Electric Charges and Fields
- Two pith balls carrying equal charges are suspended from a common point by strings of equal length. The equilibrium separation between them is r. Now the strings are rigidly clamped at half the height. The equilibrium separation between the balls now become

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

From figure, tan θ = Fe ⇒ r / 2 = kq2 mg y r2 / mg [ ∵ F = kq2 from coulomb’s law] r2 ⇒ r3 ∝ y ⇒ r'3 ∝ y ⇒ r' = 1 2 r 21 / 3 ⇒ r' = r 3√2 Correct Option: A

From figure, tan θ = Fe ⇒ r / 2 = kq2 mg y r2 / mg [ ∵ F = kq2 from coulomb’s law] r2 ⇒ r3 ∝ y ⇒ r'3 ∝ y ⇒ r' = 1 2 r 21 / 3 ⇒ r' = r 3√2
- Two identical charged spheres suspended from a common point by two massless strings of lengths l, are initially at a distance d (d << l) apart because of their mutual repulsion. The charges begin to leak from both the spheres at a constant rate. As a result, the spheres approach each other with a velocity v. Then v varies as a function of the distance x between the spheres, as :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
From figure tan θ = Fc ; θ mg kq2 = x x2 mg 2ℓ 
or x3 ∝ q2 …(1)
or x3/ 2 ∝ q …(2)
Differentiating eq. (1) w.r.t. time3x2 dx ∝ 2q dq but dq is constant dt dt dt
so x2(v) ∝ q Replace q from eq. (2)
x2(v) ∝ x3/2 or v ∝ x–1/2Correct Option: C
From figure tan θ = Fc ; θ mg kq2 = x x2 mg 2ℓ 
or x3 ∝ q2 …(1)
or x3/ 2 ∝ q …(2)
Differentiating eq. (1) w.r.t. time3x2 dx ∝ 2q dq but dq is constant dt dt dt
so x2(v) ∝ q Replace q from eq. (2)
x2(v) ∝ x3/2 or v ∝ x–1/2
- Suppose the charge of a proton and an electron differ slightly. One of them is – e, the other is (e + ∆e). If the net of electrostatic force and gravitational force between two hydrogen atoms placed at a distance d (much greater than atomic size) apart is zero, then ∆e is of the order of [Given mass of hydrogen mh = 1.67 × 10–27 kg]
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
According to question, the net electrostatic force (FE) = gravitational force (FG)
FE = FGor 1 ∆e2 = Gm2 4πε0 d2 d2 ⇒ ∆e = m 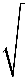
G K ∵ 
1 = k = 9 × 109 
4πε0 = 1.67 × 10–27 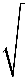
6.67 × 10–11 9 × 109
∆e ≈ 1.436 × 10–37 CCorrect Option: B
According to question, the net electrostatic force (FE) = gravitational force (FG)
FE = FGor 1 ∆e2 = Gm2 4πε0 d2 d2 ⇒ ∆e = m 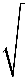
G K ∵ 
1 = k = 9 × 109 
4πε0 = 1.67 × 10–27 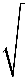
6.67 × 10–11 9 × 109
∆e ≈ 1.436 × 10–37 C
- The electric field in a certain region is acting radially outward and is given by E = Aa. A charge contained in a sphere of radius 'a' centred at the origin of the field, will be given by
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Net flux emmited from a spherical surface of radius a according to Gauss’s theorem
φnet = qin ε0 or,(Aa) (4πa2) = qin ε0
So, qin = 4πε0 A a3
Correct Option: B
Net flux emmited from a spherical surface of radius a according to Gauss’s theorem
φnet = qin ε0 or,(Aa) (4πa2) = qin ε0
So, qin = 4πε0 A a3
- A charge Q is placed at the corner of a cube. The electric flux through all the six faces of the cube is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
According to Gauss's theorem,
electric flux through a closed surface = Q where q is charge enclosed ε0
by the surface.Correct Option: D
According to Gauss's theorem,
electric flux through a closed surface = Q where q is charge enclosed ε0
by the surface.

