Moving Charges and Magnetism
- A current loop in a magnetic field
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
A current loop in a magnetic field is in equilibrium in two orientations one is stable and another unstable.
τ = →M × →B = MB sin θ
If θ = 0° ⇒ τ = 0 (stable)
If θ = π ⇒ τ = 0 (unstable) 
Do not experience a torque in some orientations Hence option (c) is correct.Correct Option: C
A current loop in a magnetic field is in equilibrium in two orientations one is stable and another unstable.
τ = →M × →B = MB sin θ
If θ = 0° ⇒ τ = 0 (stable)
If θ = π ⇒ τ = 0 (unstable) 
Do not experience a torque in some orientations Hence option (c) is correct.
- A long straight wire carries a certain current and produces a magnetic field of
2 × 10–4 = weber m²
at a perpendicular distance of 5 cm from the wire. An electron situated at 5 cm from the wire moves with a velocity 107 m/s towards the wire along perpendicular to it. The force experienced by the electron will be
(charge on electron =1.6 × 10–19 C)
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given: Magnetic field B = 2 × 10–4 weber/m²
Velocity of electron, v = 107 m/s
Lorentz force F = qvB sin θ
= 1.6 × 10–19 × 107 × 2 × 10–4 (∵ θ = 90°)
= 3.2 × 10–16 NCorrect Option: C
Given: Magnetic field B = 2 × 10–4 weber/m²
Velocity of electron, v = 107 m/s
Lorentz force F = qvB sin θ
= 1.6 × 10–19 × 107 × 2 × 10–4 (∵ θ = 90°)
= 3.2 × 10–16 N
- A circular coil ABCD carrying a current i is placed in a uniform magnetic field. If the magnetic force on the segment AB is , →F the force on the remaining segment BCDA is
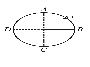
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Here, →FAB + →FBCDA = →0
= →FBCDA = - →FAB→F
(∵ →FAB = →F)Correct Option: B
Here, →FAB + →FBCDA = →0
= →FBCDA = - →FAB→F
(∵ →FAB = →F)
- A current carrying loop in the form of a right angle isosceles triangle ABC is placed in a uniform magnetic field acting along AB. If the magnetic force on the arm BC is F, what is the force on the arm AC?
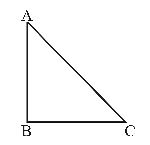
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Let a current i be flowing in the loop ABC in the direction shown in the figure. If the length of each of the sides AB and BC be x then
|→F| = ixB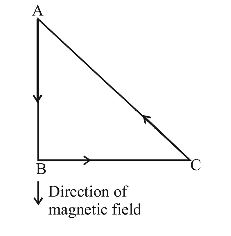
where B is the magnitude of the magnetic force. The direction of →F will be in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the paper and going into it.
By Pythagorus theorem, AC = √x² + x² = √2x
∴ Magnitude of force on AC
= i √2 x B sin 45°
= i√2xB × 1/√2
= ixb = |→F|
The direction of the force on AC is perpendicular to the plane of the paper and going out of it. Hence, force on AC = - →FCorrect Option: B
Let a current i be flowing in the loop ABC in the direction shown in the figure. If the length of each of the sides AB and BC be x then
|→F| = ixB
where B is the magnitude of the magnetic force. The direction of →F will be in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the paper and going into it.
By Pythagorus theorem, AC = √x² + x² = √2x
∴ Magnitude of force on AC
= i √2 x B sin 45°
= i√2xB × 1/√2
= ixb = |→F|
The direction of the force on AC is perpendicular to the plane of the paper and going out of it. Hence, force on AC = - →F

