Gravitation
- The figure shows elliptical orbit of a planet m about the sun S. The shaded area SCD is twice the shaded area SAB. If t1 is the time for the planet to move from C to D and t2 is the time to move from A to B then :

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
According to Kepler’s law, the areal velocity of a planet around the sun always remains constant.
SCD : A1 – t1 (areal velocity constant)
SAB : A2 – t2A1 = A2 t1 t2 t1 = t2. A1 (given A1 = 2A2) A2 = t2. 2A2 A2
∴ t1 = 2t2Correct Option: B
According to Kepler’s law, the areal velocity of a planet around the sun always remains constant.
SCD : A1 – t1 (areal velocity constant)
SAB : A2 – t2A1 = A2 t1 t2 t1 = t2. A1 (given A1 = 2A2) A2 = t2. 2A2 A2
∴ t1 = 2t2
- Kepler's third law states that square of period of revolution (T) of a planet around the sun, is proportional to third power of average distance r between sun and planet i.e. T2 = Kr3 here K is constant. If the masses of sun and planet are M and m respectively then as per Newton's
law of gravitation force of attraction between them is F = G M m here G is r2
gravitational constant. The relation between G and K is described as
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
As we know, orbital speed,

Time period T = 2πr = 2πr √r vorb √GM
Squarring both sides,T2 = 
2πr √r 
2 = 4π2 .r3 √GM GM ⇒ T2 = 4π2 = K r3 GM
⇒ GMK = 4π2.
Correct Option: A
As we know, orbital speed,

Time period T = 2πr = 2πr √r vorb √GM
Squarring both sides,T2 = 
2πr √r 
2 = 4π2 .r3 √GM GM ⇒ T2 = 4π2 = K r3 GM
⇒ GMK = 4π2.
- The radii of circular orbits of two satellites A and B of the earth, are 4R and R, respectively. If the speed of satellite A is 3 V, then the speed of satellite B will be :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Orbital velocity of a satellite in a circular orbit of radius a is given by
v = √GM / a
v ∝ √1 / a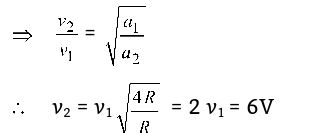
Correct Option: B
Orbital velocity of a satellite in a circular orbit of radius a is given by
v = √GM / a
v ∝ √1 / a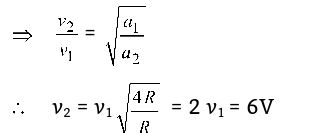
- If the gravitational force between two objects were proportional to 1/R (and not as 1/R2) where R is separation between them, then a particle in circular orbit under such a force would have its orbital speed v proportional to
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
F = k = Mv2 R R
Hence , v ∝ R0Correct Option: B
F = k = Mv2 R R
Hence , v ∝ R0
- A planet is moving in an elliptical orbit around the sun. If T, V, E and L stand respectively for its kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, total energy and magnitude of angular momentum about the centre of force, which of the following is correct ?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
In a circular or elliptical orbital motion, torque is always acting parallel to displacement or velocity. So, angular momentum is conserved. In attractive field, potential energy is negative. Kinetic energy changes as velocity increase when distance is less. So, option (c) is correct.
Correct Option: C
In a circular or elliptical orbital motion, torque is always acting parallel to displacement or velocity. So, angular momentum is conserved. In attractive field, potential energy is negative. Kinetic energy changes as velocity increase when distance is less. So, option (c) is correct.

