Fluid mechanics and hydraulics miscellaneous
- The drag force, FD on sphere kept in a uniform flow field depends on the diameter of the sphere, D; flow velocity, V, fluid density, ρ; and dynamic viscosity, μ. Which of the following options represents the non-dimensional parameters which could be used to analyze this problem?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
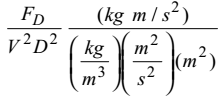
= (dimensionless parameter)ρVD = Re (reynold’s number) which is dimensionless μ Correct Option: C
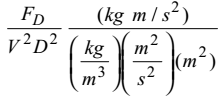
= (dimensionless parameter)ρVD = Re (reynold’s number) which is dimensionless μ
Direction: The laminar row takes place between closely spaced parallel plates as shown in figure below. The velocity profile is given by
u = V = v/h. The gap height, h is 5 mm and the space is filled with oil (specific gravity = 0.86, viscosity m = 2 × 10–1 N-s/m²). The bottom plate is stationary and the top plate moves with a steady velocity of V = 5 cm/s. The area of the plate is 0.25 m².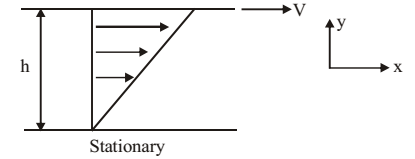
- The rate of rotation of fluid particle is given by
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
u = V 
y 
h
V = 0, ω = 0
Condition for rotation flow of laminar fluidωy = 1 
∂u − ∂ω 
= 0 2 ∂z ∂x ωz = 1 
∂V − ∂u 
2 ∂x ∂y = 1 
0 − ∂ 
V. y 

2 ∂y h = 1 
− V 
2 h = − V 2h Correct Option: A
u = V 
y 
h
V = 0, ω = 0
Condition for rotation flow of laminar fluidωy = 1 
∂u − ∂ω 
= 0 2 ∂z ∂x ωz = 1 
∂V − ∂u 
2 ∂x ∂y = 1 
0 − ∂ 
V. y 

2 ∂y h = 1 
− V 
2 h = − V 2h
- The power require to keep the plate in steady motion is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Velocity profile, U = V 
y 
h
V = 5 cm/s = 0.05 m/s
Newton’s law of viscosity,τ = μ du dy = μ d 
v. y 
= μ. V dy h h
Shear force = shear stress × surface area
F = τ × A= μ. v .A h
Power required = F.= μ. V .A × V h = μ V² A h = (2 × 10−4) × (0.05)2 × 0.25 0.005
= 2.5 × 10–5 WCorrect Option: C
Velocity profile, U = V 
y 
h
V = 5 cm/s = 0.05 m/s
Newton’s law of viscosity,τ = μ du dy = μ d 
v. y 
= μ. V dy h h
Shear force = shear stress × surface area
F = τ × A= μ. v .A h
Power required = F.= μ. V .A × V h = μ V² A h = (2 × 10−4) × (0.05)2 × 0.25 0.005
= 2.5 × 10–5 W
Direction: A rectangular channel 6.0 m wide carries a discharge of 16.0 m3 /s under uniform condition with normal depth of 1.60 m. Manning’s ‘n’ is 0.015.
- The longitudinal slope of the channel is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
B = 6 m, Q = 16 m³/s
y = 1.6 m, η = 0.015Q = 1 R2/3S1/2.A n R = A = B × y = 6 × 1.6 = 1.04 m P B + 2y 6 + 1.6 × 2 ∴ 16 = 1 × (1.04)2/3S1/2 × 6 0.015
∴ S = 0.000585.Correct Option: A
B = 6 m, Q = 16 m³/s
y = 1.6 m, η = 0.015Q = 1 R2/3S1/2.A n R = A = B × y = 6 × 1.6 = 1.04 m P B + 2y 6 + 1.6 × 2 ∴ 16 = 1 × (1.04)2/3S1/2 × 6 0.015
∴ S = 0.000585.
- For a rectangular channel section, Group I lists geometrical elements and Group II gives proportions for hydraulically efficient section.
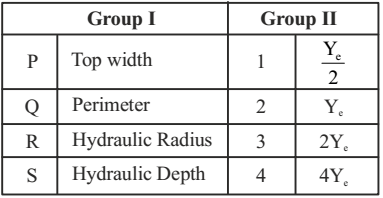
Ye is the follow depth corresponding to hydraulically efficient section. The correct match of Group I with Group II is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
For hydraulically efficient rectangular section,
Top width, B = 2ye
Perimeter = B + 2ye = 4yeHydraulic radius, Re = A P = 2ye² = ye 4ye 2 Hyraulic depth, A = 2ye² = ye. T 2ye Correct Option: C
For hydraulically efficient rectangular section,
Top width, B = 2ye
Perimeter = B + 2ye = 4yeHydraulic radius, Re = A P = 2ye² = ye 4ye 2 Hyraulic depth, A = 2ye² = ye. T 2ye

