Immunology Miscellaneous
- Recombinant live attenuated vaccine against hepatitis B was prepared from
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
A vaccine vector, or carrier, is weekend virus or bacterium into which harmless genetic material from another disease causing organism can be inserted. The vaccine virus, the virus that causes cowpox, is now used to make recombinant vector vaccines. Vaccinia is relatively large and has ample room to accept additional genetic fragments.
Correct Option: C
A vaccine vector, or carrier, is weekend virus or bacterium into which harmless genetic material from another disease causing organism can be inserted. The vaccine virus, the virus that causes cowpox, is now used to make recombinant vector vaccines. Vaccinia is relatively large and has ample room to accept additional genetic fragments.
- Match the activity spectrum of the following antibiotics
P Actinomycin D 1. Antifungal Q Daunorubicin 2. Antituberculosis R Rifamycin 3. Antitumor S Griseofulvin 4. Antiprotosoal
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Griseofulvin is an antifungal drug that is administered orally. It is used both in animals and in humans,to treat fungal infections of the skin (known as ringworm) and nails. It is derived from the mold Penicillium griseofulvum. Daunorubicin is chemotherapeutic of the anthracycline family that is given as a treatment for some types of cancer. It was initially isolated from Streptomyces peucetius.
The rifamycins are a group of antibiotics that are synthesized either naturally by the bacterium Amycolatopsis mediterranei or artificially. They are a subclass of the larger family Ansamycin. Rifamycins are particularly effective against mycobacteria, and are therefore used to treat tuberculosis, leprosy, and mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections.Correct Option: A
Griseofulvin is an antifungal drug that is administered orally. It is used both in animals and in humans,to treat fungal infections of the skin (known as ringworm) and nails. It is derived from the mold Penicillium griseofulvum. Daunorubicin is chemotherapeutic of the anthracycline family that is given as a treatment for some types of cancer. It was initially isolated from Streptomyces peucetius.
The rifamycins are a group of antibiotics that are synthesized either naturally by the bacterium Amycolatopsis mediterranei or artificially. They are a subclass of the larger family Ansamycin. Rifamycins are particularly effective against mycobacteria, and are therefore used to treat tuberculosis, leprosy, and mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections.
- In a heterogeneous population of cells containing T-cells, B-cells and macrophages, the cells are separated in the following scheme
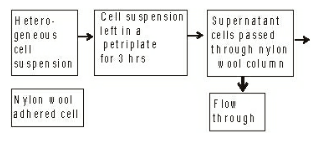
Identity the major population of cells present in petri-plate nylon wool adhered and nylon wool column flow through respectively
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
B-cells selectively adhere to the fiber of nylon wool while T-cells do not and hence found in column flow resulting in successful recovery of both cell types. Whereas macrophage attaches to the petri plates and hence its major population will be there.
Correct Option: A
B-cells selectively adhere to the fiber of nylon wool while T-cells do not and hence found in column flow resulting in successful recovery of both cell types. Whereas macrophage attaches to the petri plates and hence its major population will be there.
- Reverse vaccinology indicates
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Reverse vaccinology is development of vaccine that employs bioinformatics. It indicates, from genome sequence to vaccine development and hence the vaccine is better and more specific.
Correct Option: D
Reverse vaccinology is development of vaccine that employs bioinformatics. It indicates, from genome sequence to vaccine development and hence the vaccine is better and more specific.
- Match the items on the left column with those on the right Left
P. Programmed cell death at site of infection
Q. Hormone upregulated during flooding stress
R. Target for herbicide glyphosate
S. Pathogen-derived resistance
Right
1. TMV coat protein
2. EPSP synthase
3. Hyper-sensitive response
4. Ethylene
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Hypersensitive response is characterized by the rapid death of cells in the local region surrounding an infection carried out as a programmed mechanism for cell death. Environmental cues such as flooding, drought, chilling, wounding, and pathogen attack induce ethylene formation in plants. Glyphosate is a chemical herbicide which kills plants by inhbiting the shikimate pathway. It targets EPSP synthase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of shikimate-3-phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvate into EPSP.
Correct Option: B
Hypersensitive response is characterized by the rapid death of cells in the local region surrounding an infection carried out as a programmed mechanism for cell death. Environmental cues such as flooding, drought, chilling, wounding, and pathogen attack induce ethylene formation in plants. Glyphosate is a chemical herbicide which kills plants by inhbiting the shikimate pathway. It targets EPSP synthase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of shikimate-3-phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvate into EPSP.

