Theory of Machines Miscellaneous
- A rigid rod of length 1 m is resting at an angle θ = 45° as shown in the figure. The end P is dragged with a velocity of U = 5 m/s to the right. At the instant shown, the magnitude of the velocity V(in m/s) of point Q as it moves along the wall without losing contact is

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

VP = r Pω
⇒ 5 = 1 × sin 45° × ω⇒ ω = 5 1 × sin45°
VQ = r Qω⇒ VQ = 1 × cos45° × 5 1 × sin45°
= 5 m/sCorrect Option: A

VP = r Pω
⇒ 5 = 1 × sin 45° × ω⇒ ω = 5 1 × sin45°
VQ = r Qω⇒ VQ = 1 × cos45° × 5 1 × sin45°
= 5 m/s
- A rigid link PQ is undergoing plane motion as shown in the figure (VP and VQ are non-zero). VQP is the relative velocity of point Q with respect to point P
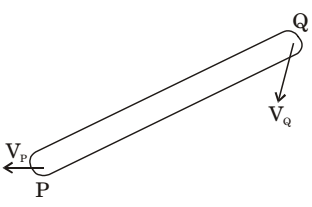
Which one of the following is TRUE?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

Resultant VQP is ⊥r to link PQ.Correct Option: D

Resultant VQP is ⊥r to link PQ.
- A slider crank mechanism with crank radius 200 mm and connecting rod length 800 mm is shown. The crank is rotating at 600 rpm in the counterclockwise direction. In the configuration shown, the crank makes an angle of 90° with the sliding direction of the slider, and a force of 5 kN is acting on the slider. Neglecting the inertia forces, the turning moment on the crank (in kNm) is _______.

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Turning moment on crankshaft,
T = FT × r= F × cosβ × r cosβ
= F × r = 5 × 0.2 = 1 kN-mCorrect Option: D
Turning moment on crankshaft,
T = FT × r= F × cosβ × r cosβ
= F × r = 5 × 0.2 = 1 kN-m
- The rod AB, of length 1 m, shown in the figure is connected to two sliders at each end through pins. The sliders can slide along QP and QR. If the velocity VA of the slider at A is 2 m/s, the velocity of the midpoint of the rod at this instant is _____ m/s.
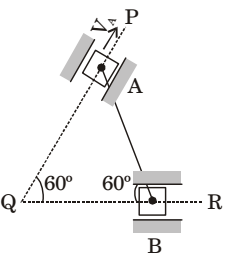
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Locate the I-centre for the link AB as shown in figure M is the mid point of AB

Given VA = 2 m/secVA = IA.ω ⇒ ω = VA IA VM = IM.ω = IM VA = IM .VA IA IA = sin30°.VA = 1 .2 = 1 m/sec 2 Correct Option: A
Locate the I-centre for the link AB as shown in figure M is the mid point of AB

Given VA = 2 m/secVA = IA.ω ⇒ ω = VA IA VM = IM.ω = IM VA = IM .VA IA IA = sin30°.VA = 1 .2 = 1 m/sec 2
Direction: An instantaneous configuration of a four-bar mechanism, whose plane is horizontal, is shown in the figure below. At this instant, the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link O2A are ω = 8 rad/s and α = 0, respectively, and the driving torque (τ) is zero. The link O2A is balanced so that its centre of mass falls at O2.
- At the same instant, if the component of the force at Joint A along AB is 30N, then the magnitude of the Joint reaction at O2
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
An instantaneous configuration of a four-bar mechanism, whose plane is horizontal, is shown in the figure below. At this instant, the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link O2A are ω = 8 rad/s and α = 0, respectively, and the driving torque (τ) is zero. The link O2A is balanced so that its centre of mass falls at O2.

Correct Option: D
An instantaneous configuration of a four-bar mechanism, whose plane is horizontal, is shown in the figure below. At this instant, the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link O2A are ω = 8 rad/s and α = 0, respectively, and the driving torque (τ) is zero. The link O2A is balanced so that its centre of mass falls at O2.


