Current Electricity
- The potential difference between the terminals of a cell in an open circuit is 2.2 V. When a resistor of 5Ω is connected across the terminals of the cell, the potential difference between the terminals of the cell is found to be 1.8 V. The internal resistance of the cell is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
E = V + ir
2.2 = 1.8 + 1.8 x r 5 ⇒ r - 10 Ω 9
Correct Option: B
E = V + ir
2.2 = 1.8 + 1.8 x r 5 ⇒ r - 10 Ω 9
- A battery is charged at a potential of 15V for 8 hours when the current flowing is 10A. The battery on discharge supplies a current of 5A for 15 hours. The mean terminal voltage during discharge is 14V. The “watt-hour” efficiency of the battery is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Efficiency is given by η - output input = 5 x 15 x 14 = 0.875 or 87.5% 10 x 8 x 15
Correct Option: A
Efficiency is given by η - output input = 5 x 15 x 14 = 0.875 or 87.5% 10 x 8 x 15
- Two batteries, one of emf 18 volt and internal
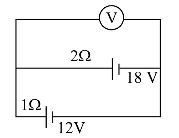
resistance 2Ω and the other of emf 12 volt and internal resistance 1Ω, are connected as shown. The voltmeter V will record a reading of
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
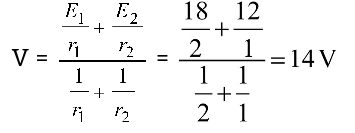
(Since the cells are in parallel).Correct Option: D
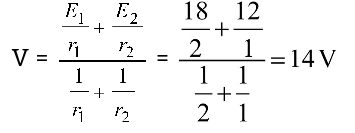
(Since the cells are in parallel).
- Two cells, having the same e.m.f., are connected in series through an external resistance R. Cells have internal resistances r1 and r2 (r1 > r2) respectively. When the circuit is closed, the potential difference across the first cell is zero. The value of R is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Current in the circuit
= E + E = 2E r1 + r2 + R r1 + r2 + R
P.D. across first cell = E – ir1= E - 2E × r1 = 0 (r1 + r2) + R Now, E = 2Er1 = 0 (r1 + r2) + R ⇒ E = 2Er1 ⇒ 2r1 = r1 + r2 + R (r1 + r2) + R
⇒ R = r1 - r2Correct Option: D
Current in the circuit
= E + E = 2E r1 + r2 + R r1 + r2 + R
P.D. across first cell = E – ir1= E - 2E × r1 = 0 (r1 + r2) + R Now, E = 2Er1 = 0 (r1 + r2) + R ⇒ E = 2Er1 ⇒ 2r1 = r1 + r2 + R (r1 + r2) + R
⇒ R = r1 - r2
- Kirchhoff’s first and second laws for electrical circuits are consequences of
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Kirchhoff's first law deals with conservation of electrical charge & the second law deals with conservation of electrical energy.
Correct Option: A
Kirchhoff's first law deals with conservation of electrical charge & the second law deals with conservation of electrical energy.

