Highway planning miscellaneous
- The following data are related to a horizontal curved portion of a two-lane highway: length of curve = 200 m, radius of curve = 300 m and width of pavement = 7.5 m. In order to provide a stopping sight distance (SSD) of 80 m, the set back distance (in m) required from the centre line of the inner lane of the pavement is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

Q = 
SSD 
× 180 = 80 × 180 = 14.9° R + 7.5 π (300 + 7.5) π S = 
R + d 

1 - cos θ 
= 2.54 m 4 2 Correct Option: A

Q = 
SSD 
× 180 = 80 × 180 = 14.9° R + 7.5 π (300 + 7.5) π S = 
R + d 

1 - cos θ 
= 2.54 m 4 2
- A rod is being designed for a speed of 110 km /hr on a horizontal curve with a super elevation of 8%. If the coefficient of side friction is 0.10, the minimum radius of the curve (in m) required for safe vehicular movement is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
e + f = V² 127R ∴ R = V² = 110² ≈ 528.5 m 127(e + f) 127(0.08 + 0.1) Correct Option: D
e + f = V² 127R ∴ R = V² = 110² ≈ 528.5 m 127(e + f) 127(0.08 + 0.1)
- On a circular curve, the rate of superelevation is e. While negotiating the curve a vehicle comes to a stop. It is seen that the stopped vehicle does not slide inwards (in the radial direction). The coefficient of side friction is f. Which of the following is true:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Since stopped vehicle does not slide inside,
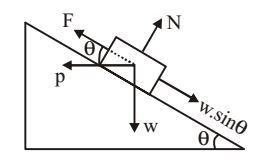
F ≥ w.sinq
F = P cosθ
P = w.f
where,
P = centrifugal force
ƒ = coeff of lateral friction
⇒ P.cosq ≥ w sin θ
wƒ. cosq ≥ w sin θ
f ≥ tan θ
⇒ ƒ ≥ e
⇒ e ≤ ƒCorrect Option: A
Since stopped vehicle does not slide inside,

F ≥ w.sinq
F = P cosθ
P = w.f
where,
P = centrifugal force
ƒ = coeff of lateral friction
⇒ P.cosq ≥ w sin θ
wƒ. cosq ≥ w sin θ
f ≥ tan θ
⇒ ƒ ≥ e
⇒ e ≤ ƒ
- A superspeedway in New Delhi has among the highest super-elevation rates of any track on the Indians Grand Prix circuit. The track requires drivers to negotiate turns with a radius of 335 m and 33° banking. Given this information, the coefficient of side friction required in order to allow a vehicle to travel at 320 km/h along the curve is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
e + ƒ = V² 9R
V = 320 km/h= 320 × 1000 = 88.89 m/s 3600
e = tanq = tan33°∴ tan33 + ƒ = 88.89² = 2.404 9.81 × 335
⇒ ƒ = 1.76Correct Option: A
e + ƒ = V² 9R
V = 320 km/h= 320 × 1000 = 88.89 m/s 3600
e = tanq = tan33°∴ tan33 + ƒ = 88.89² = 2.404 9.81 × 335
⇒ ƒ = 1.76
Direction: For a portion of national highway where a descending gradient of 1 in 25 meets with an ascending gradient of 1 in 20, a valley curve needs to be designed for a vehicle travelling at 90 kmph based on the following conditions.
1. head light sight distance equal to the stopping sight distance (SSD) of a level terrain considering length of valley curve > SSD.
2. comfort condition with allowable rate of change of centrifugal acceleration = 0.5 m/sec³. Assume total reaction time = 2.5 seconds; co-efficient of longitudinal friction of the pavement = 0.35; height of head light of the vehicle = 0.75 m; and beam angle = 1°.
- What is the length of valley curve (in m) based on the head light sight distance condition ?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
N = 
- 1 - 1 
= 0.09 25 20 S = 0.278 × 90 × 2.5 + 90² = 62.55 + 91.1136 = 153.6636 254 × 0.35
Assume L > SSDCorrect Option: A
N = 
- 1 - 1 
= 0.09 25 20 S = 0.278 × 90 × 2.5 + 90² = 62.55 + 91.1136 = 153.6636 254 × 0.35
Assume L > SSD

