Soil mechanics miscellaneous
Direction: The ground conditions at a site are as shown in the figure. The water table at the site which was initially at a depth of 5 m below the ground level got permanently lowered to a depth of 15 m below the ground level due to pumping of water over a few years. Assume the following data (i) unit weight of water = 10 kN/m3 .
(ii) unit weight of sand above water table = 18 kN/m3 .
(iii) unit weight of sand and clay below the water tabl = 20 kN/m3 .
(iv) coefficient of volume comprehensibility = 0.25 m2 /MN.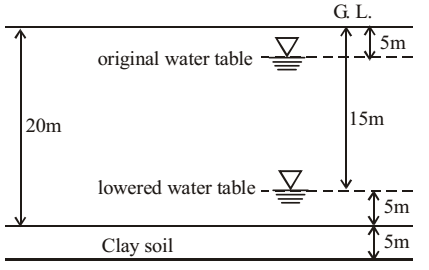
- What is the compression of the clay layer in mm due to the lowering of the water table?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Coeff. of volume comprehensibility,
= ∆V/V0 ∆σ1
Here changes in the height.∴ ∆V = ∆H V0 H0 = ∆V × H0 = mv.∆σ' × H0 V0 = 0.25 × 106 × 100 × 103 × 5000 = 125 mm 106 106 Correct Option: A
Coeff. of volume comprehensibility,
= ∆V/V0 ∆σ1
Here changes in the height.∴ ∆V = ∆H V0 H0 = ∆V × H0 = mv.∆σ' × H0 V0 = 0.25 × 106 × 100 × 103 × 5000 = 125 mm 106 106
Direction: A sand layer found at sea floor under 20 m water depth is characterised with relative density = 40%, maximum void ratio = 1.0, minimum void ratio = 0.5, and specific gravity of soil solids = 2.67. Assume the specific gravity of sea water to be 1.03 and the unit weight of fresh water to be 9.81 kN/m3
- What would be the change in the effective stress (rounded off to the nearest integer value of kPa) at 30 m depth into the sand layer if the sea water level permanently rises by 2 m?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Change in water level will not come any change in effective stress.
Correct Option: B
Change in water level will not come any change in effective stress.
Direction: Water is following through the permeability apparatus as shown in the figure. The coefficient of permeability of the soil is k m/s and the porosity of the soil sample is 0.50.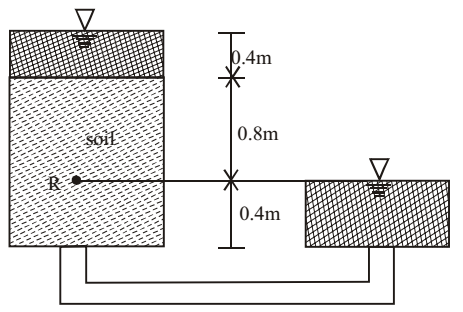
- What are discharge velocity and seepage velocity through the soil sample?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Discharge velocity, v = ki = k m/s (i = 1)
seepage velocity,= v = k = 2 km/s η 0.5 Correct Option: A
Discharge velocity, v = ki = k m/s (i = 1)
seepage velocity,= v = k = 2 km/s η 0.5
- A sample saturated cohesion less soil tested in a drained triaxial compression test showed an angle of internal friction of 30°. The deviatoric stress at failure for the sample at a confining pressure of 200 kPa is equal to
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
σ1 = σ3 tan2 α + 2c tan α.
α = 45 + Φ 2 = 45 + 30 = 60° 2
c = 0 (cohesionless soil)
∴ σ1 = σ3 tan2 60°
Confining pressure/ cell pressure = σ3 = 200
∴ σ1 = 200 × 3 = 600 kPa
Deviate stress = σ1 – σ3 = 600 – 200 = 400 kPaCorrect Option: B
σ1 = σ3 tan2 α + 2c tan α.
α = 45 + Φ 2 = 45 + 30 = 60° 2
c = 0 (cohesionless soil)
∴ σ1 = σ3 tan2 60°
Confining pressure/ cell pressure = σ3 = 200
∴ σ1 = 200 × 3 = 600 kPa
Deviate stress = σ1 – σ3 = 600 – 200 = 400 kPa

