Moving Charges and Magnetism
- A milli voltmeter of 25 milli volt range is to be converted into an ammeter of 25 ampere range. The value (in ohm) of necessary shunt will be :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Galvanometer is converted into ammeter, by connected a shunt, in parallel with it.

GS = VG = 25 × 10-3 G + S I 25 = GS = 0.001 Ω G + S
Here S << G so
S = 0.001 ΩCorrect Option: A
Galvanometer is converted into ammeter, by connected a shunt, in parallel with it.

GS = VG = 25 × 10-3 G + S I 25 = GS = 0.001 Ω G + S
Here S << G so
S = 0.001 Ω
- A closely wound solenoid of 2000 turns and area of cross-section 1.5 × 10–4 m² carries a current of 2.0 A. It suspended through its centre and perpendicular to its length, allowing it to turn in a horizontal plane in a uniform magnetic field 5 × 10–2 tesla making an angle of 30° with the axis of the solenoid. The torque on the solenoid will be:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Torque on the solenoid is given by τ = MB sin θ
where θ is the angle between the magnetic field and the axis of solenoid.
M = niA
∴ τ = niA B sin 30°
= 2000 × 2 × 1.5 × 10-4 × 5 × 10-2 × 1/2
= 1.5 × 10-2 N - mCorrect Option: D
Torque on the solenoid is given by τ = MB sin θ
where θ is the angle between the magnetic field and the axis of solenoid.
M = niA
∴ τ = niA B sin 30°
= 2000 × 2 × 1.5 × 10-4 × 5 × 10-2 × 1/2
= 1.5 × 10-2 N - m
-
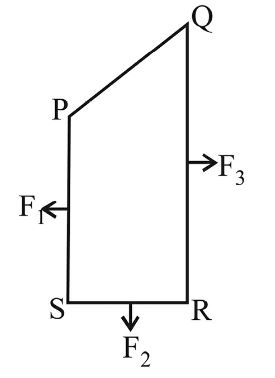
A closed loop PQRS carrying a current is placed in a uniform magnetic field. If the magnetic forces on segments PS, SR, and RQ are F1 , F2 and F3 respectively and are in the plane of the paper and along the directions shown, the force on the segment QP is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
According to the figure the magnitude of force on the segment QM is F3 – F1 and PM is F2.
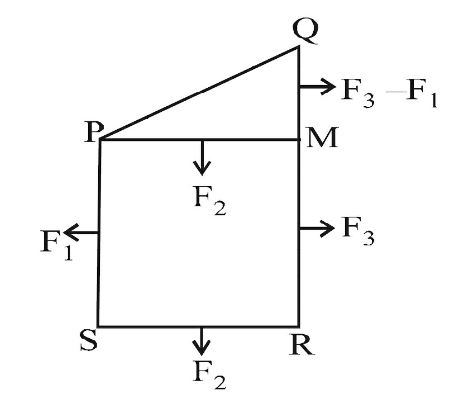
Therefore, the magnitude of the force on segment PQ is √(F3 - F1)² + F2²Correct Option: B
According to the figure the magnitude of force on the segment QM is F3 – F1 and PM is F2.

Therefore, the magnitude of the force on segment PQ is √(F3 - F1)² + F2²
- When a charged particle moving with velocity →v is subjected to a magnetic field of induction →B, the force on it is non-zero. This implies that
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Force on a particle moving with velocity v in a magnetic field B is F = q(→v × →B)
If angle between →v & →B is either zero or 180º, then value of F will be zero as cross product of →v and →B will be zero.
So option (b) is correct.Correct Option: B
Force on a particle moving with velocity v in a magnetic field B is F = q(→v × →B)
If angle between →v & →B is either zero or 180º, then value of F will be zero as cross product of →v and →B will be zero.
So option (b) is correct.
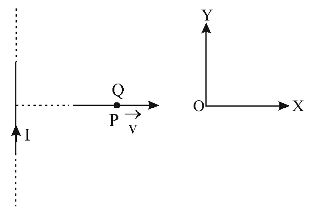
- A very long straight wire carries a current I. At the instant when a charge + Q at point P has velocity →c , as shown, the force on the charge is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The direction of →B is along (-̂k)
∴ The magnetic force
→F = Q(→v × →B) = Q(v̂i) × B(-̂k) = QvB̂j
⇒ →F is along OY.Correct Option: A
The direction of →B is along (-̂k)
∴ The magnetic force
→F = Q(→v × →B) = Q(v̂i) × B(-̂k) = QvB̂j
⇒ →F is along OY.

