Neural Control and Coordination
- In mammalian eye, the ‘fovea’ is the center of the visual field, where:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Fovea centralis is the most sensitive part of retina. It has high density of cones, but rods are not found.
Correct Option: D
Fovea centralis is the most sensitive part of retina. It has high density of cones, but rods are not found.
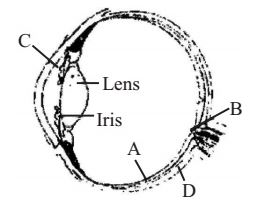
- Parts A, B, C and D of the human eye are shown in the diagram. Select the option which gives correct identification along with its functions/characteristics:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Retina is the innermost layer of eyeball and it contains three layers of cells - ganglion cells, bipolar cells and photoreceptor cells. Photoreceptor cells are not present in blind spot. The space between the cornea and the lens is called the aqueous chamber and contains a thin watery fluid called aqueous humor. Choroid is anterior part of external sclera layer of eyeball while ciliary body is anterior part of middle choroid layer.
Correct Option: D
Retina is the innermost layer of eyeball and it contains three layers of cells - ganglion cells, bipolar cells and photoreceptor cells. Photoreceptor cells are not present in blind spot. The space between the cornea and the lens is called the aqueous chamber and contains a thin watery fluid called aqueous humor. Choroid is anterior part of external sclera layer of eyeball while ciliary body is anterior part of middle choroid layer.
- Cornea transplant in humans is almost never rejected. This is because
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Cornea transplant in humans is almost never rejected. This is because it has no blood supply. Cornea is a transparent layer of tissue, continuous with the sclerotic, that forms the front part of the vertebrate eye, over the iris and lens.
Correct Option: B
Cornea transplant in humans is almost never rejected. This is because it has no blood supply. Cornea is a transparent layer of tissue, continuous with the sclerotic, that forms the front part of the vertebrate eye, over the iris and lens.
- What is intensity of sound in normal conversation?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The word noise is taken from the latin word nausea and is defined as unwanted or unpleasant sound that causes discomfort.
Source Intensity (dB) Breathing 10 Broadcasting studio 20 Trickling clock 30 Library 30 – 35 Normal conversetion 35 – 60 Telephone office Noise 60 – 80 Alarm clock 70 – 80 Traffic 50 – 90 Motorcycle 105 Jet fly over 100 – 110 Train whistle 110 Air craft 110 – 120 Correct Option: B
The word noise is taken from the latin word nausea and is defined as unwanted or unpleasant sound that causes discomfort.
Source Intensity (dB) Breathing 10 Broadcasting studio 20 Trickling clock 30 Library 30 – 35 Normal conversetion 35 – 60 Telephone office Noise 60 – 80 Alarm clock 70 – 80 Traffic 50 – 90 Motorcycle 105 Jet fly over 100 – 110 Train whistle 110 Air craft 110 – 120
- When we migrate from dark to light, we fail to see for sometime but after a time visibility becomes normal. It is an example of
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
It takes some time for rhodopsin to split into scotopsin and retinal (bleading) and release of transmitter passing nerve inpulse via bipolar and ganglion cells to the optic nerves. This is a case of adaptation. It differs from accomodations which is a reflex mechanism by which the focus of the eye change to make the images of distant and near objects sharp on the retina.
Correct Option: B
It takes some time for rhodopsin to split into scotopsin and retinal (bleading) and release of transmitter passing nerve inpulse via bipolar and ganglion cells to the optic nerves. This is a case of adaptation. It differs from accomodations which is a reflex mechanism by which the focus of the eye change to make the images of distant and near objects sharp on the retina.

