Current Electricity
- n equal resistors are first connected in series and then connected in parallel. What is the ratio of the maximum to the minimum resistance ?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
In series, Rs = nR
In parallel, 1 = 1 + 1 + ... n terms Rp R R
∴ Rs/Rp = n² /1 = n²
Correct Option: C
In series, Rs = nR
In parallel, 1 = 1 + 1 + ... n terms Rp R R
∴ Rs/Rp = n² /1 = n²
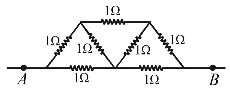
- In the network shown in the Fig, each resistance is 1Ω. The effective resistance between A and B is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
At A current is distributed and at B currents are collected. Between A and B, the distribution is symmetrical. It has been shown in the figure. It appears that current in AO and OB remains same. At O, current i4 returns back without any change. If we detach O from AB there will not be any change in distribution. Now, CO & OD will be in series hence its total resistance = 2Ω
It is in parallel with CD, so, equivalent resistance = 2 x 1 = 2 Ω 2 + 1 3
This equivalent resistance is in series with AC & DB, so, total resistance= 2 + 1 + = 8 Ω 3 3 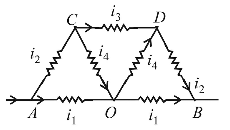
Now 8/3 Ω is parallel to AB, that is, 2Ω, so total resistance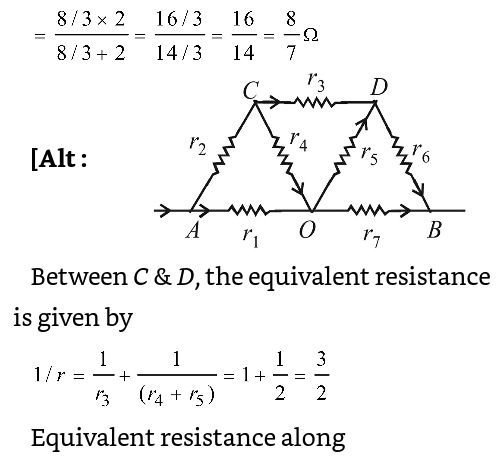
ABCD = 1 + 2 + 1 = 8 Ω 3 3 
Correct Option: D
At A current is distributed and at B currents are collected. Between A and B, the distribution is symmetrical. It has been shown in the figure. It appears that current in AO and OB remains same. At O, current i4 returns back without any change. If we detach O from AB there will not be any change in distribution. Now, CO & OD will be in series hence its total resistance = 2Ω
It is in parallel with CD, so, equivalent resistance = 2 x 1 = 2 Ω 2 + 1 3
This equivalent resistance is in series with AC & DB, so, total resistance= 2 + 1 + = 8 Ω 3 3 
Now 8/3 Ω is parallel to AB, that is, 2Ω, so total resistance
ABCD = 1 + 2 + 1 = 8 Ω 3 3 
- In the circuit shown in Fig, the current in 4 Ω resistance is 1.2 A. What is the potential difference between B and C.
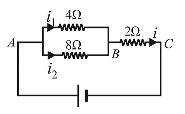
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The potential difference across 4Ω resistance is given by V = 4 × i1 = 4 × 1.2 = 4.8 volt
So, the potential across 8Ω resistance is also 4.8 volt.Current i2 = V = 4.8 =0.6 amp 8 8
Current in 2Ω resistance i = i1 + i2
∴ i = 1.2 + 0.6 = 1.8 amp
Potential difference across 2Ω resistance
VBC = 1.8 × 2 = 3.6voltsCorrect Option: A
The potential difference across 4Ω resistance is given by V = 4 × i1 = 4 × 1.2 = 4.8 volt
So, the potential across 8Ω resistance is also 4.8 volt.Current i2 = V = 4.8 =0.6 amp 8 8
Current in 2Ω resistance i = i1 + i2
∴ i = 1.2 + 0.6 = 1.8 amp
Potential difference across 2Ω resistance
VBC = 1.8 × 2 = 3.6volts
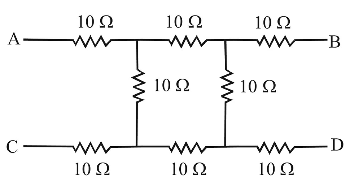
- What will be the equivalent resistance of circuit shown in figure between two points A and D
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
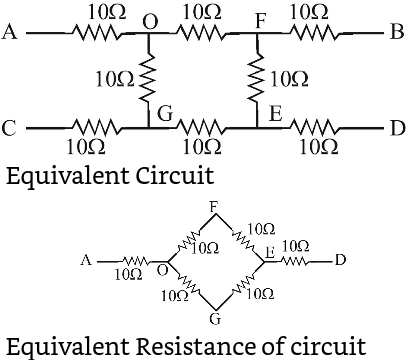
= 10 Ω + 20 × 20 + 10 = 10 + 10 + 10 = 30 Ω 20 + 20
Correct Option: C

= 10 Ω + 20 × 20 + 10 = 10 + 10 + 10 = 30 Ω 20 + 20
- Two wires of the same metal have same length, but their cross-sections are in the ratio 3:1. They are joined in series. The resistance of thicker wire is 10Ω. The total resistance of the combination will be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Length of each wire = l; Area of thick wire (A1) = 3A; Area of thin wire (A2) = A and resistance of thick wire (R1) = 10 Ω.
Resistance (R) = ρ l ∝ 1 (if l is constant) A A ∴ R1 = A2 = A = 1 R2 A1 3A 3
or, R2 = 3R1 = 3 × 10 = 30 Ω
The equivalent resistance of these two resistors in series
= R1 + R2 = 30 + 10 = 40Ω.Correct Option: C
Length of each wire = l; Area of thick wire (A1) = 3A; Area of thin wire (A2) = A and resistance of thick wire (R1) = 10 Ω.
Resistance (R) = ρ l ∝ 1 (if l is constant) A A ∴ R1 = A2 = A = 1 R2 A1 3A 3
or, R2 = 3R1 = 3 × 10 = 30 Ω
The equivalent resistance of these two resistors in series
= R1 + R2 = 30 + 10 = 40Ω.

