Engineering Mechanics Miscellaneous
- Match 4 correct pairs between List-I and List-ll for questions.
List-I
A. Collision of particles
B. Stability
C. Satellite motion
D. Spinning top
List-II
1. Euler's equation of motion
2. Minimum kinetic energy
3. Minimum potential energy
4. Impulse momentum principle
5. Conservation of moment of momentum
Codes:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
(a) -4, (b) –3, (c) –2, (d) –1
Correct Option: A
(a) -4, (b) –3, (c) –2, (d) –1
- A ball of mass 3 kg moving with a velocity of 4 m/s undergoes a perfectly-elastic directcentral impact with a stationary ball of mass m. After the impact is over, the kinetic energy of the 3 kg ball is 6 J. The possible value(s) of m is/are
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
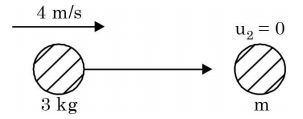
Conservation of linear momentum,
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
⇒ u2 = 0
3 × 4 = 3 × v1 + mv2 ...(i)
∵ Coefficient of restitution, e = 1 for perfectly elastic collision,
v2 – v1 = (u1 – u2)
⇒ v2 – v1 = u1 = 4
⇒ v2 – v1 = 4 ...(ii)
Conservation of energy,1 m1u²1 + 1 m2u²2 = 1 m1v²1 + 1 m2v²2 2 2 2 2 ⇒ 1 × 3 × (4)² + 0 = 6 + 1 m2v²2 2 2
⇒ (24 - 6)2 = m2v²2
⇒ mv²2 = 36 ...(iii)
∵ v1 = v2 – 4
Putting in equation (i)
⇒ 12 = 3v2 – 12 + mv2
⇒ v2 (3 + m) = 24 ...(iv)
Putting in equation (iii),&RArr; 
24 
² = 36 3 + m
⇒ (3 + m)² = 16m
⇒ 9 + m² + 6m – 16m = 0
⇒ m² – 10m + 9 = 0
⇒ m² – 9m – m + 9 = 0
(m – 9)(m – 1) = 0
m = 1,9 kgCorrect Option: B

Conservation of linear momentum,
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
⇒ u2 = 0
3 × 4 = 3 × v1 + mv2 ...(i)
∵ Coefficient of restitution, e = 1 for perfectly elastic collision,
v2 – v1 = (u1 – u2)
⇒ v2 – v1 = u1 = 4
⇒ v2 – v1 = 4 ...(ii)
Conservation of energy,1 m1u²1 + 1 m2u²2 = 1 m1v²1 + 1 m2v²2 2 2 2 2 ⇒ 1 × 3 × (4)² + 0 = 6 + 1 m2v²2 2 2
⇒ (24 - 6)2 = m2v²2
⇒ mv²2 = 36 ...(iii)
∵ v1 = v2 – 4
Putting in equation (i)
⇒ 12 = 3v2 – 12 + mv2
⇒ v2 (3 + m) = 24 ...(iv)
Putting in equation (iii),&RArr; 
24 
² = 36 3 + m
⇒ (3 + m)² = 16m
⇒ 9 + m² + 6m – 16m = 0
⇒ m² – 10m + 9 = 0
⇒ m² – 9m – m + 9 = 0
(m – 9)(m – 1) = 0
m = 1,9 kg
- A small ball of mass 1 kg moving with a velocity of 12 m/s undergoes a direct central impact with a stationary ball of mass 2 kg. The impact is perfectly elastic. The speed (in m/s) of 2 kg mass ball after the impact will be ______.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
For elastic collision m1u1 + m1u2 = m1v1 + m2v2 ...(i)
By Moment conservation principle,
m1 = 1 kg u1 = 12 m/s
m2 = 2 kg u2 = 0 m/s1 m1u²1 + 1 m2u²2 = 1 m1v²1 + 1 m2v²2.........(II) 2 2 2 2
By Energy conservation principle,
From equation (i)
12 = v1 + 2v2 ...(iii)
From equation (ii)1 × 1 × 144 + 1 × 2 × 0 = 1 × 1 × v²1 + 1 × 2 × v²2 2 2 2 2
⇒ 144 = v²1 + 2v²2...(iv)
From equations (iii) and (iv)
144 = 144 + 4v²2 - 48v2 + 2²2
⇒ 6v²2 - 48v2 = 0
⇒ 6v2 (v2 – 8) = 0
⇒ v2 = 8 m/sCorrect Option: C
For elastic collision m1u1 + m1u2 = m1v1 + m2v2 ...(i)
By Moment conservation principle,
m1 = 1 kg u1 = 12 m/s
m2 = 2 kg u2 = 0 m/s1 m1u²1 + 1 m2u²2 = 1 m1v²1 + 1 m2v²2.........(II) 2 2 2 2
By Energy conservation principle,
From equation (i)
12 = v1 + 2v2 ...(iii)
From equation (ii)1 × 1 × 144 + 1 × 2 × 0 = 1 × 1 × v²1 + 1 × 2 × v²2 2 2 2 2
⇒ 144 = v²1 + 2v²2...(iv)
From equations (iii) and (iv)
144 = 144 + 4v²2 - 48v2 + 2²2
⇒ 6v²2 - 48v2 = 0
⇒ 6v2 (v2 – 8) = 0
⇒ v2 = 8 m/s
- A ball of mass 0.1 kg, initially at rest, dropped from height of 1 m. Ball hits the ground and bounces off the ground. Upon impact with the ground, the velocity reduces by 20%. The height (in m) to which the ball will rise is _______.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
v = √2gh = √2 × 9.01 × 1 ⇒ 4.4294 m/s
v' = 0 × v = 3.5432 m/sh = v² = 0.64 m 2g Correct Option: C
v = √2gh = √2 × 9.01 × 1 ⇒ 4.4294 m/s
v' = 0 × v = 3.5432 m/sh = v² = 0.64 m 2g
- A 1 kg mass of clay, moving with a velocity of 10 m/s, strikes a stationary wheel and sticks to it. The solid wheel has a mass of 20 kg and a radius of 1 m. Assuming that the wheel is set into pure rolling motion, the angular velocity of the wheel immediately after the impact is approximately

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Taking both clay & wheel as system
Li = Lf (about A)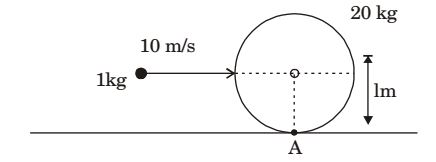
Li = mvr = 1 × 10 × 1 = 10
Lf = mvcm r + Iω= 20 × rω × r + mr²ω = 20ω + 10ω 2
Lf = 30ω
Li = Lf
10 = 30ω
ω = 1/3 rad/secCorrect Option: B
Taking both clay & wheel as system
Li = Lf (about A)
Li = mvr = 1 × 10 × 1 = 10
Lf = mvcm r + Iω= 20 × rω × r + mr²ω = 20ω + 10ω 2
Lf = 30ω
Li = Lf
10 = 30ω
ω = 1/3 rad/sec

