Biochemical Miscellaneous
Direction: A bioreactor of working volume 50 m3 produces a metabolite (X) in batch culture under given operating conditions from a substrate (S). The final concentration of metabolite (X) at the end of each run was 1.1 kg m–3. The bioreactor was operated to complete 70 runs in each year.
- What will be the overall productivity of the system in kg year–1 m–3 ?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Overall productivity =Total number of runs × final concentration at each end
= 70 runs × 1.1 kg m–3 = 77 kg m–3 year–1Correct Option: D
Overall productivity =Total number of runs × final concentration at each end
= 70 runs × 1.1 kg m–3 = 77 kg m–3 year–1
- Aeration in a biorector is provided by
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Air is provided through sparger in bioreactors.
Correct Option: C
Air is provided through sparger in bioreactors.
- In a bioreactor baffles are incorporated to
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The main roles of baffles are prevent vertex formation, improve aeration and help in mixing.
Correct Option: A
The main roles of baffles are prevent vertex formation, improve aeration and help in mixing.
- During the media preparation for cultivation of cells, insoluble precipitates of calcium phosphates are often formed. Identify which method can be adopted to avoid this problem?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The equilibrium solubility of four calcium salts (calcium oxalate hydrate, calcium citrate tetrahydrate, calcium phosphate, calcium glycerophosphate) were determined at controlled pH values (7.5, 6.0, 4.5 and < or = 3.0) and in distilled water.
Correct Option: D
The equilibrium solubility of four calcium salts (calcium oxalate hydrate, calcium citrate tetrahydrate, calcium phosphate, calcium glycerophosphate) were determined at controlled pH values (7.5, 6.0, 4.5 and < or = 3.0) and in distilled water.
- Batch fermentation of glucose to ethanol yields a productivity of 4.5 g1–1 hl–1. If the yeast cell concentration in the fermentation brought is 5% (v/v) and the intracellular NAD/NADH concentration in the yeast cells in 10 µM the cycling rate of NAD+ ⇔ NADH will be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
P = 4.5 gm/l.hr Ethanol production yeast cell conc.(X) = 5% v/v
NAD+/NADH ceme in yeast cell = 10 µm (m = ml/lit)
= (me/ωt) the cycling rate of NAD+ ⇌ NADH will be.X = 5 ml in 1 liter of broth 100
NAD+/NADH = 10–5 ml/lit.50 ml/lit = 10-5 ml/lit No. of cy dest = cycle rate 100 unit time 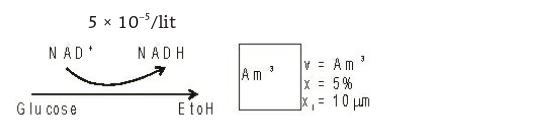
Total NAD+/NADH conc = 5 × 10–5(v/v) Now, cycle rate = 
1 
cycle / hr = 20,000 cycle/hr. 5 × 10-5
Correct Option: B
P = 4.5 gm/l.hr Ethanol production yeast cell conc.(X) = 5% v/v
NAD+/NADH ceme in yeast cell = 10 µm (m = ml/lit)
= (me/ωt) the cycling rate of NAD+ ⇌ NADH will be.X = 5 ml in 1 liter of broth 100
NAD+/NADH = 10–5 ml/lit.50 ml/lit = 10-5 ml/lit No. of cy dest = cycle rate 100 unit time 
Total NAD+/NADH conc = 5 × 10–5(v/v) Now, cycle rate = 
1 
cycle / hr = 20,000 cycle/hr. 5 × 10-5

