Biotechnology Principles and Processes
- The plasmid
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The term ‘plasmid’ was introduced by Lederberg in 1952 for extragenomic DNA segment. It is a small circular molecule of DNA found in bacterial cell in addition to the larger circular bacterial DNA.
Correct Option: D
The term ‘plasmid’ was introduced by Lederberg in 1952 for extragenomic DNA segment. It is a small circular molecule of DNA found in bacterial cell in addition to the larger circular bacterial DNA.
- In bacterial chromosomes, the nucleic acid polymers are
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Bacterial chromosomes comprises of circular DNA.
Correct Option: B
Bacterial chromosomes comprises of circular DNA.
- What is true for plasmid?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Plasmids are small intranuclear circular DNAs which carry extra chromosomal genes in bacteria.
Correct Option: A
Plasmids are small intranuclear circular DNAs which carry extra chromosomal genes in bacteria.
- Agarose extracted from sea weeds finds use in:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
In gel electrophoresis agarose extracted from sea weed used as gel agarose, made of 0.7% gel show good resolution of large DNA and 2% gel will show good resolution of small fragments.
Correct Option: D
In gel electrophoresis agarose extracted from sea weed used as gel agarose, made of 0.7% gel show good resolution of large DNA and 2% gel will show good resolution of small fragments.
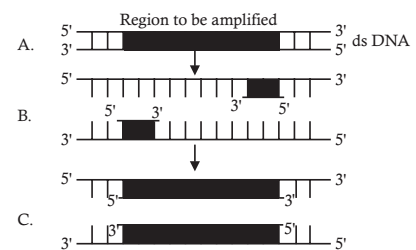
- The figure below shows three steps (A, B, C) of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Select the option giving correct identification together with what it represents?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
PCR is a technique for enzymatically replicating DNA without using a living organism such as E. coli or yeast. It is commonly used in medical and biological research labs for a variety of tasks like detection of hereditary diseases, identification of genetic fingerprints etc.
The correct steps shown in the above figure are:
A – Denaturation at a temperature of about 94° to 98°C. During the denaturation, the double strand melts open to single stranded DNA, and all enzymatic reactions stop.
B – Annealing (binding of DNA primer to the separated strands. Occurs at 50° to 65°Celsius, which is lower than the optimal temperature of the DNA polymerases)
C – Extension or elongation of the strands using the DNA primer with heat-stable DNA polymerases, most frequently Taq (Thermus aquaticus) at 72ºC.Correct Option: C
PCR is a technique for enzymatically replicating DNA without using a living organism such as E. coli or yeast. It is commonly used in medical and biological research labs for a variety of tasks like detection of hereditary diseases, identification of genetic fingerprints etc.
The correct steps shown in the above figure are:
A – Denaturation at a temperature of about 94° to 98°C. During the denaturation, the double strand melts open to single stranded DNA, and all enzymatic reactions stop.
B – Annealing (binding of DNA primer to the separated strands. Occurs at 50° to 65°Celsius, which is lower than the optimal temperature of the DNA polymerases)
C – Extension or elongation of the strands using the DNA primer with heat-stable DNA polymerases, most frequently Taq (Thermus aquaticus) at 72ºC.

