Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- The refracting angle of a prism is ‘A’, and refractive index of the material of the prism is cot(A/2). The angle of minimum deviation is :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
As we know, the refractive index of the material of the prism
μ = sin 
δm + A 
2 sin (A / 2) cot (A / 2) = sin 
A + δm 
= cos (A / 2) 2 sin (A / 2) sin (A / 2)
[∵ μ = cot (A / 2) ]⇒ sin 
A + δm 
= sin(90° + A / 2) 2
⇒ δmin = 180° - 2ACorrect Option: A
As we know, the refractive index of the material of the prism
μ = sin 
δm + A 
2 sin (A / 2) cot (A / 2) = sin 
A + δm 
= cos (A / 2) 2 sin (A / 2) sin (A / 2)
[∵ μ = cot (A / 2) ]⇒ sin 
A + δm 
= sin(90° + A / 2) 2
⇒ δmin = 180° - 2A
- A biconvex lens has a radius of curvature of magnitude 20 cm. Which one of the following options best describe the image formed of an object of height 2 cm placed 30 cm from the lens?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
R = 20 cm
h0 = 2
u = –30 cm We have, 1 = (μ - 1) 
1 - 1 
f R1 R2 = 
3 - 1 

1 - 
- 1 

2 20 20 ⇒ 1 = 
3 - 1 
× 2 f 2 20
∴ f = 20 cm= 1 = 1 - 1 ⇒ 1 = 1 + 1 f v u 20 v 30 1 = 1 - 1 = 10 v 20 30 600
v = 60 cmm = hi = v h0 u ⇒ hi = v × h0 = 60 × 2 = - 4 cm u 30
So, image is inverted.
Correct Option: C
R = 20 cm
h0 = 2
u = –30 cm We have, 1 = (μ - 1) 
1 - 1 
f R1 R2 = 
3 - 1 

1 - 
- 1 

2 20 20 ⇒ 1 = 
3 - 1 
× 2 f 2 20
∴ f = 20 cm= 1 = 1 - 1 ⇒ 1 = 1 + 1 f v u 20 v 30 1 = 1 - 1 = 10 v 20 30 600
v = 60 cmm = hi = v h0 u ⇒ hi = v × h0 = 60 × 2 = - 4 cm u 30
So, image is inverted.
- Two identical thin plano-convex glass lenses (refractive index 1.5) each having radius of curvature of 20 cm are placed with their convex surfaces in contact at the centre. The intervening space is filled with oil of refractive index 1.7. The focal length of the combination is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Using lens maker’s formula,
1 = (μ - 1) 
1 - 1 
f R1 R2 
1 = 
1.5 - 1 

1 - 1 
f1 1 ∞ -20
⇒ f1 = 40cm1 = 
1.7 - 1 

1 - 1 
f2 1 -20 +20 ⇒ f2 = - 100 cm 7 and 1 = 
1.5 - 1 

1 - 1 
f3 1 ∞ 20
⇒ f3 = 40cm1 = 1 + 1 + 1 feq f1 f2 f3 ⇒ 1 = 1 + 1 + 1 feq 40 -100 / 7 40
∴ feq = - 50 cm
Therefore, the focal length of the combination is – 50 cm.
Correct Option: B
Using lens maker’s formula,
1 = (μ - 1) 
1 - 1 
f R1 R2 
1 = 
1.5 - 1 

1 - 1 
f1 1 ∞ -20
⇒ f1 = 40cm1 = 
1.7 - 1 

1 - 1 
f2 1 -20 +20 ⇒ f2 = - 100 cm 7 and 1 = 
1.5 - 1 

1 - 1 
f3 1 ∞ 20
⇒ f3 = 40cm1 = 1 + 1 + 1 feq f1 f2 f3 ⇒ 1 = 1 + 1 + 1 feq 40 -100 / 7 40
∴ feq = - 50 cm
Therefore, the focal length of the combination is – 50 cm.
- Light enters at an angle of incidence in a transparent rod of refractive index n. For what value of the refractive index of the material of the rod the light once entered into it will not leave it through its lateral face whatsoever be the value of angle of incidence?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Let a ray of light enter at A and the refracted beam is AB. This is incident at an angle θ. For no refraction at the lateral face, θ > C or, sin θ > sin C But θ + r = 90° ⇒ θ = (90° – r)

∴ sin (90° – r) > sin C
or cos r > sin C ......(1)
From Snell’s law,n = sin i ⇒ sin r = sin i sin r n ∴ cos r = √1 - sin² r = 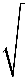

1 - sin2 i 
n2
∴ equation (1) gives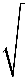

1 - sin2 i 
> sin C n2 ⇒ 1 - sin2 i > sin2 C n2 Also , sin C = 1 n ∴ 1 - sin2 i > 1 or 1 > sin2 i + 1 n2 n2 n2 n2 or 1 (sin2 i + 1) < 1 or n2 > (sin2 i + 1) n2
Maximum value of sin i = 1
n2 > 2 ⇒ n > √2Correct Option: A
Let a ray of light enter at A and the refracted beam is AB. This is incident at an angle θ. For no refraction at the lateral face, θ > C or, sin θ > sin C But θ + r = 90° ⇒ θ = (90° – r)

∴ sin (90° – r) > sin C
or cos r > sin C ......(1)
From Snell’s law,n = sin i ⇒ sin r = sin i sin r n ∴ cos r = √1 - sin² r = 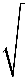

1 - sin2 i 
n2
∴ equation (1) gives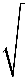

1 - sin2 i 
> sin C n2 ⇒ 1 - sin2 i > sin2 C n2 Also , sin C = 1 n ∴ 1 - sin2 i > 1 or 1 > sin2 i + 1 n2 n2 n2 n2 or 1 (sin2 i + 1) < 1 or n2 > (sin2 i + 1) n2
Maximum value of sin i = 1
n2 > 2 ⇒ n > √2
- A light ray falls on a rectangular glass slab as shown. The index of refraction of the glass, if total internal reflection is to occur at the vertical face, is

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
For point A , aμg = sin 45° sin r ⇒ sin r = 1 √2 aμg
For point B, sin (90° – r) = gµa where, (90° – r) is critical angle.
∴ cos r = gμa = 1 ⇒ aμg = 1 aμg cos r = 1 = 1 √1 - sin² r √{1 - (1 / 2 aμg2) ⇒ aμg2 = 1 = 2 aμg2 1 - 1 2 aμg2 - 1 2 aμg2 ⇒ 2 aμg2 - 1 = 2 ⇒ aμg = 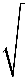
3 2 Correct Option: A
For point A , aμg = sin 45° sin r ⇒ sin r = 1 √2 aμg
For point B, sin (90° – r) = gµa where, (90° – r) is critical angle.
∴ cos r = gμa = 1 ⇒ aμg = 1 aμg cos r = 1 = 1 √1 - sin² r √{1 - (1 / 2 aμg2) ⇒ aμg2 = 1 = 2 aμg2 1 - 1 2 aμg2 - 1 2 aμg2 ⇒ 2 aμg2 - 1 = 2 ⇒ aμg = 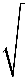
3 2

