Electrical machines miscellaneous
- A single -winding single-phase motor has
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: B
NA
- If a single-winding single-phase motor is running in a particular direction
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: C
NA
- An iron-cored choke with 1 mm air-gap length, draws 1 A when fed from a constant voltage ac source of 220 V. If the length of air-gap is increased to 2 mm, the current drawn by the choke would
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: C
NA
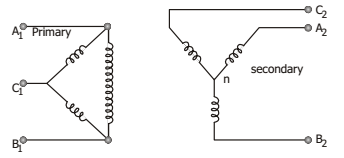
- In a 3-phase Δ/ Y transformer shown in the figure, the phase displacement of secondary line voltages with corresponding primary line voltages will be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Consider any pair of line terminals on primary and secondary sides.
Consider pair AB.
Let VA1B1 be reference on primary side
VA1B1 = V ∠0°
VB1C1 = V ∠– 120°
VC1A1 = V ∠120°
VA2n = k VA1C1 = − k VC1A1 = − k ∠120°
VnB2 = k VA1B1 = k V ∠0°
VA2B2 = VA2n − VnB2 = k V( ∠−60° + ∠0°)
= √3 kV ∠−30°
Thus line voltage VA2B2 on secondary side which equals √3 kV ∠−30°, lags corres-ponding line voltage VA1B1 on primary side, which is V ∠0°; by 30°.Correct Option: B
Consider any pair of line terminals on primary and secondary sides.
Consider pair AB.
Let VA1B1 be reference on primary side
VA1B1 = V ∠0°
VB1C1 = V ∠– 120°
VC1A1 = V ∠120°
VA2n = k VA1C1 = − k VC1A1 = − k ∠120°
VnB2 = k VA1B1 = k V ∠0°
VA2B2 = VA2n − VnB2 = k V( ∠−60° + ∠0°)
= √3 kV ∠−30°
Thus line voltage VA2B2 on secondary side which equals √3 kV ∠−30°, lags corres-ponding line voltage VA1B1 on primary side, which is V ∠0°; by 30°.
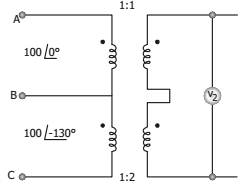
- Two single-phase transformers with turns ratio 1 and 2 respectively are connected to a 3-phase supply on the primary side as shown in the figure. The voltmeter V2, will read
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Voltmeter V2 read rms magnitude of the sum of two voltage phasors,
viz., 100 ∠0° + 2 × 100 ∠ – 120° υ2
= | 100 ∠0° + 200 ∠ – 120° |
= | 100 – 100 – j 100 √3 |
= | – j 100 √3 | = 173.2 VCorrect Option: B
Voltmeter V2 read rms magnitude of the sum of two voltage phasors,
viz., 100 ∠0° + 2 × 100 ∠ – 120° υ2
= | 100 ∠0° + 200 ∠ – 120° |
= | 100 – 100 – j 100 √3 |
= | – j 100 √3 | = 173.2 V

