp emits yellow light of wavelength 0.6 µm. Assuming it to be 25% efficient in converting electrical energy to light, the number of photons of yellow light it emits per second is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Give that, only 25% of 200 W converter electrical energy into light of yellow colour

hc 
× N = 200 × 25 λ 100
Where N is the No. of photons emitted per second, h = plank’s constant, c, speed of light.N = 200 × 25 × λ 100 hc = 200 × 25 × 0.6 × 10-6 1.5 × 1020 100 × 6.2 × 10-34 × 3 × 108 Correct Option: A
Give that, only 25% of 200 W converter electrical energy into light of yellow colour

hc 
× N = 200 × 25 λ 100
Where N is the No. of photons emitted per second, h = plank’s constant, c, speed of light.N = 200 × 25 × λ 100 hc = 200 × 25 × 0.6 × 10-6 1.5 × 1020 100 × 6.2 × 10-34 × 3 × 108
- For photoelectric emission from certain metal the cut-off frequency is ν. If radiation of frequency 2ν impinges on the metal plate, the maximum possible velocity of the emitted electron will be (m is the electron mass)
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
From photo-electric equation,
hν' = hν +
Kmax ...(i)h.2v = hv + 1 mV2max 2
[∴ v' = 2v]⇒ hv = 1 mV2max 2 ⇒ vmax = 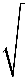
2hv m Correct Option: B
From photo-electric equation,
hν' = hν +
Kmax ...(i)h.2v = hv + 1 mV2max 2
[∴ v' = 2v]⇒ hv = 1 mV2max 2 ⇒ vmax = 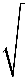
2hv m
- Two radiations of photons energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV, successively illuminate a photosensitive metallic surface of work function 0.5 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons is :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
According to Einsten’s photoelectric effect, the K.E. of the radiated electrons
K.Emax = E – W1 mv21 2
= (1 – 0.5) eV = 0.5 eV1 mv22 2
= (2.5 – 0.5) eV = 2 eV= 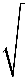
= = 1:2 v1 0.5 1 v2 2 √4 Correct Option: B
According to Einsten’s photoelectric effect, the K.E. of the radiated electrons
K.Emax = E – W1 mv21 2
= (1 – 0.5) eV = 0.5 eV1 mv22 2
= (2.5 – 0.5) eV = 2 eV= 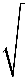
= = 1:2 v1 0.5 1 v2 2 √4

