Refrigeration and Air-conditioning Miscellaneous
- A building has to be maintained at 21 °C (dry bulb) and 14.5°C(wet bulb). The dew point temperature under these conditions is 10.17°C. The outside temperature is –23°C (dry bulb) and the internal and external surface heat transfer coefficients are 8 W/m2K and 23 W/ m2K respectively. If the building wall has a thermal conductivity of 1.2 W/mK, the minimum thickness (in m) of the wall required to prevent condensation is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: B
NA
- For a typical sample of ambient air (at 30°C, 75% relative humidity and standard atmospheric pressure), the amount of moisture in kg per kg of dry air will be approximately.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given data:
Dry bulb temperature:
Tdb = 35°C
Relative humidity
φ = 75° = 0.75
At 35°C, Ps = .05628 barφ = Pv ⇒ 0.75 = Pv Ps .05628
Pv = 0.75× .05628 =.04221 bar
Specific humidity,ω = .622Pv = .622 × .04221 P - Pv 1.0135 - .04221
= 0.0270 kg/kg of dry air.Correct Option: B
Given data:
Dry bulb temperature:
Tdb = 35°C
Relative humidity
φ = 75° = 0.75
At 35°C, Ps = .05628 barφ = Pv ⇒ 0.75 = Pv Ps .05628
Pv = 0.75× .05628 =.04221 bar
Specific humidity,ω = .622Pv = .622 × .04221 P - Pv 1.0135 - .04221
= 0.0270 kg/kg of dry air.
- Moist air is treated as an ideal gas mixture of water vapor and dry air (molecular weight of air = 28.84 and molecular weight of water = 18). At a location, the total pressure is 100 kPa, the temperature is 30°C and the relative humidity is 55%. Given that the saturation pressure of water at 30°C is 4246 Pa, the mass of water vapor per kg of dry air is ______ grams.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
w = 0.622 Pv P - Pv φ = Pv Ps ⇒ 0.55 = Pv Ps
⇒ Pv = 2235.3w = 0.622 × 2235.3 - 2235.3 (100 × 103)
w = 0.0142 kg/kg of dry air
w = 14.2 gm/kg of dry airCorrect Option: A
w = 0.622 Pv P - Pv φ = Pv Ps ⇒ 0.55 = Pv Ps
⇒ Pv = 2235.3w = 0.622 × 2235.3 - 2235.3 (100 × 103)
w = 0.0142 kg/kg of dry air
w = 14.2 gm/kg of dry air
- For air with a relative humidity of 80%
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
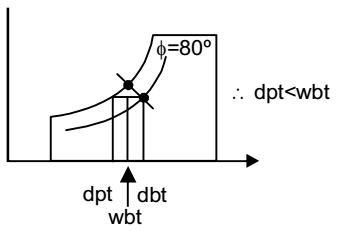
Correct Option: B

- For air at a given temperature, as the relative humidity is increased isothermally,
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
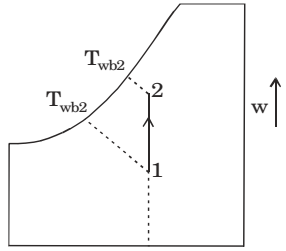
DBT = DBT2
DBT →
φ ↑, Twb ↓
Relative humidity is increased isothermally.Correct Option: A

DBT = DBT2
DBT →
φ ↑, Twb ↓
Relative humidity is increased isothermally.

