Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- An electron of mass m and charge e is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of V volt in vacuum. Its final speed will be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Kinetic energy of electron accelerated through a potential V= eV
⇒ 1 mv2 = eV 2 ⇒ v2 = 2eV m ⇒ v = 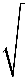
2eV m Correct Option: C
Kinetic energy of electron accelerated through a potential V= eV
⇒ 1 mv2 = eV 2 ⇒ v2 = 2eV m ⇒ v = 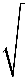
2eV m
- The nature of ions knocked out from hot surfaces is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: C
NA
- If the threshold wavelength for a certain metal is 2000 Å, then the work-function of the metal is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Threshold wavelength (λ) = 2000 Å = 2000 × 10–10 m. Work function
(W) = hc = (6.6 × 1034) × (3 × 108) λ 2000 × 10-10
= 9.9× 10-19 J= 9.9 × 10-19 = 6.2 eV 1.6 × 10-19 Correct Option: B
Threshold wavelength (λ) = 2000 Å = 2000 × 10–10 m. Work function
(W) = hc = (6.6 × 1034) × (3 × 108) λ 2000 × 10-10
= 9.9× 10-19 J= 9.9 × 10-19 = 6.2 eV 1.6 × 10-19
- Kinetic energy of an electron, which is accelerated in a potential difference of 100 V is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Potential difference (V) = 100 V. The kinetic energy of an electron = 1 eV = 1 × (1.6 × 10–19)
= 1.6 × 10–19 J. Therefore kinetic energy in
100 volts = (1.6 × 10–19) × 100 = 1.6 × 10–17J.
[Alt : K.E. = qV
= 1.6 × 10–19 × 100 J = 1.6 × 10–17]Correct Option: A
Potential difference (V) = 100 V. The kinetic energy of an electron = 1 eV = 1 × (1.6 × 10–19)
= 1.6 × 10–19 J. Therefore kinetic energy in
100 volts = (1.6 × 10–19) × 100 = 1.6 × 10–17J.
[Alt : K.E. = qV
= 1.6 × 10–19 × 100 J = 1.6 × 10–17]
- In photoelectric effect the work function of a metal is 3.5 eV. The emitted electrons can be stopped by applying a potential of ––1.2 V. Then
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
hν = W0 + Ek = 3.5 + 1.2 = 4.7 eV
Correct Option: A
hν = W0 + Ek = 3.5 + 1.2 = 4.7 eV

