Theory of Machines Miscellaneous
- Consider a single degree of freedom system with viscous damping excited by a harmonic force. At resonance, the phase angle (in degree) of the displacement with respect to the exciting force is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: C
NA
- A mass-spring-dashpot system with mass m = 10 kg, spring constant k = 6250 N/m is excited by a harmonic excitation of 10 cos(25t) N. At the steady state, the vibration amplitude of the mass is 40 mm. The damping coefficient (c, in Ns/m) of the dashpot is __________.
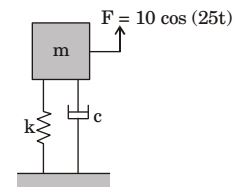
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
X = F = 40 mm = 0.04 √(k - mω²)² + (Cω)²
F = 10 N
ω = 25⇒ 0.04 = 10 √(6250 - 10 × 25²)² + (C × 25)²
C = 10Ns/mCorrect Option: A
X = F = 40 mm = 0.04 √(k - mω²)² + (Cω)²
F = 10 N
ω = 25⇒ 0.04 = 10 √(6250 - 10 × 25²)² + (C × 25)²
C = 10Ns/m
- A single degree of freedom system has a mass of 2 kg, stiffness 8 N/m and viscous damping ratio 0.02. The dynamic magnification factor at an excitation frequency of 1.5 rad/s is ______
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
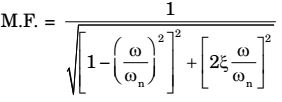
ω = 1.5 rad/sωn = √ k = √ 8 = 2 rad/s m 2
ξ = 0.02MF = 1 √[1 - (0.75)²]² + (2 × 0.02 × 0.75)²
∴ M.F. = 2.28Correct Option: C
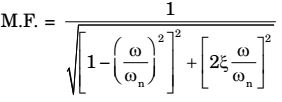
ω = 1.5 rad/sωn = √ k = √ 8 = 2 rad/s m 2
ξ = 0.02MF = 1 √[1 - (0.75)²]² + (2 × 0.02 × 0.75)²
∴ M.F. = 2.28
- In a spring-mass system, the mass is m and the spring constant is k. The critical damping coefficient of the system is 0.1 kg/s. In another spring-mass system, the mass is 2m and the spring constant is 8k. The critical damping coefficient (in kg/s) of this system is ______.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
x = C 2√mk
⇒ C = 2ξ√mkC2 = 2ξ2√m2k2 C1 2ξ1√m1k1 C2 = √16 0.1
C2 = 0.4 kg/sCorrect Option: B
x = C 2√mk
⇒ C = 2ξ√mkC2 = 2ξ2√m2k2 C1 2ξ1√m1k1 C2 = √16 0.1
C2 = 0.4 kg/s
- Which of the following statements are TRUE for damped vibrations?
P. For a system having critical damping, the value of damping ratio is unity and system does not undergo a vibratory motion.
Q. Logarithmic decrement method is used to determine the amount of damping in a physical system.
R. In case of damping due to dry friction between moving surfaces resisting force of constant magnitude acts opposite to the relative motion.
S. For the case of viscous damping, drag force is directly proportional to the square of relative velocity.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: C
NA

