Soil mechanics miscellaneous
- In an unconsolidated undrained triaxial test, it is observed that an increase in cell pressure from 150 kPa to 250 kPa leads to a pore pressure increase of 80 kPa. It is further observed that, an increase of 50 kPa in deviatoric stress results in an increase of 25 kPa in the pore pressure. The value of Skemptons’s pore pressure parameter B is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Skempton’s pore pressure parameter, B
B = ∆U ∆σ3 = 80 = 80 = 0.8 250 – 150 100 Correct Option: C
Skempton’s pore pressure parameter, B
B = ∆U ∆σ3 = 80 = 80 = 0.8 250 – 150 100
- A given cohesion less soil has emax = 0.85 and emin = 0.50. In the field, the soil is compacted to a mass density of 1800 kg/ m3 at a water content of 8%. Take the mass density of water as 1000 kg/m3 and Gs as 2.7. The relative density (in%) of the soil is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
P = Grw(1 + w) 1 + e ⇒ 1800 = 2.7 × 1000 × (1.08) 1 + e ∴ 1 + e = 2.7 × 1000 × 1.08 1800
∴ e = 0.02ID = emax - e × 100 emax - emin = 0.85 - 0.62 × 100 0.85 - 0.5
= 65.714%Correct Option: D
P = Grw(1 + w) 1 + e ⇒ 1800 = 2.7 × 1000 × (1.08) 1 + e ∴ 1 + e = 2.7 × 1000 × 1.08 1800
∴ e = 0.02ID = emax - e × 100 emax - emin = 0.85 - 0.62 × 100 0.85 - 0.5
= 65.714%
- The per cent voids in mineral aggregate (VMA) and per cent air voids (Vv) in a compacted cylindrical bituminous mix specimen are 15 and 4.5 respectively. The per cent voids filled with bitumen (VFB) for this specimen is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: C
NA
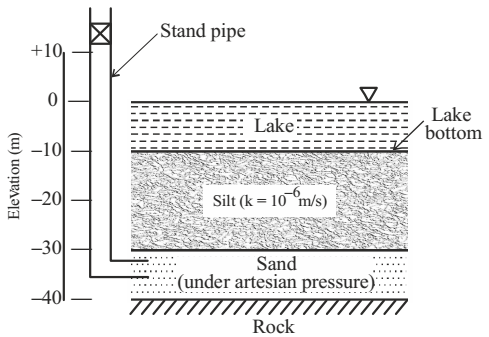
- The soil profile below a lake with water level at elevation = 0 m and lake bottom at elevation = –10 m is shown in the figure, where k is the permeability coefficient. A piezometer (stand pipe) installed in the sand layer shows a reading of +10 m elevation. Assume that the piezometric head is uniform in the sand layer. The quantity of water (in m3/s) flowing into the lake from the sand layer through the silt layer per unit area of the lake bed is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
By Darcy’s law
q = Ki A
We want q per unit area∴ q = KiA K.i A
K = Co-efficient of permeability = 10–6 m/s
i = hydraulic gradient = L/h
L = Length of silt layer in direction of flow
L = 20 m. (from figure)
h = difference in water levels of the overhead and bottom of lake.
= 20 m. (from figure)∴ q = K.i = K × L h q = 10–6 × 20 20
q = 1 × 10–6 m3 /secCorrect Option: C
By Darcy’s law
q = Ki A
We want q per unit area∴ q = KiA K.i A
K = Co-efficient of permeability = 10–6 m/s
i = hydraulic gradient = L/h
L = Length of silt layer in direction of flow
L = 20 m. (from figure)
h = difference in water levels of the overhead and bottom of lake.
= 20 m. (from figure)∴ q = K.i = K × L h q = 10–6 × 20 20
q = 1 × 10–6 m3 /sec
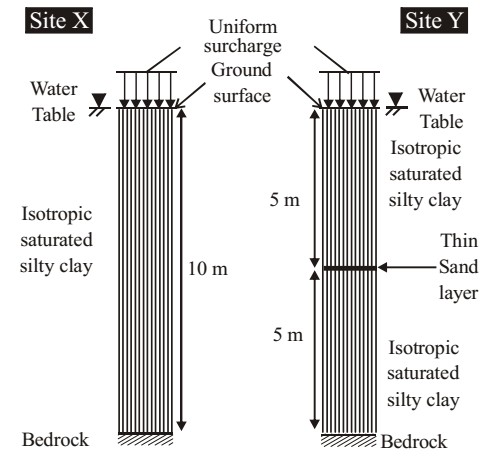
- Identical surcharges are placed at ground surface at sites X and Y, with soil conditions shown alongside and water table at ground surface. The silty clay layres at X and Y are identical. The thin sand layer at Y is continouous and freedraining with a very large discharge capacity. If primary consolidation at X is estimated to complete in 36 months, what would be the corresponding time for compeltion of primary cosnolidation at Y?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Time factor,
Tv = Cvt d2
∴ t ∝ d2
At site X, d1 = 10 m and t1 = 36 months
At site Y, d2 = 5 m and t2 =?t1 = d12 t2 d22
∴ t2 = 36 × 52∴ t2 = 36 × 52 = 9 months 102 Correct Option: C
Time factor,
Tv = Cvt d2
∴ t ∝ d2
At site X, d1 = 10 m and t1 = 36 months
At site Y, d2 = 5 m and t2 =?t1 = d12 t2 d22
∴ t2 = 36 × 52∴ t2 = 36 × 52 = 9 months 102

