Architecture and Planning Miscellaneous-topic
- In a mixed use development on a 2.0 hectare site with 2.0 FAR, the ratio of residential to commercial floor area is 3:2. The minimum parking (in ECS) needed per 100 sqm of residential and commercial floor area is 1.0 and 1.25 respectively. Considering fullFAR utilization, the total par king requirement is ____________ ECS.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
440 to 440
Site Area = 2.0 hectare = 20,000 sq.m. Maximum
FAR = 2.0. Thus, Maximum Built-up Area = 40,000 sq.m.
It is given that, Ratio of residential: commercial floor area = 3: 2
Thus, Area for residential as per 3: 2 ratio = 24,000 sq.m. & Area for commercial as per 3: 2 ratio = 16,000 sq.m.
Minimum parking (in ECS) needed per 100 sq.m, of residential area = 1.
Thus, ECS required for 24,000 sq.m, of residential area = 240
Minimum parking (in ECS) needed per 100 sq.m, of commercial area = 1.25.
Thus, ECS required for 16,000 sq.m, of commercial area = 200
Thus, total ECS required for 40,000 sq.m, of maximum built-up area = 240 + 200 = 440Correct Option: A
440 to 440
Site Area = 2.0 hectare = 20,000 sq.m. Maximum
FAR = 2.0. Thus, Maximum Built-up Area = 40,000 sq.m.
It is given that, Ratio of residential: commercial floor area = 3: 2
Thus, Area for residential as per 3: 2 ratio = 24,000 sq.m. & Area for commercial as per 3: 2 ratio = 16,000 sq.m.
Minimum parking (in ECS) needed per 100 sq.m, of residential area = 1.
Thus, ECS required for 24,000 sq.m, of residential area = 240
Minimum parking (in ECS) needed per 100 sq.m, of commercial area = 1.25.
Thus, ECS required for 16,000 sq.m, of commercial area = 200
Thus, total ECS required for 40,000 sq.m, of maximum built-up area = 240 + 200 = 440
- A building with 100 sqm roof area is connected to a 72 cum rainwater collection tank. If the rainfall is 60 mm per hour and the loss during water storage is 20%, then the time taken to fill the tank completely is_______ hours.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
15.0 to 15.0
Roof Area of the building = 100 sq.m.
Rainfall is 60 mm per hour. = 0.06 m per hour.
Thus, water collection on the roof per hour = 100 × 0.06 = 6 m³ per hour.
Thus, time to fill the 72 cum storage tank without loss = 72/6 = 12 hours.
But, there is loss of 20% during water storage.
Thus, loss of water storage per hour = (20/100) × 6 = 1.2m³
Thus, water getting stored per hour = 6 – 1.2 = 4.8 m³
Thus, to fill the 72 cum capacity water storage tank the time required = 72/4.8 = 15 hours.Correct Option: C
15.0 to 15.0
Roof Area of the building = 100 sq.m.
Rainfall is 60 mm per hour. = 0.06 m per hour.
Thus, water collection on the roof per hour = 100 × 0.06 = 6 m³ per hour.
Thus, time to fill the 72 cum storage tank without loss = 72/6 = 12 hours.
But, there is loss of 20% during water storage.
Thus, loss of water storage per hour = (20/100) × 6 = 1.2m³
Thus, water getting stored per hour = 6 – 1.2 = 4.8 m³
Thus, to fill the 72 cum capacity water storage tank the time required = 72/4.8 = 15 hours.
- Match the following urban conservation themes in Group-I with their respective descriptions in Group-II
Group I Group II P. Restoration 1. Piece by piece reassembly Q. Reconstitution 2. Returning to previous stage R. Reconstruction 3. Physical addition S. Replication 4. Re-creation of vanished elements 5. Reproduction of an exact copy
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The seven degr ees of Intervention for Architectural Conservation are as follows:
1. Prevention of deterioration or Nonintervention:
In some circumstances, assessment may show that any intervention is undesirable. This form of intervention attempts to prolong the life of heritage by removing the external causes of decay.
2. Preservation of the existing fabric or Maintenance :
A place of cultur al heritage value should be maintained regularly and according to a plan. This form of intervention is limited to the protection and maintenance without distorting its cultural significance.
3. Consolidation and Stabilisation of the fabric:
Places of cultural her it age value should be protected from collapse or processes of decay and deterioration. Consolidation or stabilisation is carried out, in order to prevent further collapse or decay or deterioration.
4. Repair and Restoration :
The rest or ation process typically involves repairing the damaged fabric and materials to return to the previous form. It may involve reassembly and may involve the removal of accretions. Restoration should be based on respect for existing material and techniques. 5. Reproduction:
Reproduction is partial reconstruction of vanished parts based upon evidence using new materials through replication (usually limited to repetitive elements or parts of buildings, such as balusters, etc.). t should be taken up only when considerable amount of evidence.
6. Reconstruction :
Reconstruction is recreating the original form/style of vanished parts using any material - by reusing old materials or by using new materials and techniques, but with compositions and construction similar to the original and based on the same.
7. Re-use or Adaptation or rehabilitation of H istoric buildings :
Adaptation or Rehabilitation means modifying a historic place to suit it a new compatible use, involving the least possible loss of cultural heritage value. This is predominantly applied in cases of revitalisation of heritage zones or areas.Correct Option: B
The seven degr ees of Intervention for Architectural Conservation are as follows:
1. Prevention of deterioration or Nonintervention:
In some circumstances, assessment may show that any intervention is undesirable. This form of intervention attempts to prolong the life of heritage by removing the external causes of decay.
2. Preservation of the existing fabric or Maintenance :
A place of cultur al heritage value should be maintained regularly and according to a plan. This form of intervention is limited to the protection and maintenance without distorting its cultural significance.
3. Consolidation and Stabilisation of the fabric:
Places of cultural her it age value should be protected from collapse or processes of decay and deterioration. Consolidation or stabilisation is carried out, in order to prevent further collapse or decay or deterioration.
4. Repair and Restoration :
The rest or ation process typically involves repairing the damaged fabric and materials to return to the previous form. It may involve reassembly and may involve the removal of accretions. Restoration should be based on respect for existing material and techniques. 5. Reproduction:
Reproduction is partial reconstruction of vanished parts based upon evidence using new materials through replication (usually limited to repetitive elements or parts of buildings, such as balusters, etc.). t should be taken up only when considerable amount of evidence.
6. Reconstruction :
Reconstruction is recreating the original form/style of vanished parts using any material - by reusing old materials or by using new materials and techniques, but with compositions and construction similar to the original and based on the same.
7. Re-use or Adaptation or rehabilitation of H istoric buildings :
Adaptation or Rehabilitation means modifying a historic place to suit it a new compatible use, involving the least possible loss of cultural heritage value. This is predominantly applied in cases of revitalisation of heritage zones or areas.
- Match the Buildings in Group-I with their Architects in Group-II
Group I Group II P. Guggenheim Museum, Bilbao 1. Richard Rogers Q. The Shard, London 2. Norman Foster R. Commerz Bank, Frankfurt 3. Frank Gehry S. Heydar Aliyev Centre, Baku 4. Renzo Piano 5. Zaha Hadid
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
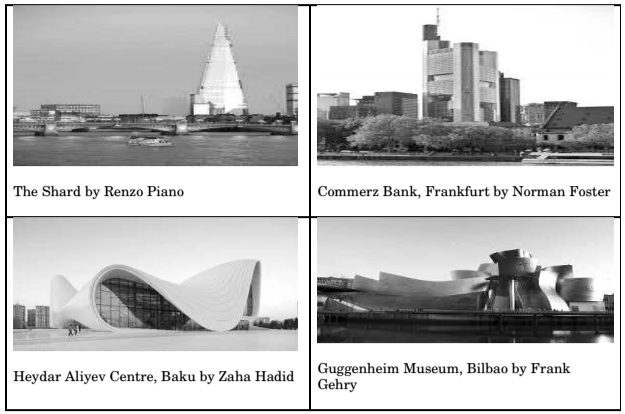
Correct Option: A

- Match the Temples in Group-I with their Dynastic period in Group-II
Group I Group II P. Brihadeshvara 1. Gupta Temple Q. Kailasanatha 2. Chalukya Temple R. Bhitragaon 3. Lodhi Temple S. Lad Khan Temple 4. Chola 5. Pallava
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
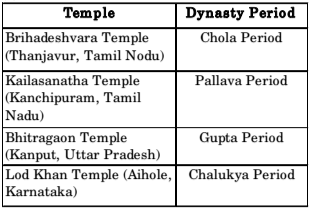
Correct Option: A


