Electromagnetic theory miscellaneous
- A slab of uniform magnetic field deflects a moving charged particle by 45º as shown in the figure.kinetic energy of the charged particle at the entry and exit points in the magnetic field will change in the ratio of—

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The force on a charge moving in a magnetic field is F = q V × B; the force is ⊥ to both V and B. Hence the magnitude of V is not changed and thus kinetic energy at the entry and exit points will be same.
Correct Option: C
The force on a charge moving in a magnetic field is F = q V × B; the force is ⊥ to both V and B. Hence the magnitude of V is not changed and thus kinetic energy at the entry and exit points will be same.
- An electric dipole of moment P is placed in front of a grounded sphere as shown in the fig. The charge induced on the surface of the sphere is—

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The charge induced on a spherical surface is given by
– QR/D
where Q is the inducing point charge, D is the distance of the point charge from the centre of the sphere and R the radius of the sphere.
Total charge induced in the present case isQ = – qR 
1 - 1 
d + d '/2 d – d '/2 = –qR (–d') = qd'R d2 d2 – (d '2)/4 (d '2)/4
Now for a dipole d′ is very small, i.e., d′ << d. Hence, Q′ = PR/ d2 where, P = qd′, the dipole moment.
Correct Option: B
The charge induced on a spherical surface is given by
– QR/D
where Q is the inducing point charge, D is the distance of the point charge from the centre of the sphere and R the radius of the sphere.
Total charge induced in the present case isQ = – qR 
1 - 1 
d + d '/2 d – d '/2 = –qR (–d') = qd'R d2 d2 – (d '2)/4 (d '2)/4
Now for a dipole d′ is very small, i.e., d′ << d. Hence, Q′ = PR/ d2 where, P = qd′, the dipole moment.
- A circular ring carrying a uniformly distributed charge Q and a point charges – Q on the axis of the ring are shown in the fig. The magnitude of the dipole moment of the charge system is—

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
For points far away, the charge on the ring may be considered to be located at the centre of the ring. Hence, the dipole moment becomes Qd.
Correct Option: A
For points far away, the charge on the ring may be considered to be located at the centre of the ring. Hence, the dipole moment becomes Qd.
- A point charge Q is located on the surface of a sphere of radius R as shown in the figure. The average electric field on the surface of the sphere will be—

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The point charge Q elevates a total electric displacement flux of Q. If a plane is passed through the point of location of charge and tangential to the sphere, half the flux is on one side and half on the other. The first half of flux is passing through the spherical surface. Thus the average displacement density has a direction opposite to that of
→ n
and the magnitude is
Q/2 4∏R2
so, average electric field isEav = Q –→ where, –→ is the unit vector. 8∏∈0R2 (-n) n
Correct Option: C
The point charge Q elevates a total electric displacement flux of Q. If a plane is passed through the point of location of charge and tangential to the sphere, half the flux is on one side and half on the other. The first half of flux is passing through the spherical surface. Thus the average displacement density has a direction opposite to that of
→ n
and the magnitude is
Q/2 4∏R2
so, average electric field isEav = Q –→ where, –→ is the unit vector. 8∏∈0R2 (-n) n
- Two point charges Q and – Q are located on two opposite corners of a square as shown in figure. If the potential at the corner A is taken as 1 V, then the potential at B, the centre of the square will be—
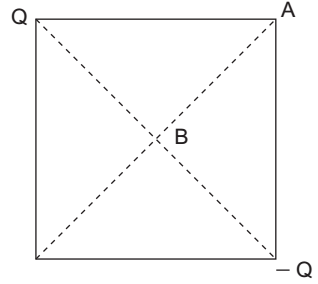
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The plane midway between a and – a, i.e., the one passing through ABC and perpendicular to the plane of the paper is an equipotential plane.
Hence the potential at B is the same as that of A or C, i.e., 1 V.Correct Option: C
The plane midway between a and – a, i.e., the one passing through ABC and perpendicular to the plane of the paper is an equipotential plane.
Hence the potential at B is the same as that of A or C, i.e., 1 V.

