Moving Charges and Magnetism
- A particle having charge q moves with a velocity through a region in which both an electric field and a magnetic field are present .The force on the particle is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Force due to electric field = q→E
Force due to magnetic field = q(→v × →B)
Net force experienced = q→E + q(→v × →B)Correct Option: D
Force due to electric field = q→E
Force due to magnetic field = q(→v × →B)
Net force experienced = q→E + q(→v × →B)
- Two long parallel wires are at a distance of 1 metre. Both of them carry one ampere of current. The force of attraction per unit length between the two wires is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
F = μ0 × 2i1i2I = 10-7 × 2 × 1 × 1 × 1 = 2 × 10-7 N/m. 4π r 1
[This relates to the definition of ampere]Correct Option: A
F = μ0 × 2i1i2I = 10-7 × 2 × 1 × 1 × 1 = 2 × 10-7 N/m. 4π r 1
[This relates to the definition of ampere]
- A coil carrying electric current is placed in uniform magnetic field, then
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
A current carrying coil has magnetic dipole moment. Hence, a torque →pm acts →B on it in magnetic field.
Correct Option: A
A current carrying coil has magnetic dipole moment. Hence, a torque →pm acts →B on it in magnetic field.
- A straight wire of length 0.5 metre and carrying a current of 1.2 ampere is placed in uniform magnetic field of induction 2 tesla. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the length of the wire. The force on the wire is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
F = Bi ℓ = 2 ×1.2 × 0.5 = 1.2 N
Correct Option: B
F = Bi ℓ = 2 ×1.2 × 0.5 = 1.2 N
- In an ammeter 0.2% of main current passes through the galvanometer. If resistance of galvanometer is G, the resistance of ammeter will be :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
As 0.2% of main current passes through the galvanometer hence 998/1000 current through the shunt.
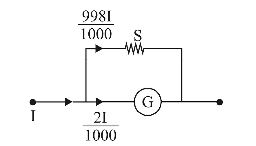

2I 
G = 
9981 
S ⇒ S = G 1000 1000 499
Total resistance of Ammeter R = = 
G 
G = SG 499 G S + G 
G 
+ G 500 499 Correct Option: C
As 0.2% of main current passes through the galvanometer hence 998/1000 current through the shunt.


2I 
G = 
9981 
S ⇒ S = G 1000 1000 499
Total resistance of Ammeter R = = 
G 
G = SG 499 G S + G 
G 
+ G 500 499

