Laws of Motion
- A ball of mass 150 g, moving with an acceleration 20 m/s², is hit by a force, which acts on it for 0.1 sec. The impulsive force is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Mass = 150 gm
= 150 kg 1000
Force = Mass × acceleration= 150 × 20N = 3N 1000
= Impulsive force = F Δt = 3 × 0.1 = 0.3N
Correct Option: C
Mass = 150 gm
= 150 kg 1000
Force = Mass × acceleration= 150 × 20N = 3N 1000
= Impulsive force = F Δt = 3 × 0.1 = 0.3N
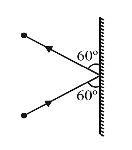
- A 3 kg ball strikes a heavy rigid wall with a speed of 10 m/s at an angle of 60º. It gets reflected with the same speed and angle as shown here. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.20s, what is the average force exerted on the ball by the wall?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Change in momentum along the wall
= mv cos60º – mv cos 60º = 0
Change in momentum perpendicular to the wall
= mv sin60º – (– mv sin60º) = 2mv sin60º∴ Applied force = Change in momentum Time = 2mv sin 60° 0.20 = 2 × 3 × 10 × √3 = 50 × 3√3 2 × 20
= 150√3 newtonCorrect Option: C
Change in momentum along the wall
= mv cos60º – mv cos 60º = 0
Change in momentum perpendicular to the wall
= mv sin60º – (– mv sin60º) = 2mv sin60º∴ Applied force = Change in momentum Time = 2mv sin 60° 0.20 = 2 × 3 × 10 × √3 = 50 × 3√3 2 × 20
= 150√3 newton
- A 10 N force is applied on a body produces an acceleration of 1 m/s². The mass of the body is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
By Newton's IInd law of motion, F = ma
⇒ 10 = m (1) ⇒ m = 10 kg.Correct Option: B
By Newton's IInd law of motion, F = ma
⇒ 10 = m (1) ⇒ m = 10 kg.
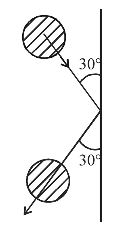
- A 0.5 kg ball moving with speed of 12 m/s strikes a hard wall at an angle of 30° with the wall. It is reflected with the same speed and at the same angle. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.25 seconds, the average force acting on the wall is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
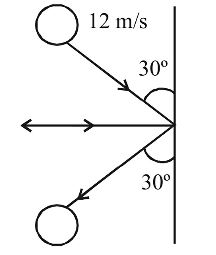
Resolving the velocities in vertical and horizontal directions, resolved parts of first velocity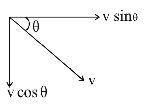
v cosθ perpendicular to the wall and v sinθ parallel to the wall. In the second case, they are –v sin θ & v cos θ respectively. Here, –ve sign is because direction is opposite to the earlier ones. So we see a net change in velocity perpendicular to way
= v sin θ – (–v sin θ) = 2v sin θ
This change has occured in 0.25 sec, so, rate of change of velocity= 2v sin θ 0.25 = 2 × 12 × sin 30° ⇒ 24 × 1 = 48 0.25 2 × 0.25
Thus, acceleration a = 48 m/sec²
Force applied = m . a = 0.5 × 48 = 24 NCorrect Option: A

Resolving the velocities in vertical and horizontal directions, resolved parts of first velocity
v cosθ perpendicular to the wall and v sinθ parallel to the wall. In the second case, they are –v sin θ & v cos θ respectively. Here, –ve sign is because direction is opposite to the earlier ones. So we see a net change in velocity perpendicular to way
= v sin θ – (–v sin θ) = 2v sin θ
This change has occured in 0.25 sec, so, rate of change of velocity= 2v sin θ 0.25 = 2 × 12 × sin 30° ⇒ 24 × 1 = 48 0.25 2 × 0.25
Thus, acceleration a = 48 m/sec²
Force applied = m . a = 0.5 × 48 = 24 N
- A satellite in a force free space sweeps stationary interplanetary dust at a rate (dM/dt) = αv. The acceleration of satellite is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Thrust on the satellite,
F = -vdM -v(αv) = -αv² dt Acceleration - F - -αv² M M Correct Option: B
Thrust on the satellite,
F = -vdM -v(αv) = -αv² dt Acceleration - F - -αv² M M

